How to Fix Error 400 Bad Request
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
How to Fix: Error 400 Bad Request
Error 400 Bad Request is an HTTP status code that indicates an invalid request that the web server can’t understand or process. In most cases, Error 400 occurs due to a malformed request syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing. If you’re getting this error, the instructions in this article will help you fix it.

Error Code 400 has many variations. The error page can be customized so that every website can have its unique description. Here are a few examples:
HTTP Error 400
HTTP Error 400 – Bad Request
400 – Bad Request
Bad Request – Invalid URL
400 Bad Request. Request Header Or Cookie Too Large
Bad Request – Your browser sent a request that this server could not understand
If a website doesn’t have a customized Error 400 page, it will show the default version with slight differences depending on the browser. However, Firefox and Safari will just show a blank page with no error code.
What Causes Error Code 400 Bad Request?
When you try to access a website, your device sends a request to its web server. However, the web server may not understand or process the request and return the 400 status code. This error code indicates that the server can’t process the request due to an issue on the client side. Below is a list of causes for this error.
- Bad URL syntax. The URL you typed in may contain illegal characters, or you mistyped the URL. You may also have a “malformed URL”, which means that you have an extra percentage sign (%) in the URL string.
- The file is too big. Most websites have file upload limits. If you attempt to upload a file that exceeds the maximum file size limit, the server can interpret it as a bad request and trigger the error.
- Corrupt browser cookies or cache. If your browser cookies are outdated or your cache is corrupted, the server may be unable to process the request.
- DNS-related issues. You may get Error 400 when the locally-stored DNS data is out of sync with the current DNS registration for the domain. For example, the website you want to access may have moved to a new domain name or web host.
- Interference from browser extensions. Certain browser extensions can interfere with the request sent to the website server, causing the server to interpret the request as invalid.
While in most cases, this error occurs due to a client-side issue, it may also occur due to a server-side issue, in which case only the website owner can resolve it.
Before you try any of our fixes, double-check the domain address, as this is one of the most common causes of Error Code 400.
Video Tutorial on How to Fix Error 400 Bad Request
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Method 1. Clear Web Browser Cookies and Cache
- Clear Cookies and Cache in Google Chrome
- Clear Cookies and Cache in Mozilla Firefox
- Clear Cookies and Cache in Microsoft Edge
- Method 2. Disable Browser Extensions
- Clear Cookies and Cache in Mozilla Firefox
- Disable Extensions on Mozilla Firefox
- Disable Extensions on Microsoft Edge
- Method 3. Clear DNS Cache
- Video Tutorial on How to Fix Error 400 Bad Request
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Cookies and cache store website data on your browser to improve your browsing experience. Your browser cache contains website files such as texts and images to reduce the number of requests to the website server and improve load times. Your browser stores cookies that contain session history and your preferences and settings.
However, your browser cache may become corrupt, and your cookies may expire, triggering Error 400. You will also get this error if a website sends cookie data that is too large.
Clearing your browser’s cookies and cache may fix the error. Note that clearing your browser cookies and cache won’t affect the custom settings you’ve made to your browser.
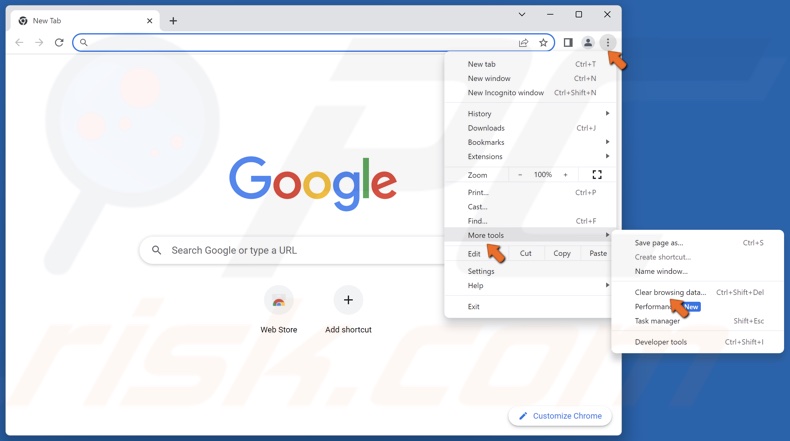
1. Open Chrome. Click the three-dot menu button at the top-right corner, select More tools, and click Clear browsing data.
