How to Clear Google Chrome DNS Cache
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
How to Clear Google Chrome DNS Cache Using chrome://net-internals/#dns
If you can’t access a website using Google Chrome, it may be because the website has changed the DNS entry. Chrome features a built-in DNS cache that you can clear using the chrome://net-internals/#dns command and then be able to access the website.

What is Domain Name System (DNS)?
The Domain Name System (DNS) translates domain names into IP addresses, allowing browsers to access websites and load Internet resources.
Every device connected to the Internet has a unique IP address that other devices can use to locate the device. DNS servers eliminate the need for you to memorize website IP addresses.
What is the DNS Cache?
A DNS cache records all queries from your browser to a DNS server. When you enter a website URL into your browser, it sends a request to the DNS server asking for the URL’s IP address. After receiving the IP address, your browser can load the correct website.
A DNS cache is not only stored on your operating system but also on your browser. Google Chrome was a built-in DNS and proxy caching server.
The primary purpose of Chrome’s DNS cache is to speed up browsing and allow you to reach websites when your ISP-provided DNS servers are down.
What Is DNS Cache Flushing?
Clearing Chrome’s DNS cache may help improve performance as it clears all DNS entries on the browser. Furthermore, clearing Chrome’s DNS cache refreshes the DNS records stored in the browser.
To access the Internet, your DNS has to work correctly. If the DNS entry of a specific website is changed or your Chrome DNS cache has become corrupt, you won’t be able to access it. Therefore, clearing Chrome’s DNS cache will allow you to access previously inaccessible websites and may improve browser performance overall.
DNS flushing or clearing means deleting existing cached DNS entries from Google Chrome. Once the DNS cache is flushed, Chrome will ask for new IP addresses and DNS information for websites when you try to access them.
