How to Fix WiFi Network Not Showing Up on Windows 11
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
How to Fix WiFi Network Not Showing Up on Windows 11
Windows 11 users frequently report that their WiFi network is not showing up in the network connections list. Various things can cause this issue, so there is no one-size-fits-all solution. If you’re having trouble fixing this issue, this article will explain the causes of it and show you several ways to fix it.

Why Is My WiFi Network Not Showing Up?
- Windows disabled the WLAN AutoConfig Service. The WLAN AutoConfig Service facilitates the discovery and connection to WiFi networks on your PC. WiFi networks won’t show up in the connections list if the service experiences issues or is not running.
- Your WiFi network adapter is disabled. Your network adapter may have been turned off accidentally. As a result, you won’t see your wireless network in the list.
- The router’s Service Set Identifier (SSID) broadcast is hidden. SSID is what makes your WiFi network visible to your network adapter. If SSID is disabled in the router settings, the WiFi network won’t show up in the available networks list.
- Incompatible channel bandwidth. If your router broadcasts a 5GHz signal, your WiFi adapter with a 2.4GHz antenna won’t detect it. Therefore, you need a 5GHz WiFi adapter or configure your router to use 2.4GHz.
Before trying any of our fixes, here are a few things you should try:
- Toggle the WiFi key on your keyboard. You may have accidentally turned off your WiFi adapter on your laptop by pressing the WiFi key on your keyboard.
- Disable Airplane mode. Your WiFi network not showing up in the network connections list may be because you accidentally turned on Airplane mode.
- Restart your Internet router. Restarting your router will reset some of your network settings and remove temporary files. If your router has a Restart button – press it. If it doesn’t, power off the router by pressing the On/Off button or unplugging it from the power outlet. wait a few minutes and power on the router.
- Enable SSID broadcast. Check if the SSID broadcast in your Internet router settings is enabled, and enable it if it isn’t.
- Match the broadcast frequency between your router and the WiFi adapter. If your Internet router is configured to use the 5GHz frequency, while your WiFi adapter doesn’t support 5GHz, configure your router to broadcast in 2.4GHz.
Video Tutorial on How to Fix WiFi Network Not Showing Up
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Method 1. Set the WLAN AutoConfig Service to Start Automatically
- Method 2. Disable and Re-enable the WiFi Adapter
- Method 3. Set the WiFi Adapter Channel Width to Auto
- Method 4. Update/Reinstall the WiFi Adapter Driver
- Method 5. Reset TCP/IP Settings
- Method 6. Configure Wireless Router Settings
- Video Tutorial on How to Fix WiFi Network Not Showing Up
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Method 1. Set the WLAN AutoConfig Service to Start Automatically
The WLAN AutoConfig Service is essential to Windows because it facilitates the discovery and connection to WiFi networks. Your WiFi network won’t show up if this service experiences issues or stops running. The steps below will show you how to configure the WLAN AutoConfig Service to start automatically to ensure it’s always running.