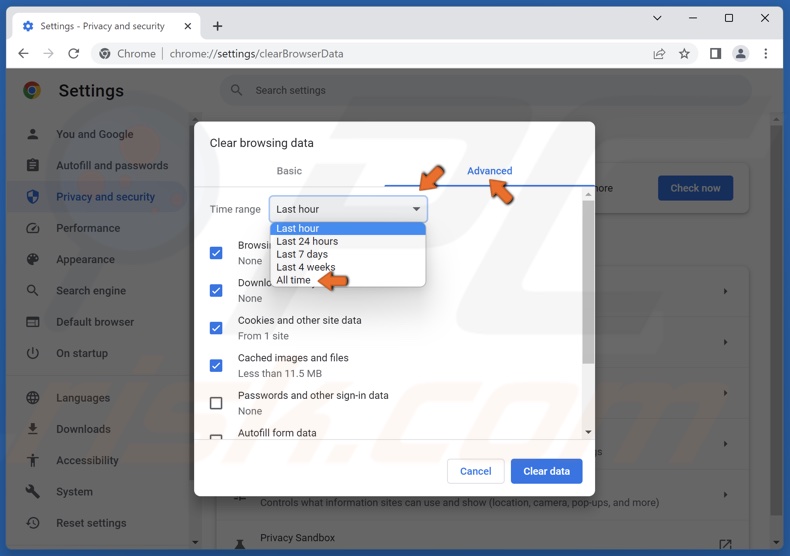
2. Select the Advanced tab.
3. Open the Time range drop-down menu and select All time.
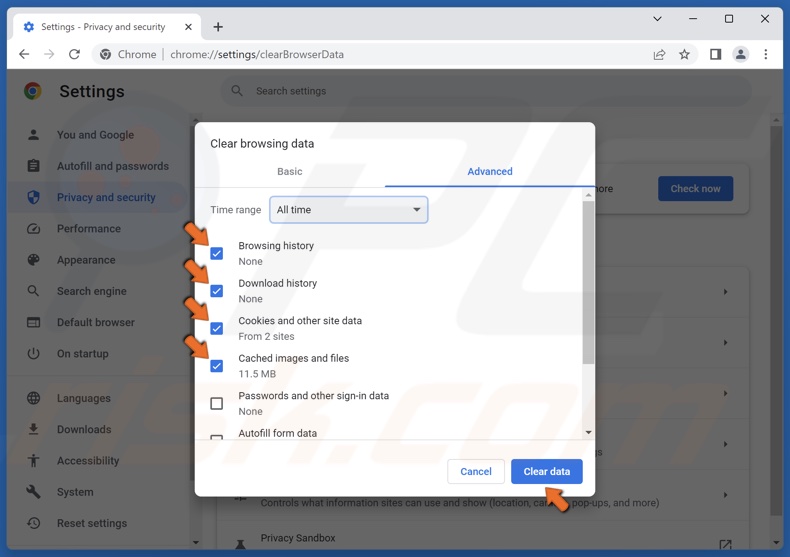
4. Mark the Browsing history, Download history, Cookies and other site data, and Cached images and files checkboxes.
5. Click Clear data.