What is chrome://net-internals/#dns?
net-internals/#dns (also known as Net-Internals) is a NetLog event stream virtualization tool that allows you to see real-time logs or load NetLog dumps of later dates that contain Chrome’s network-related events and state.
A NetLog dump is a log that contains Chrome’s network-related events and state. The NetLog in Chrome can help troubleshoot and debug issues.
Video Tutorial on How to Clear Google Chrome DNS Cache
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Clear Chrome DNS Cache Using chrome://net-internals/#dns
- Video Tutorial on How to Clear Google Chrome DNS Cache
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Clear Chrome DNS Cache Using chrome://net-internals/#dns
To clear your Google Chrome DNS cache, you have to enter the chrome://net-internals/#dns command in the omnibox and click the Clear host cache button. Then, enter chrome://net-internals/#sockets command in the omnibox and click the Flush socket pools button.
1. Open Google Chrome.
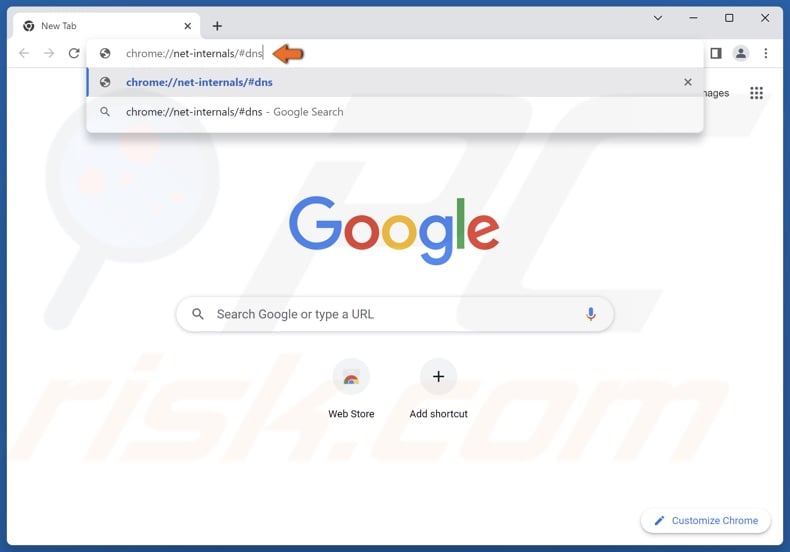
2. In the Chrome omnibox, type in:
chrome://net-internals/#dns
3. Press Enter.
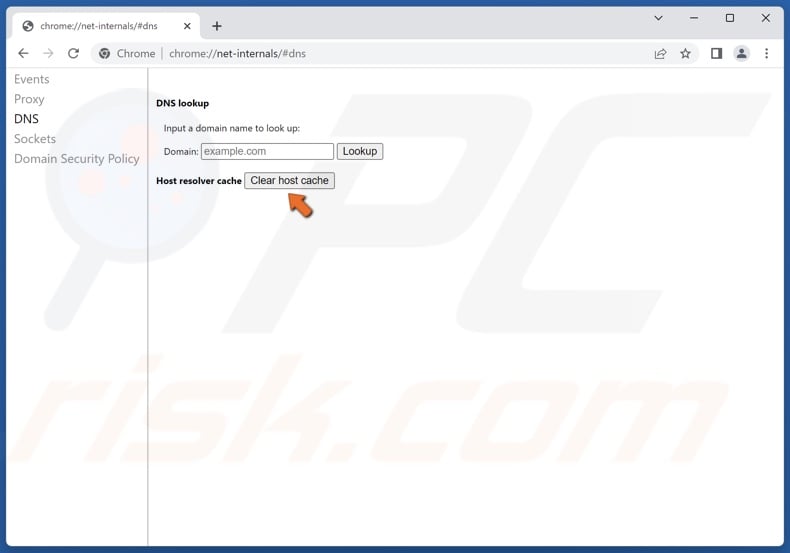
4. Click the Clear host cache button.
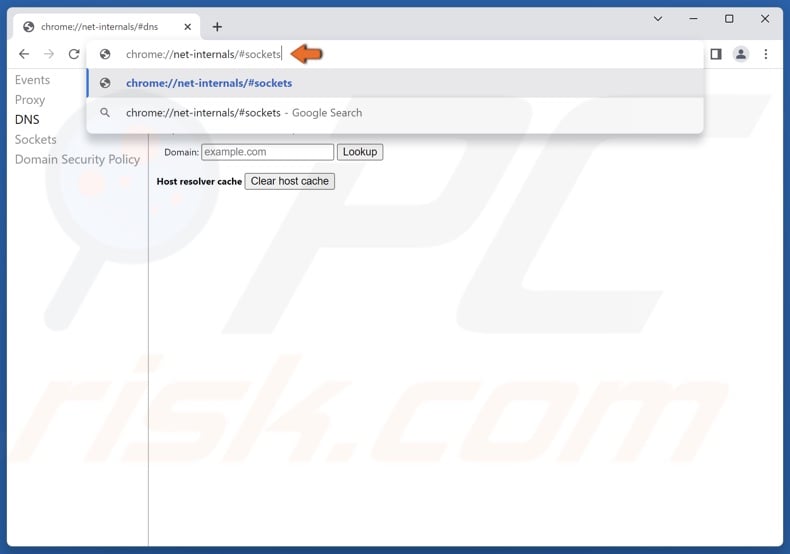
5. Then, in the Chrome omnibox, type in:
chrome://net-internals/#sockets
6. Press Enter.
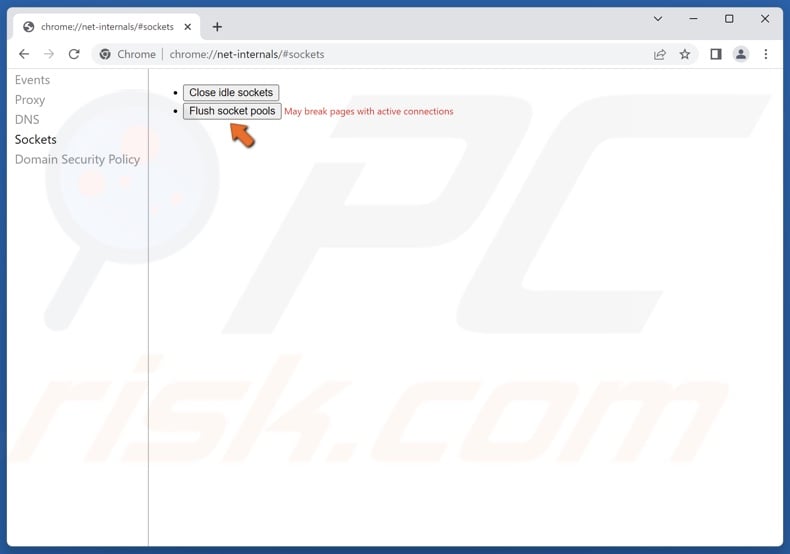
7. Click the Flush socket pools button.
If you still can’t access a specific website, you may need to clear your Windows DNS cache. Read or article on How to Flush DNS Cache on Windows 11.
Share:

Rimvydas Iliavicius
Researcher, author
Rimvydas is a researcher with over four years of experience in the cybersecurity industry. He attended Kaunas University of Technology and graduated with a Master's degree in Translation and Localization of Technical texts. His interests in computers and technology led him to become a versatile author in the IT industry. At PCrisk, he's responsible for writing in-depth how-to articles for Microsoft Windows.

▼ Show Discussion