1. Hold down Windows+R keys to open Run.
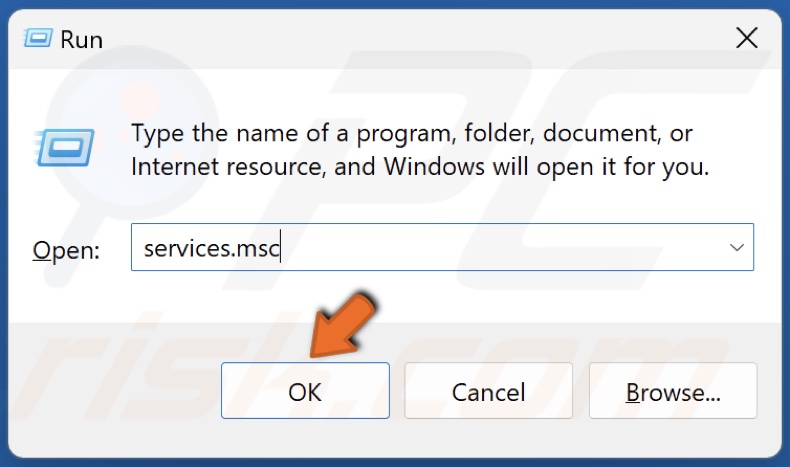
2. Type services.msc in the Run dialog and click OK.
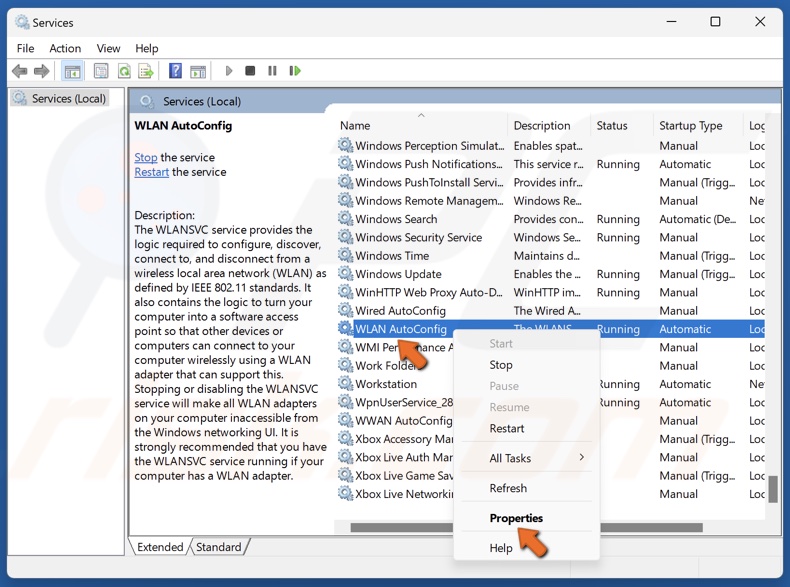
3. In the Services window, scroll down and find WLAN AutoConfig.
4. Right-click WLAN AutoConfig and select Properties.
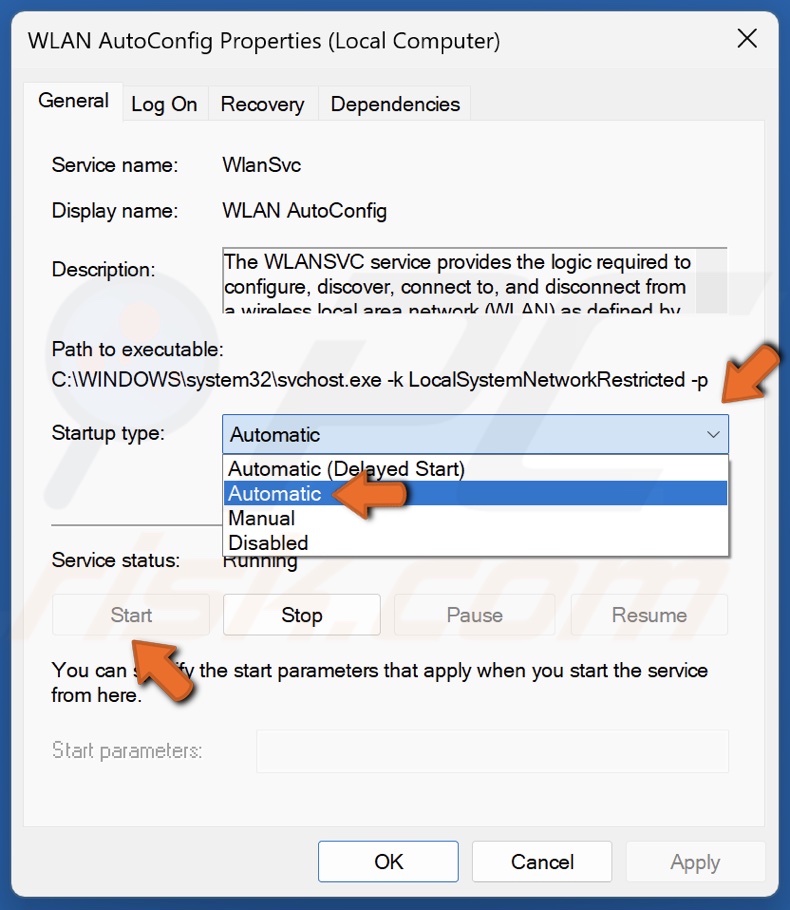
5. Open the Startup type drop-down menu and select Automatic.
6. Click Start under the Service status section.
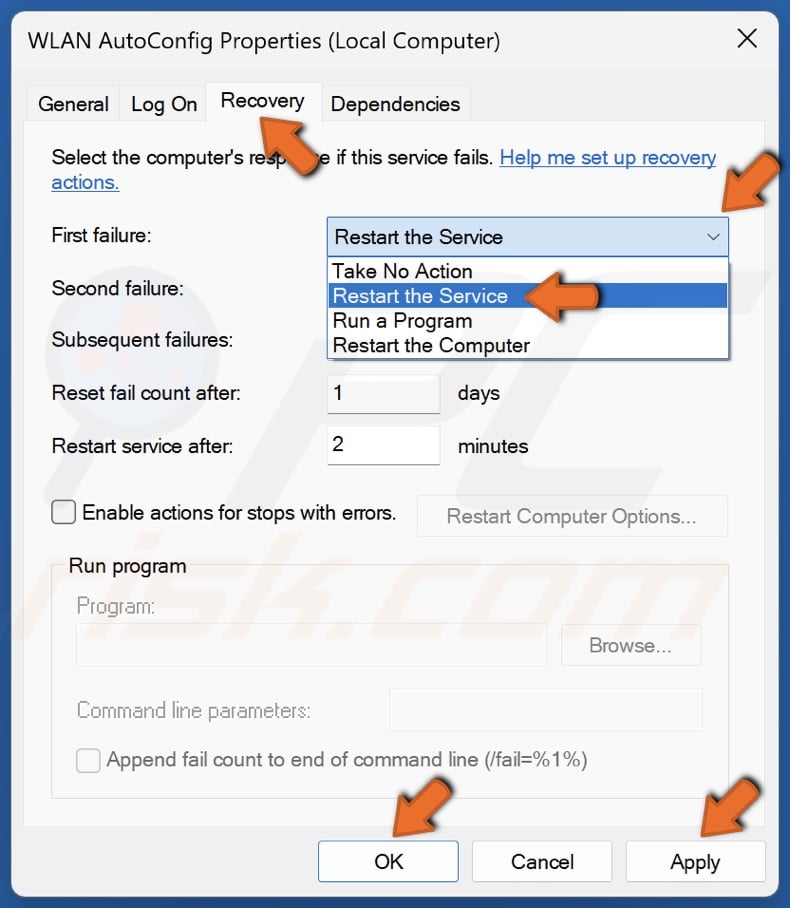
7. Then, select the Recovery tab.
8. Open the First failure drop-down menu and select Restart the Service.
9. Click Apply and click OK.
Method 2. Disable and Re-enable the WiFi Adapter
A temporary glitch in your WiFi adapter may prevent Windows 11 from detecting a nearby network. Therefore, disabling and re-enabling your WiFi adapter may fix the WiFi network not showing up.