1. Open Firefox. Click the menu button at the top-right corner and click Settings.
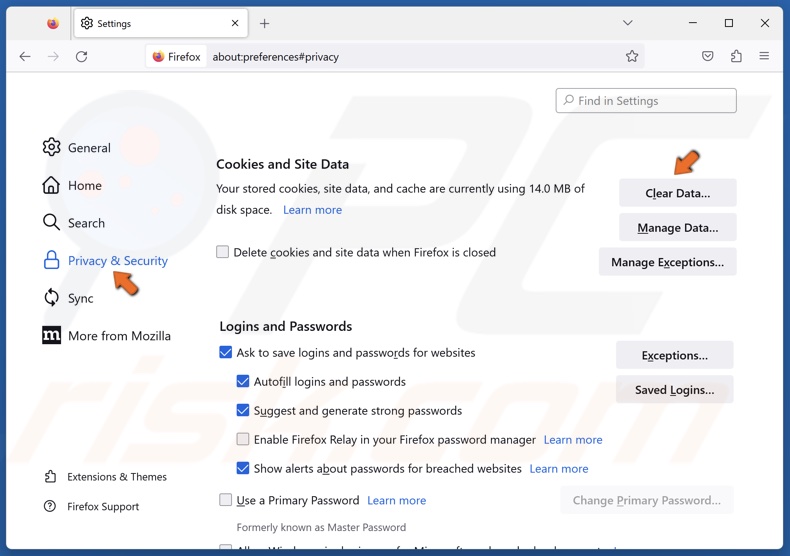
2. Select the Privacy & Security panel.
3. Scroll down and click Clear Data in the Cookies and Site Data section.
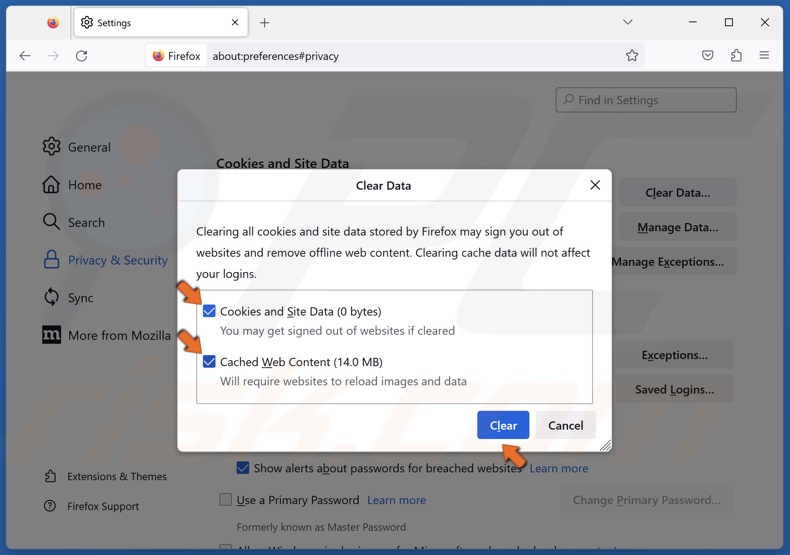
4. Mark the Cookies and Site Data and Cached Web Content checkboxes and click Clear.
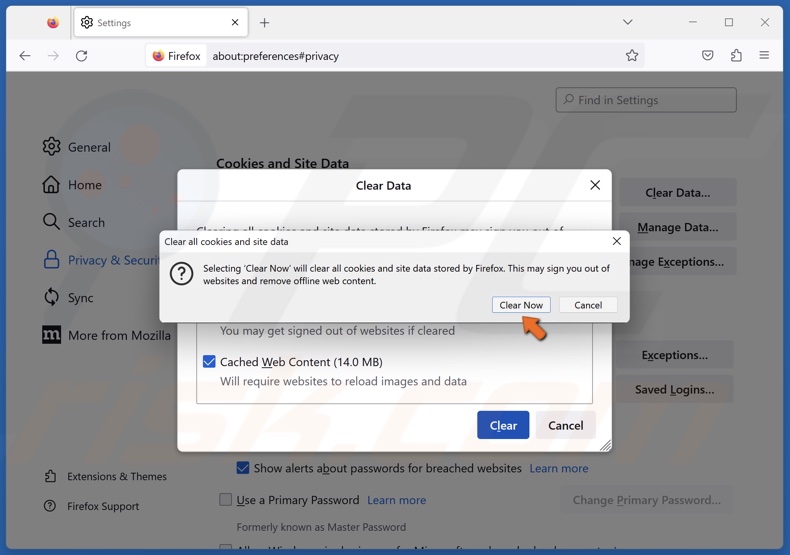
5. Click Clear Now.
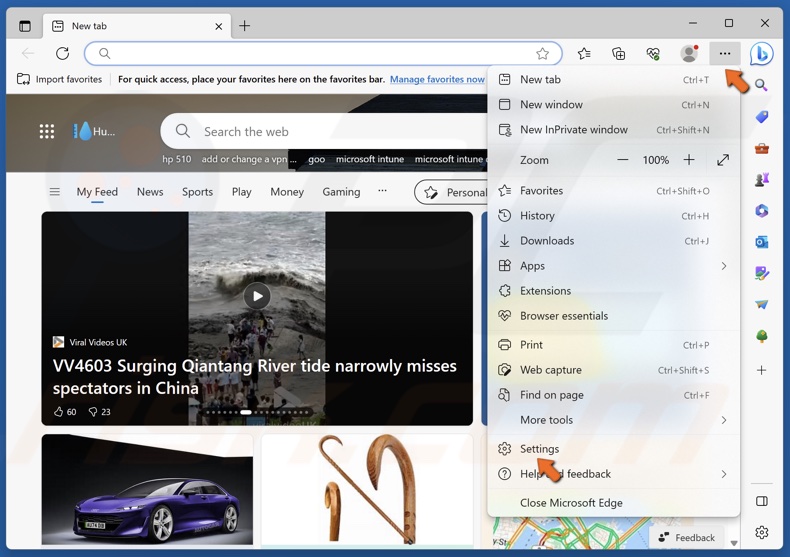
1. Open Edge. Click the three-dot menu button at the top-right corner and click Settings.
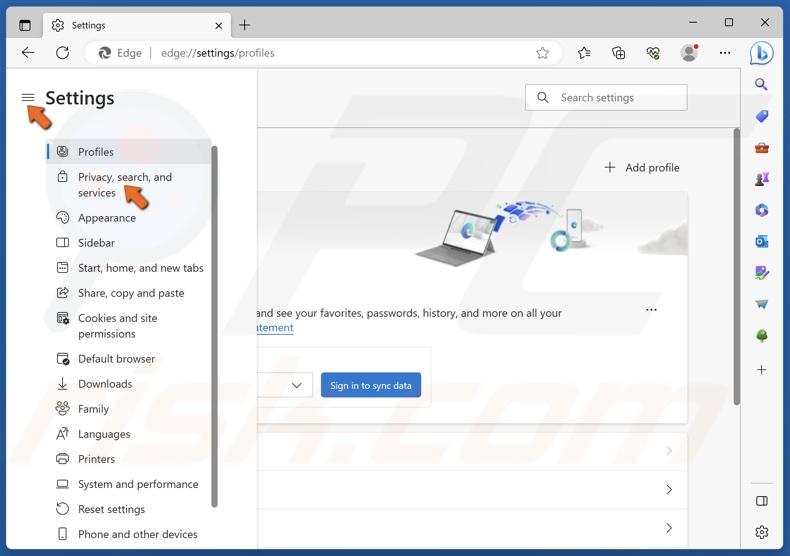
2. Click Privacy, search, and services in the right pane.
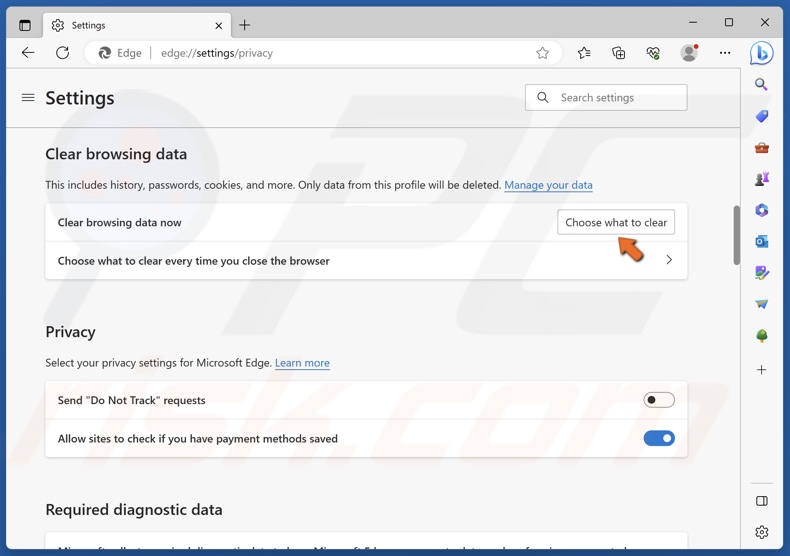
3. Scroll down and click Choose what to clear.
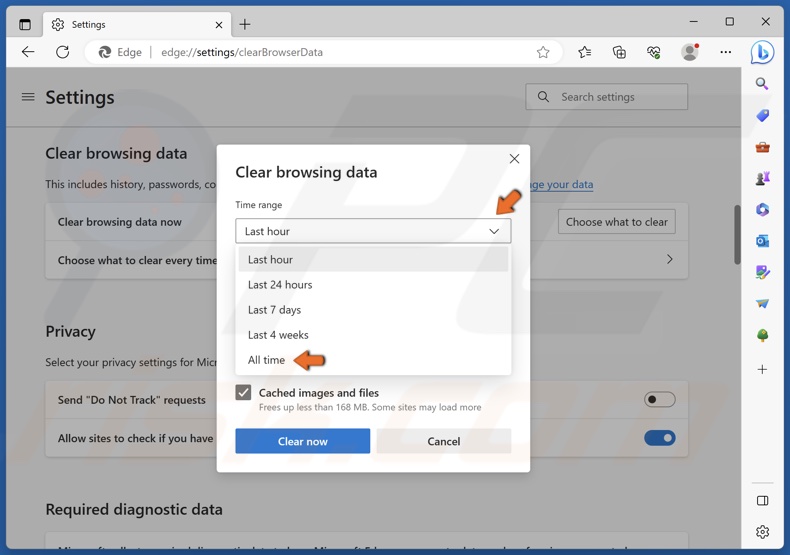
4. Open the Time range drop-down menu and select All time.
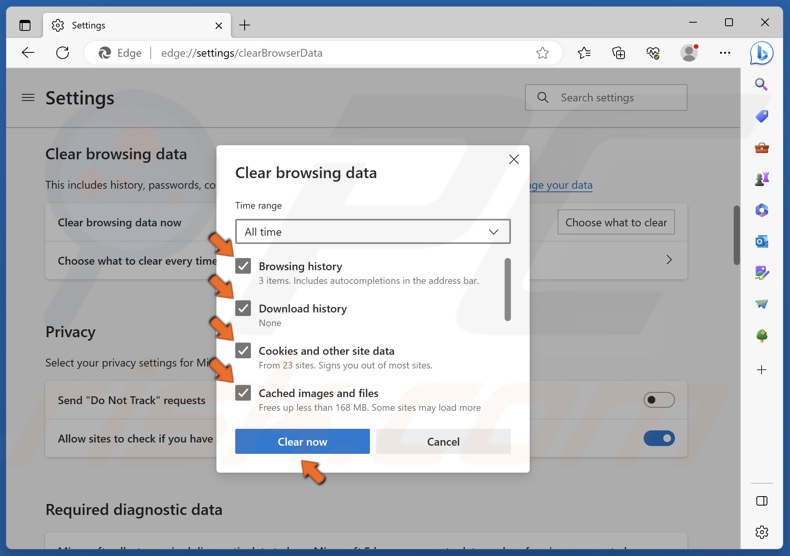
5. Mark the Browsing history, Download history, Cookies and other site data, and Cached images and files checkboxes.
6. Click Clear now.
Method 2. Disable Browser Extensions
Certain browser extensions can interfere with the request sent to the website server. Extension interference may cause a website server to interpret the request as invalid and trigger Error 400 Bad Request. In addition, some extensions can affect your browser cookies, which will also trigger the error.
We recommend that you disable all of your browser extensions and try to access the website giving you Error Code 400. If you access the website, it means that one or more extensions were to blame. Then, enable extensions one by one, checking if you can still access the website after enabling an extension.