1. Hold down Windows+R keys to open Run.
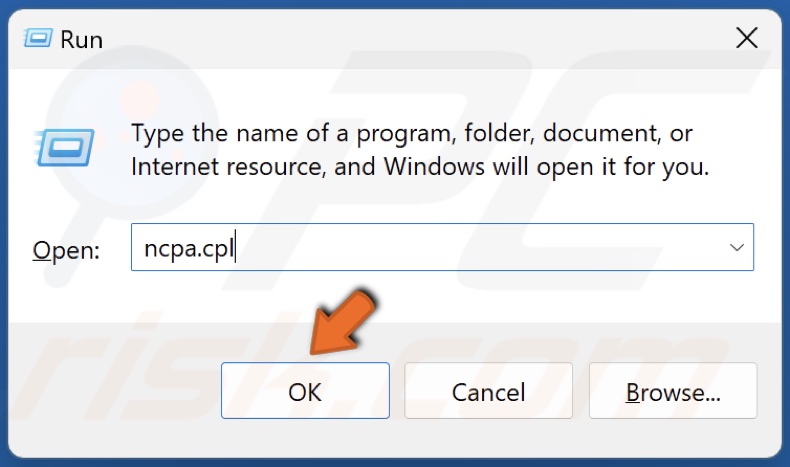
2. Type ncpa.cpl in the Run dialog and click OK.
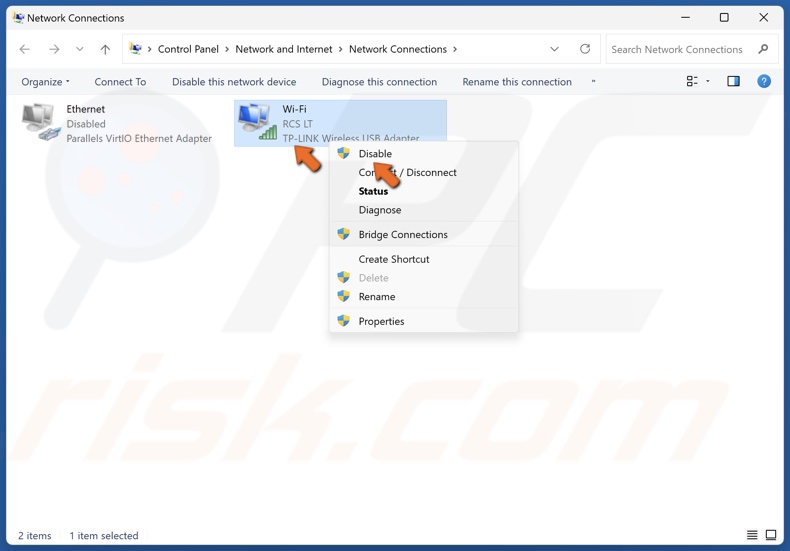
3. Right-click your WiFi adapter, click Disable, and wait a few minutes.
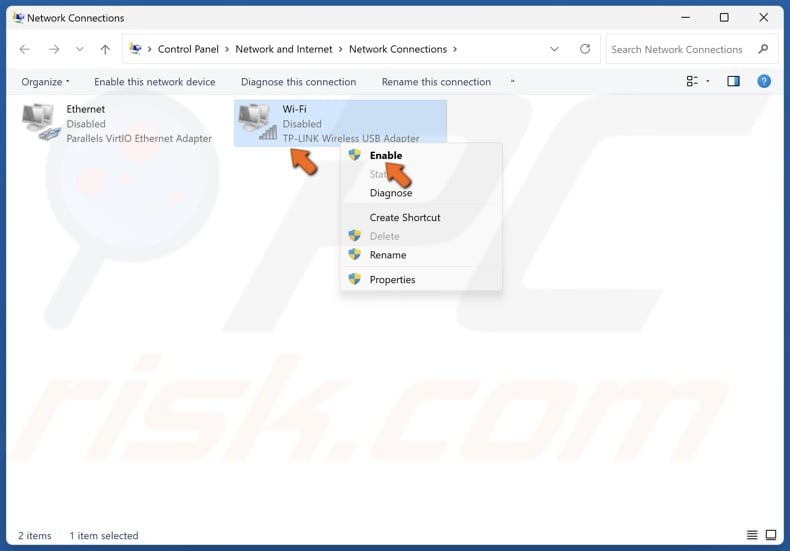
4. Then, Right-click your WiFi adapter again and click Enable.
Method 3. Set the WiFi Adapter Channel Width to Auto
Your WiFi adapter’s channel width may have been configured to a specific frequency. As a result, the WiFi network may not show up in the network list because the frequency is too low or high. Setting your WiFi Adapter’s channel width to Auto may fix the issue.