Disable Extensions on Google Chrome
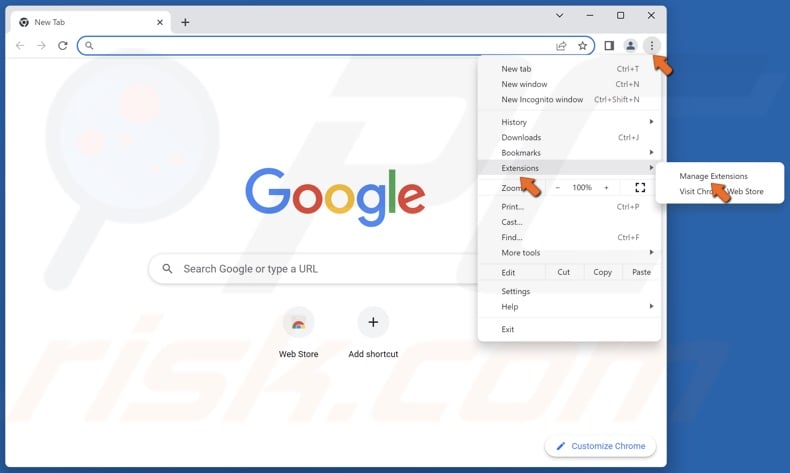
1. Open Chrome. Click the three-dot menu button at the top-right corner, select Extensions, and click Manage Extensions.
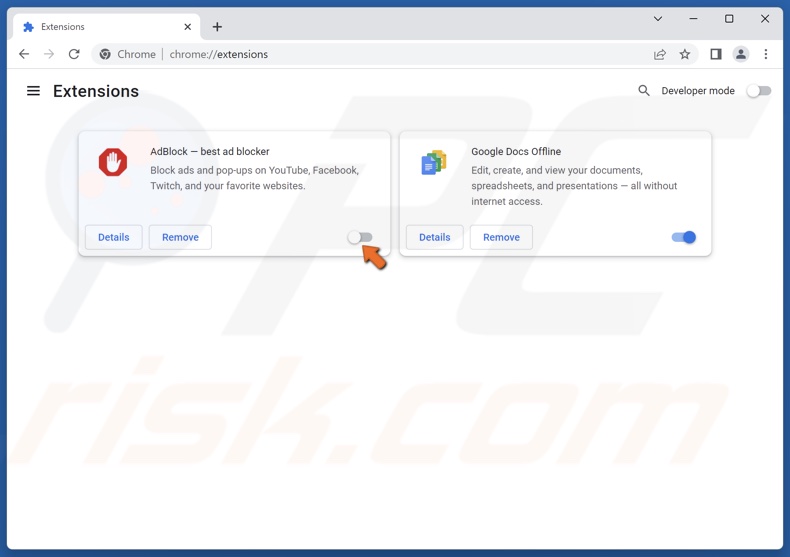
2. Toggle off the slider next to an extension to disable it. Disable all of your extensions and check if that fixes the error.
Disable Extensions on Mozilla Firefox

1. Open Firefox. Click the menu button at the top-right corner and click Add-ons and themes.
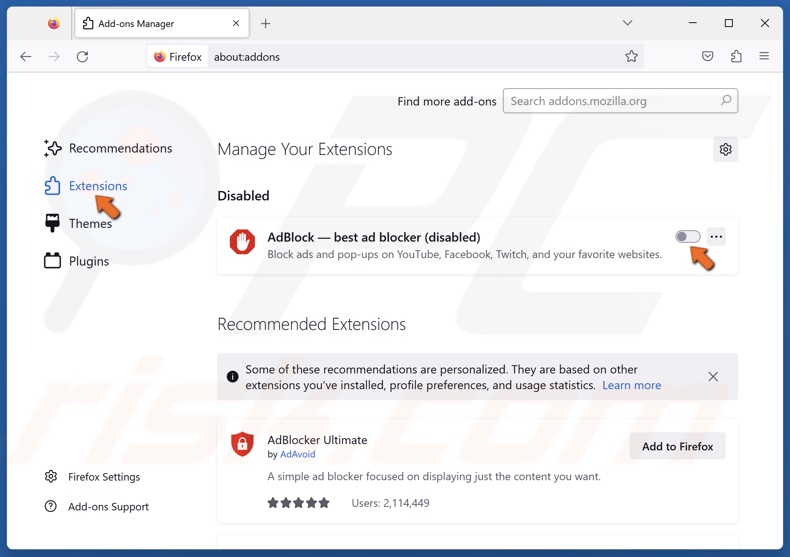
2. Select the Extensions panel.
3. Toggle off the slider next to an extension to disable it. Disable all of your extensions and check if that fixes the error.