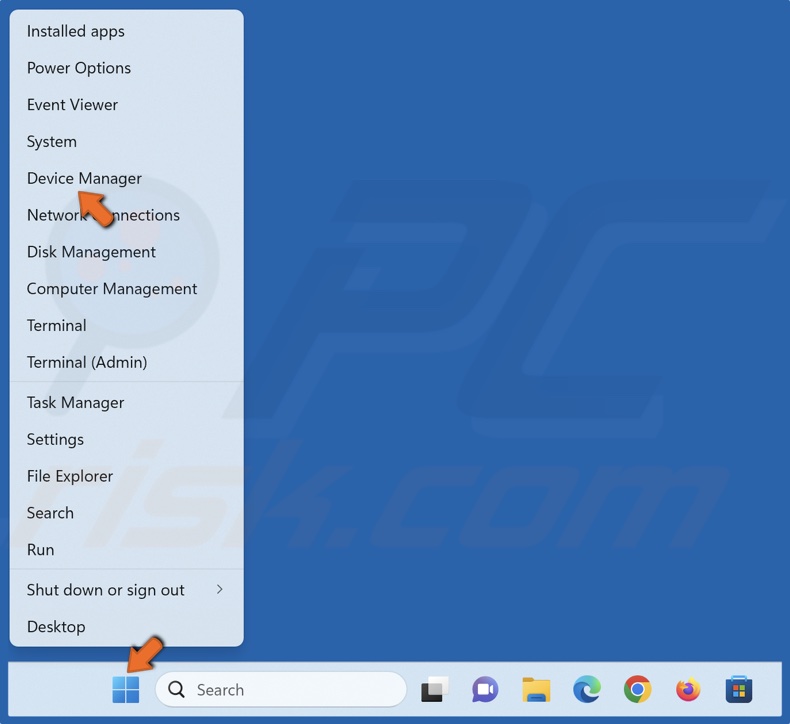
1. Right-click the Start button and click Device Manager.
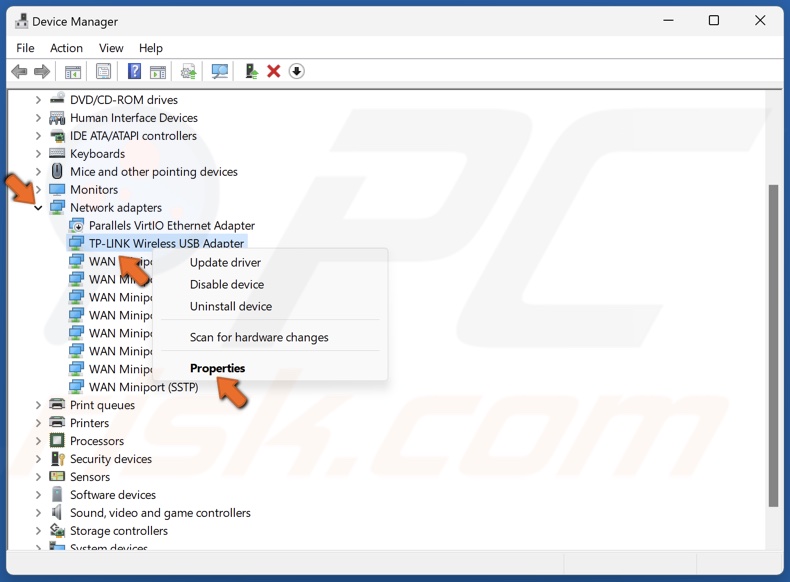
2. In the Device Manager, expand the network adapters list and find your WiFi adapter.
3. Right-click your WiFi network adapter and click Properties.
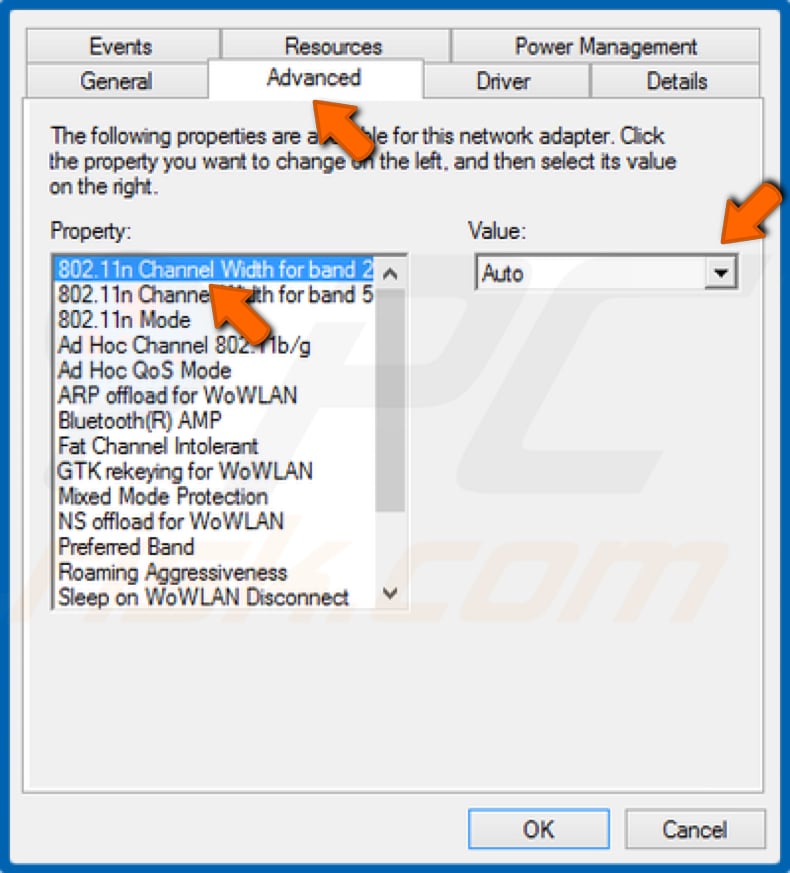
4. Select the Advanced tab.
5. In the Property section, select the 802.11n Channel Width for 2.4GHz option.
6. Open the Value context menu and select Auto.
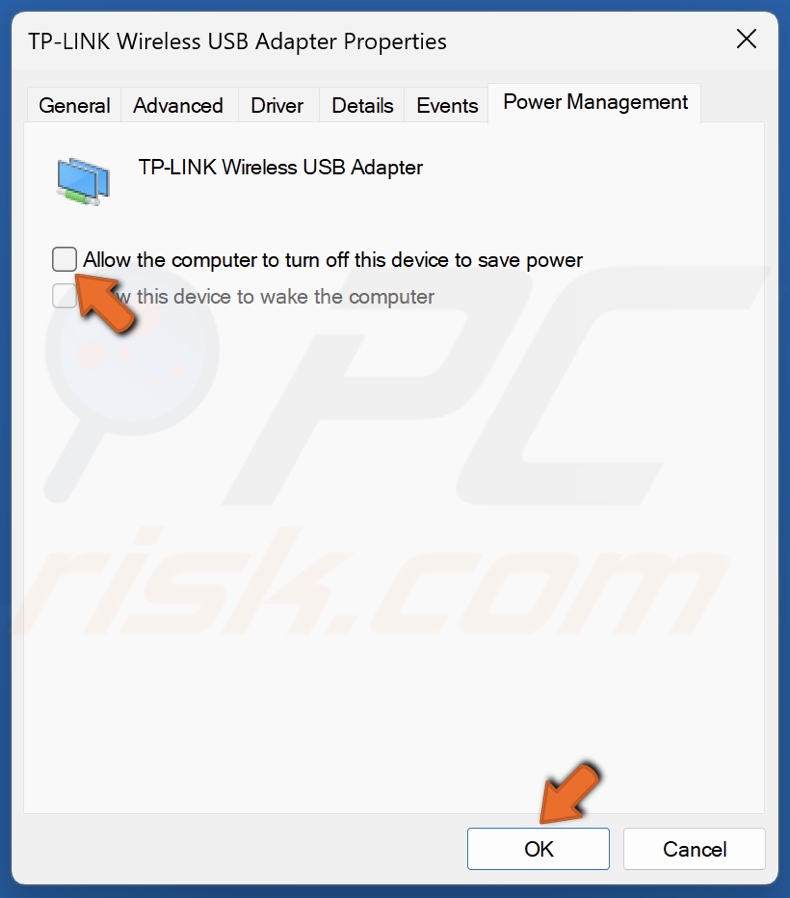
7. You may also want to modify your adapter’s power settings. Select the Power Management tab.
8. Uncheck the Allow computer to Turn off device to save power option.
9. Click OK to save the settings.
Method 4. Update/Reinstall the WiFi Adapter Driver
If your computer can’t detect your WiFi network, you may need to reinstall your network adapter driver. Reinstalling it will fix any bugs or glitches in the software and reset the connection.
Your PC will install the default driver already present on your PC, so you don’t need an Internet connection to apply this method.

1. Right-click the Start button and click Device Manager.
2. In the Device Manager, expand the Network adapters list and find your WiFi adapter.
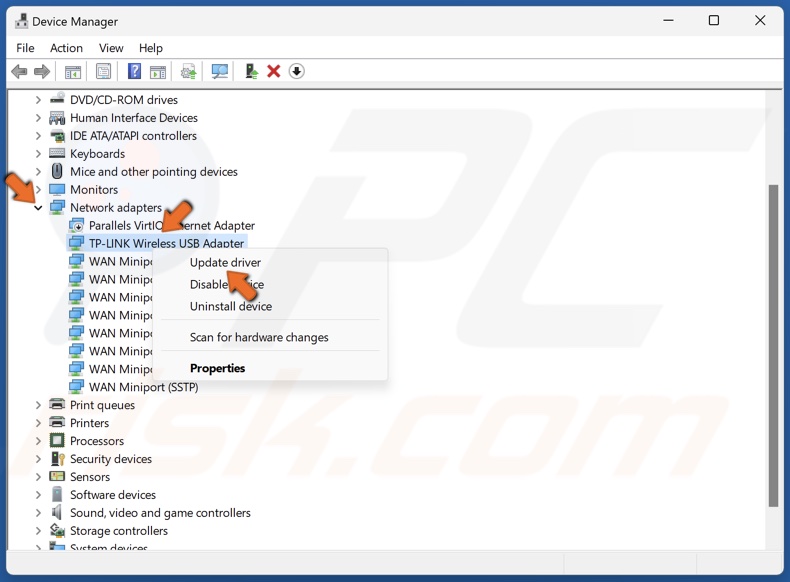
3. Right-click your WiFi adapter and click Update driver.
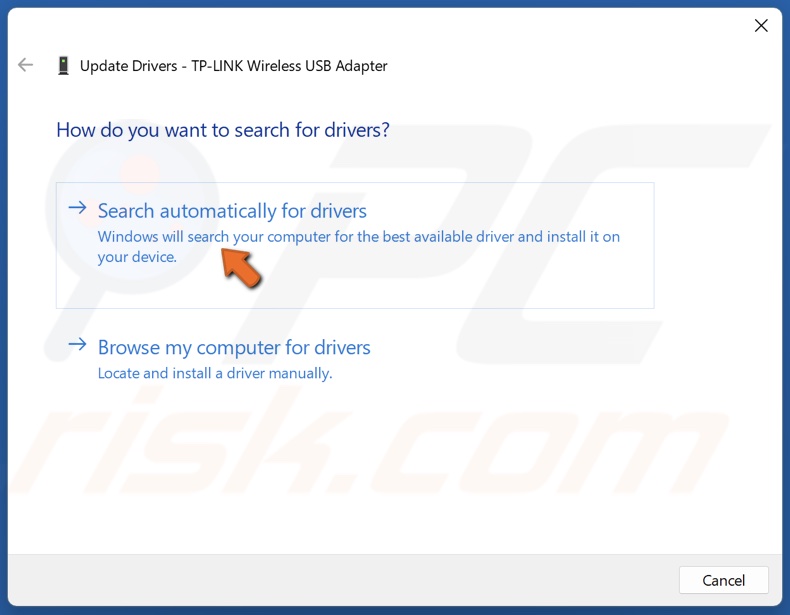
4. Select Search automatically for drivers. Windows will scan your PC for the best available driver and install it.
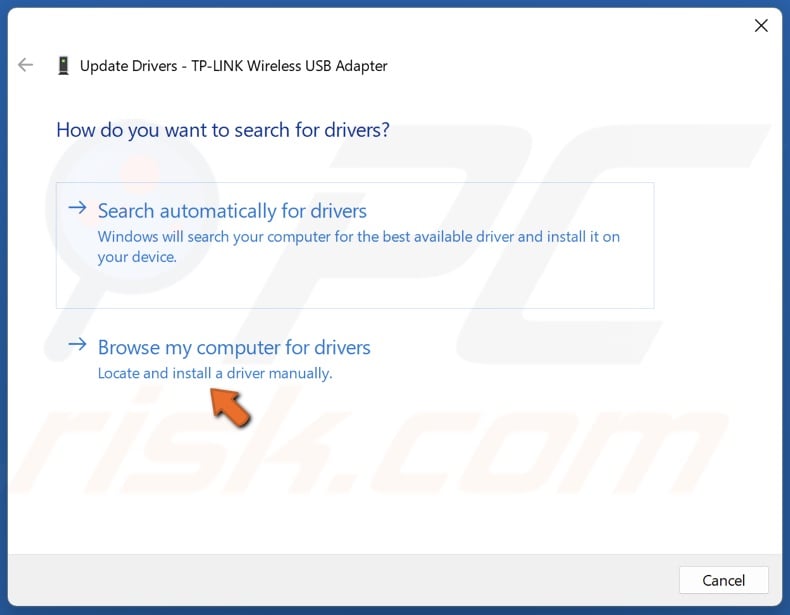
5. Alternatively, select Browse my computer for drivers.
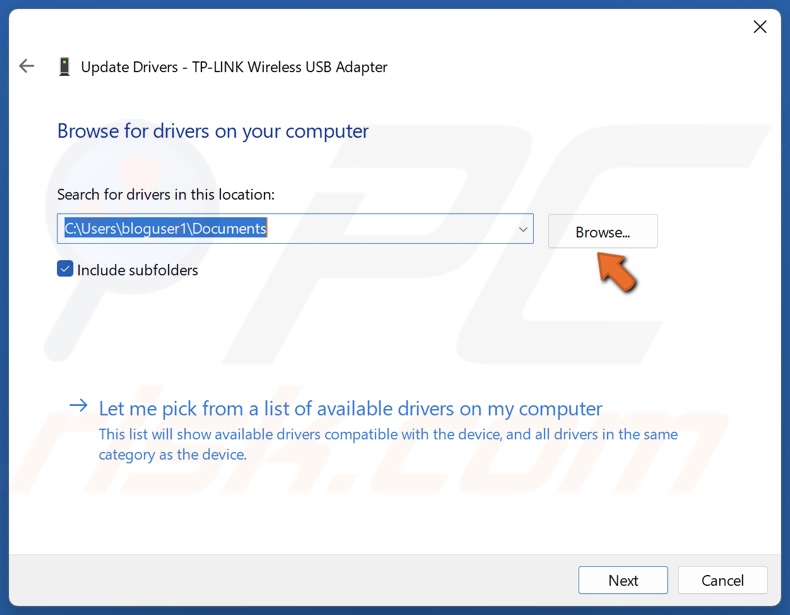
6. Click Browse and select a driver downloaded from the hardware vendor’s website.
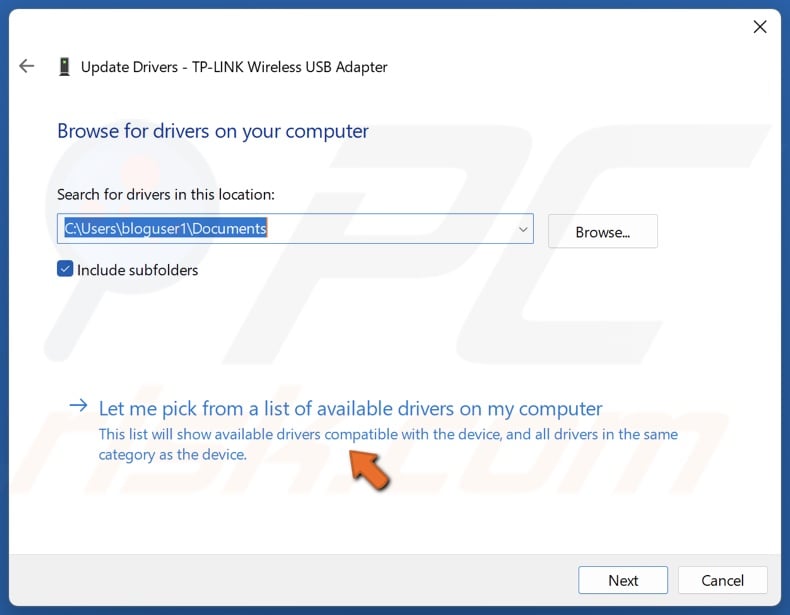
7. Or select Let me pick from a list of available drivers on my computer.
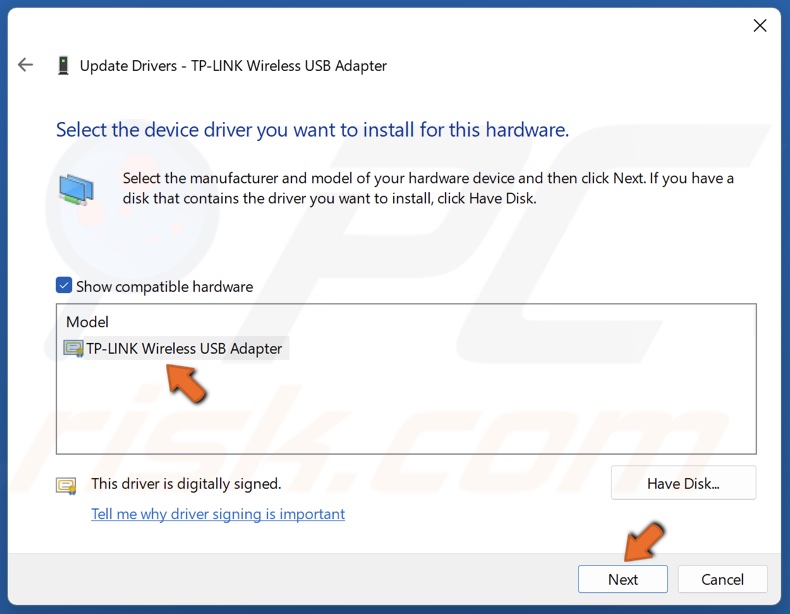
8. Choose a driver from the drivers list and click Next. Try selecting an older driver version.