Disable Extensions on Microsoft Edge
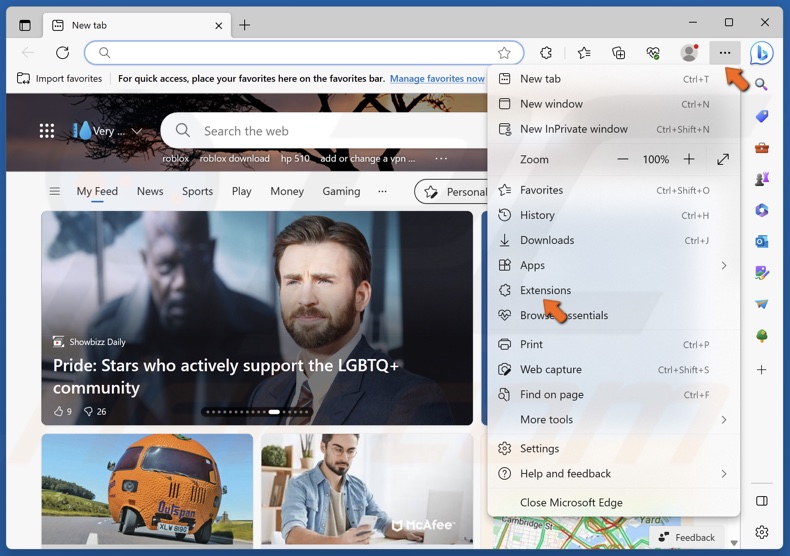
1. Open Edge. Click the three-dot menu button at the top-right corner and click Extensions.
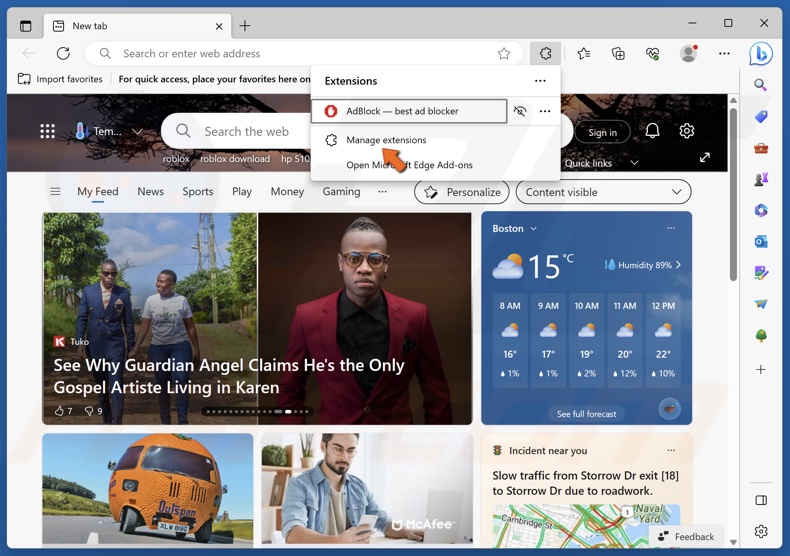
2. Click Manage extensions.
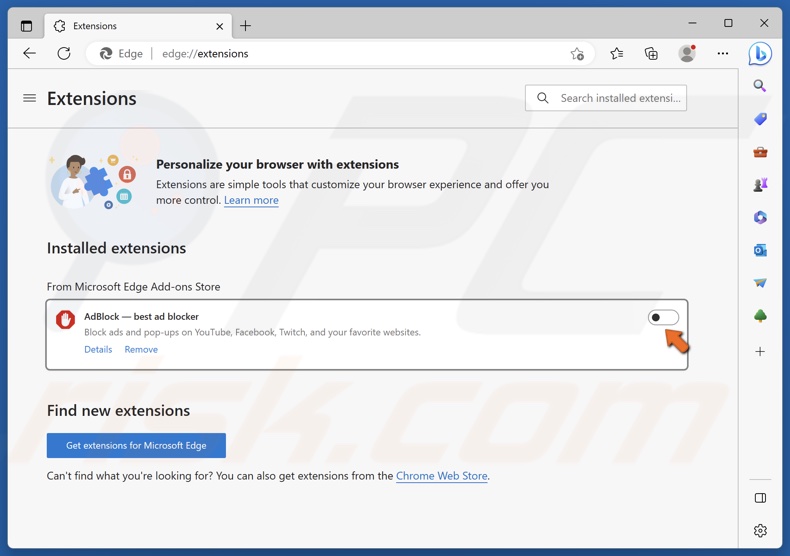
3. Toggle off the slider next to an extension to disable it. Disable all of your extensions and check if that fixes the error.