9. Click Close.
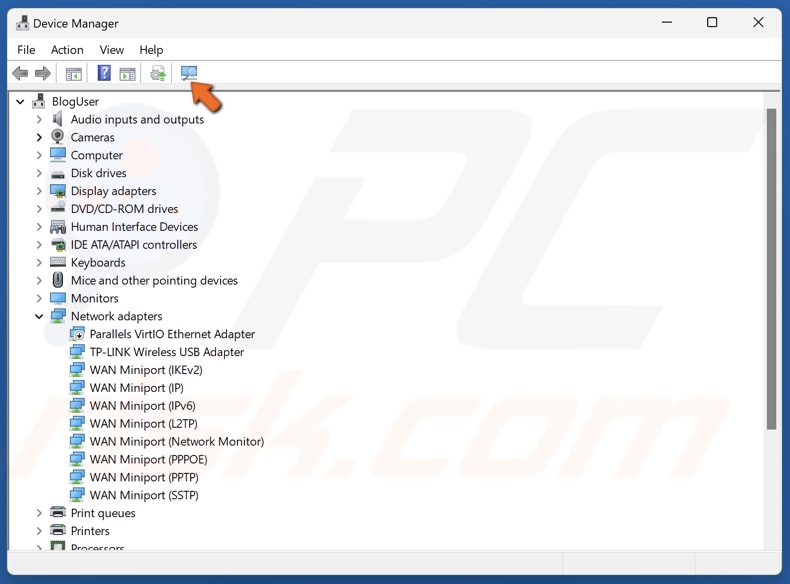
10. Click the Scan for hardware changes button in the toolbar.
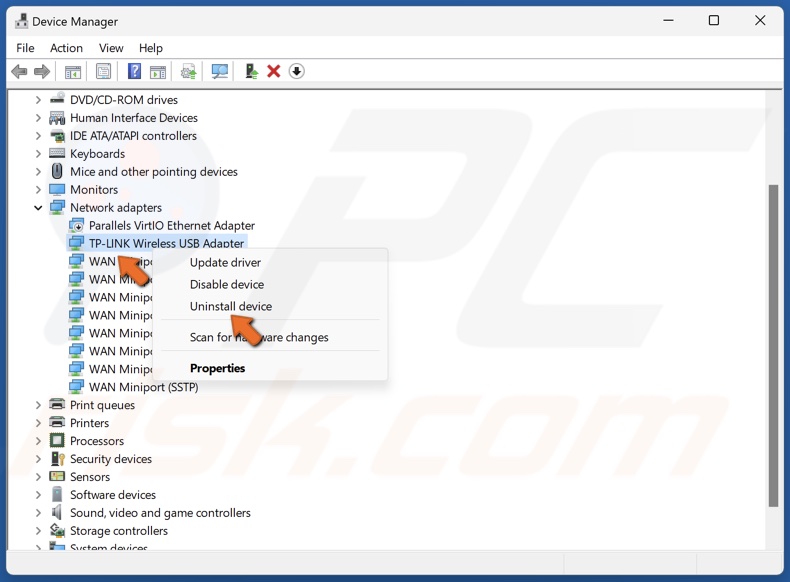
11. If updating the driver didn’t fix the issue, right-click your WiFi adapter and click Uninstall device.
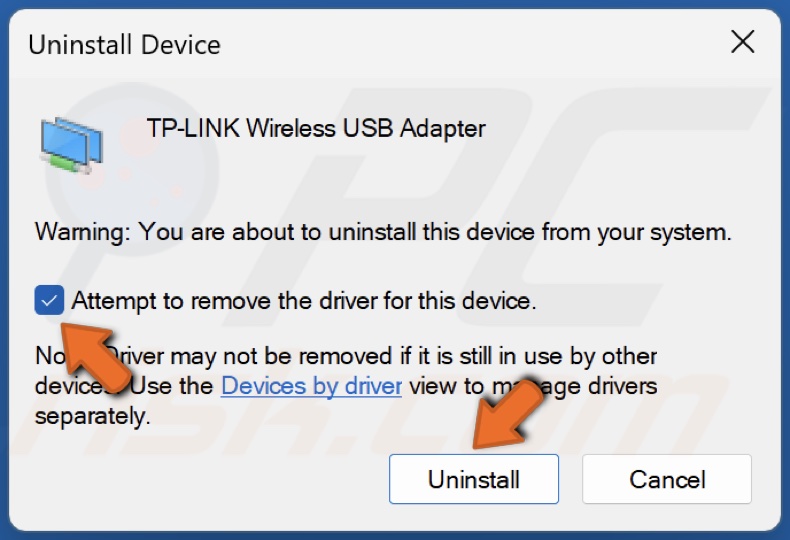
12. Mark the Attempt to remove the driver for this device checkbox and click Uninstall.
13. Close the Device Manager window and restart your PC. After the restart, your PC will automatically install the default driver for your network adapter automatically.
Method 5. Reset TCP/IP Settings
If your computer still can’t see your wireless network, your network settings may have been misconfigured. In this case, running the netsh winsock reset command will reset the socket settings of the TCP/IP stack, which should fix the problem.
1. Hold down Windows+R keys to open Run.
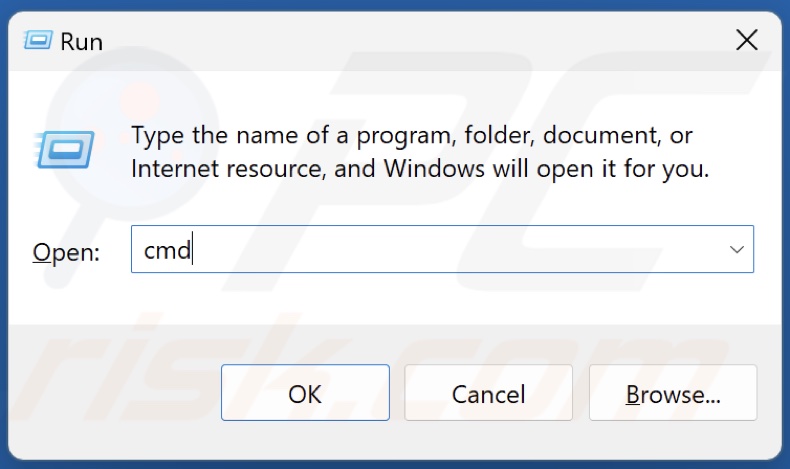
2. Type CMD in the Run dialog and hold down Ctrl+Shift+Enter keys to open Command Prompt as an administrator.
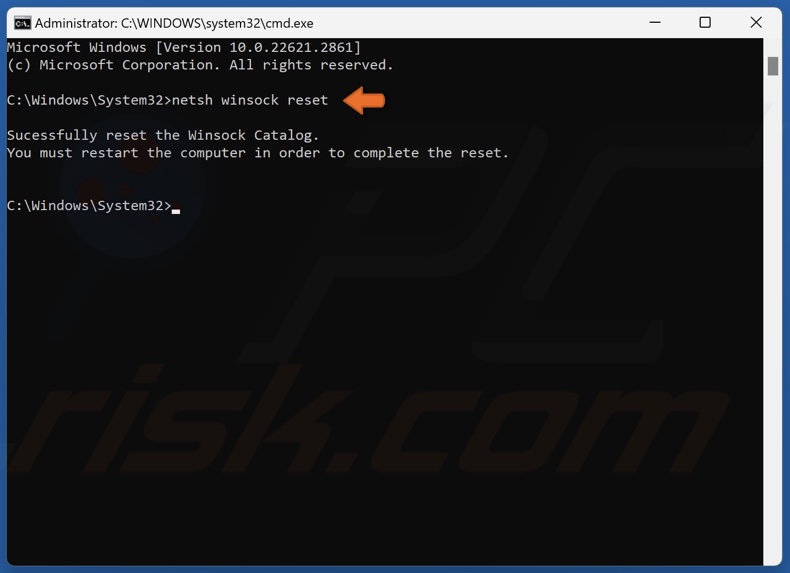
3. In the Command Prompt, type in:
netsh winsock reset
4. Press Enter to execute the command.
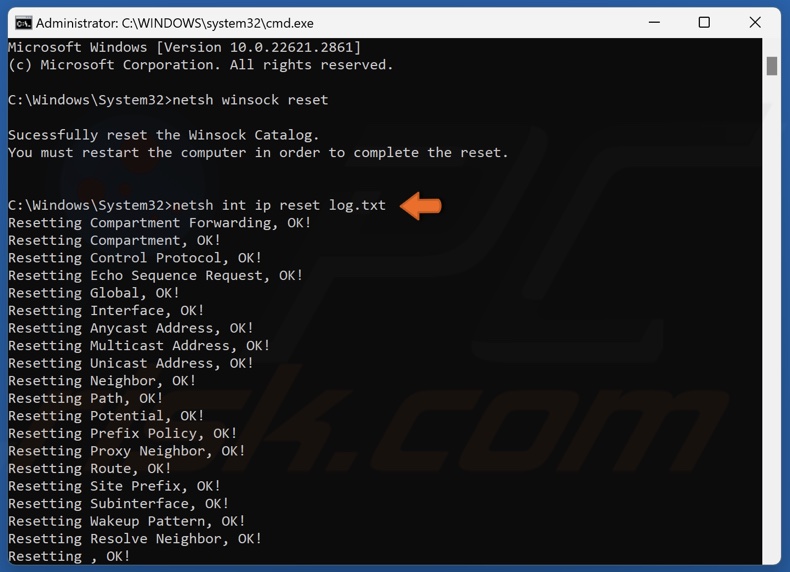
5. Then, type in:
netsh int ip reset log.txt
6. Press Enter to execute the command.
7. Close the Command Prompt and restart your PC.
Method 6. Configure Wireless Router Settings
Your WiFi network not showing up in the connections list can be attributed to misconfigured router settings. For example, if the WiFi adapter in your computer uses the 2.4GHz frequency only, it won’t detect a 5GHz signal from your router.