Method 3. Clear DNS Cache
Your Windows operating system stores web server IP addresses in the DNS cache so that it wouldn’t go through the DNS lookup process each time you try to visit a website. However, a corrupted or outdated DNS cache may trigger Error Code 400. In this case, clearing the DNS cache will fix the error.
1. Hold down Windows+R keys to open Run.
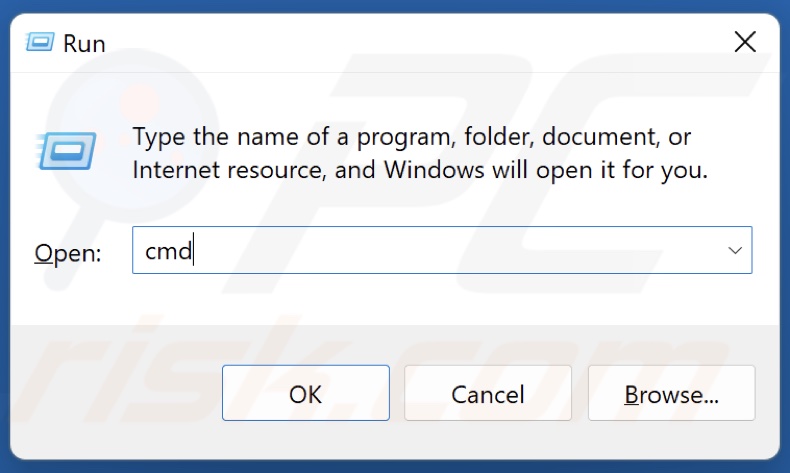
2. Type in CMD in the Run dialog and hold down Ctrl+Shift+Enter keys to open Command Prompt as an administrator.
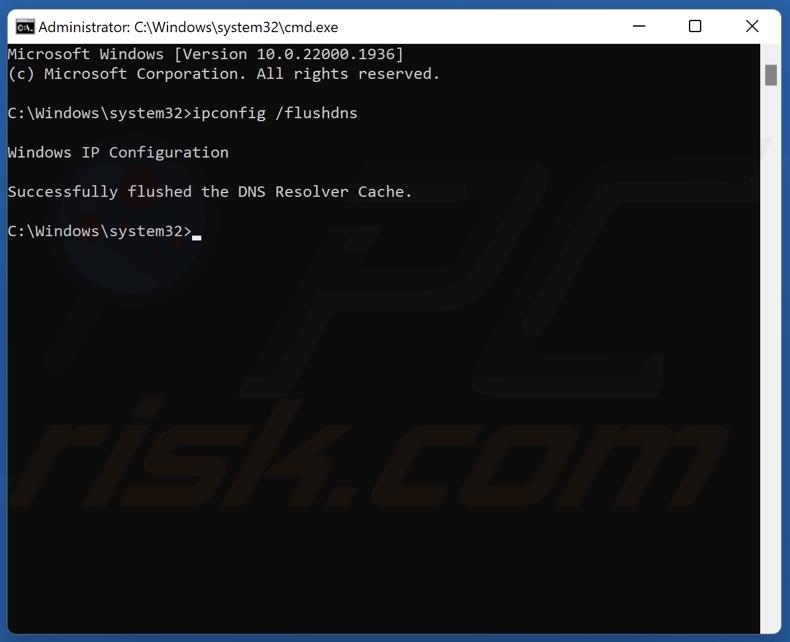
3. In the Command Prompt window, type in:
ipconfig /flushdns
4. Press the Enter key. This command will clear the DNS cache files and reset the DNS resolver cache
Did this article help you fix Error 400 Bad Request on your Windows PC? Let us know in the comments section below.
Share:

Rimvydas Iliavicius
Researcher, author
Rimvydas is a researcher with over four years of experience in the cybersecurity industry. He attended Kaunas University of Technology and graduated with a Master's degree in Translation and Localization of Technical texts. His interests in computers and technology led him to become a versatile author in the IT industry. At PCrisk, he's responsible for writing in-depth how-to articles for Microsoft Windows.

▼ Show Discussion