Furthermore, you won’t see your WiFi network if the Service Set Identifier (SSID) broadcast is hidden. The instructions below will show you how to configure your SSID and configure broadcast frequency settings. We use a TP-Link N750 wireless router.
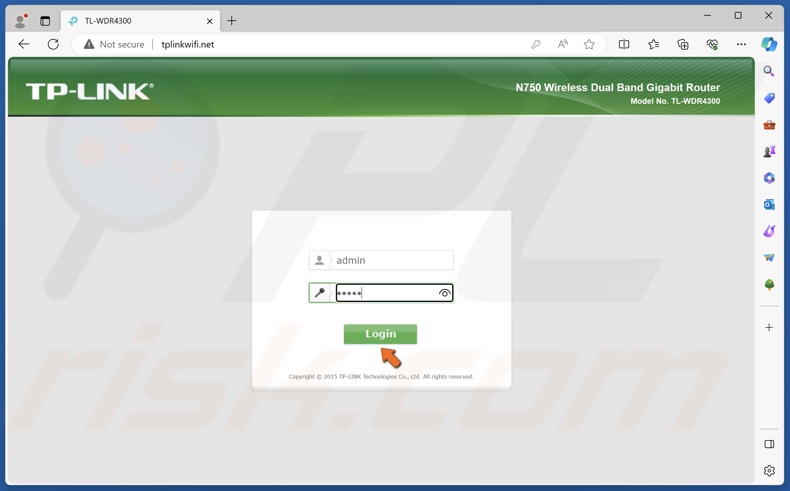
1. Open your web browser and go to the IP address or URL indicated at the bottom of the router.
2. Enter the user name and password and access the router’s settings. The default name and password are also indicated at the bottom of the router.
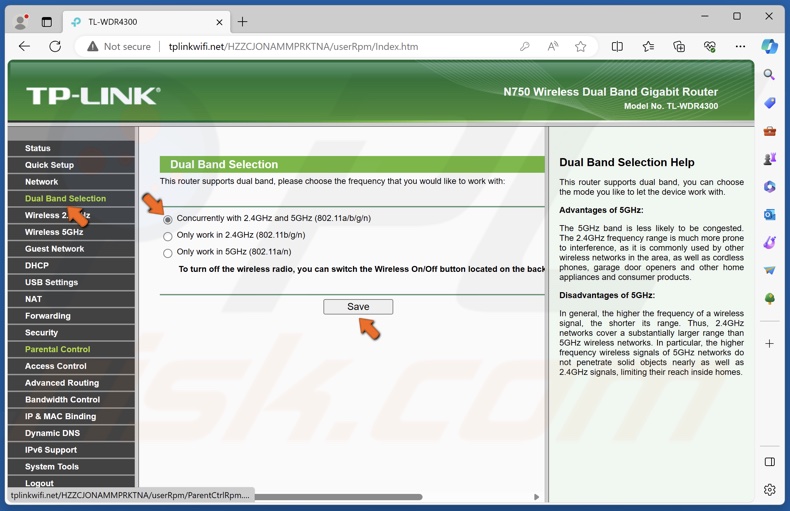
3. If your router is Dual Band and supports both 2.4GHz and 5Ghz, go to the Dual Band settings and make sure that 2.4GHz and 5GHz are enabled.
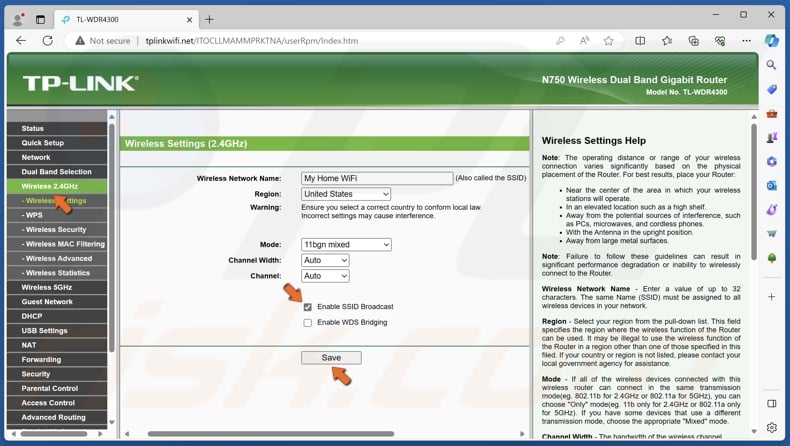
4. Then, go to the wireless settings for 2.4GHz and enable SSID broadcasting.
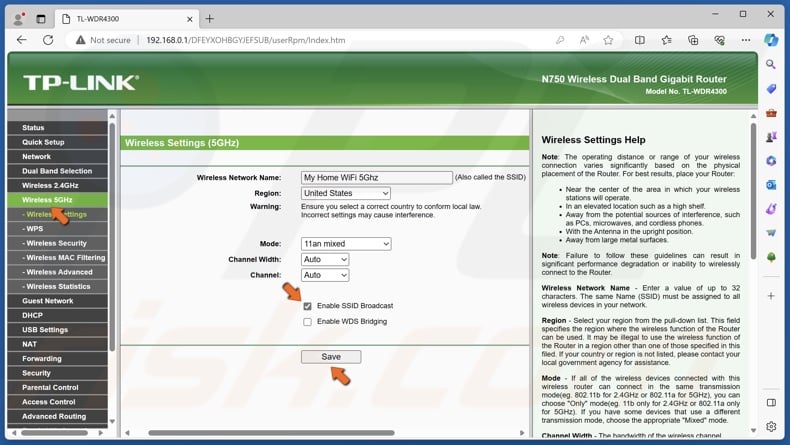
5. Lastly, go to the wireless settings for 5GHz and enable SSID broadcasting.
Did this article help you fix WiFi network not showing up in the network list? Let us know in the comments below. If you know a way to fix this issue we didn’t mention in this article, please share it with others in the comments.
Share:

Rimvydas Iliavicius
Researcher, author
Rimvydas is a researcher with over four years of experience in the cybersecurity industry. He attended Kaunas University of Technology and graduated with a Master's degree in Translation and Localization of Technical texts. His interests in computers and technology led him to become a versatile author in the IT industry. At PCrisk, he's responsible for writing in-depth how-to articles for Microsoft Windows.

▼ Show Discussion