How to Fix a Memory Leak in Windows 10
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
How to Avoid and Fix Memory Leaks in Windows 10
Some software can slow down your computer if it leaks memory (when a program fails to 'release' memory it has used). By default, a closed program should allow other software to use that same area of memory. If, however, the program is still using the memory having been closed, that is where memory leak problems begin.
A memory leak is a Random Access Memory (RAM) loss caused by one or more programs. Memory leaks are usually only temporary since restarting the computer empties RAM memory. If, however, the computer remains switched on with various processes running in the background, some processes might cause memory leaks.
As mentioned above, closed programs should not use Random Access Memory and should release previously-allocated memory. If you experience memory leaks each time you work with your computer, there is a problem that needs to be solved.
To fix memory leaks in Windows 10, you might need to kill a program using Task Manager, run a memory diagnostic tool, disable startup programs, defragment the hard drive, scan the system for malware, edit Windows Registry, and take other measures.
Video Showing How to Fix Memory Leaks in Windows 10:
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Edit Registry
- Disable Superfetch
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
- Scan Your System for Malware
- Defragment Your Hard Drive
- Update Your Drivers
- Video Showing How to Fix Memory Leaks in Windows 10
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Edit Registry
Windows Registry is a collection of databases of configuration settings in Microsoft Windows operating systems. To open Registry Editor, you will first need to open the Run dialog box.
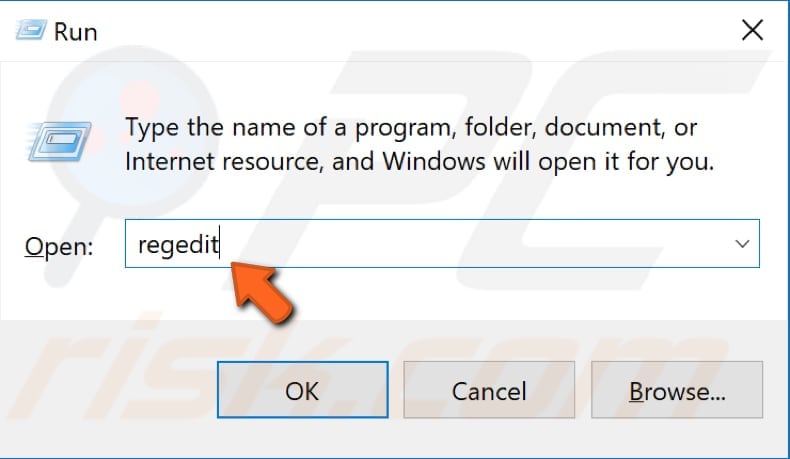
Press Windows Windows key + R or right-click Start, select "Run" and type "regedit". Press Enter or click "OK".
NOTE: Create a restore point before you make any changes in Windows Registry (editing the Registry incorrectly can lead to more serious problems).
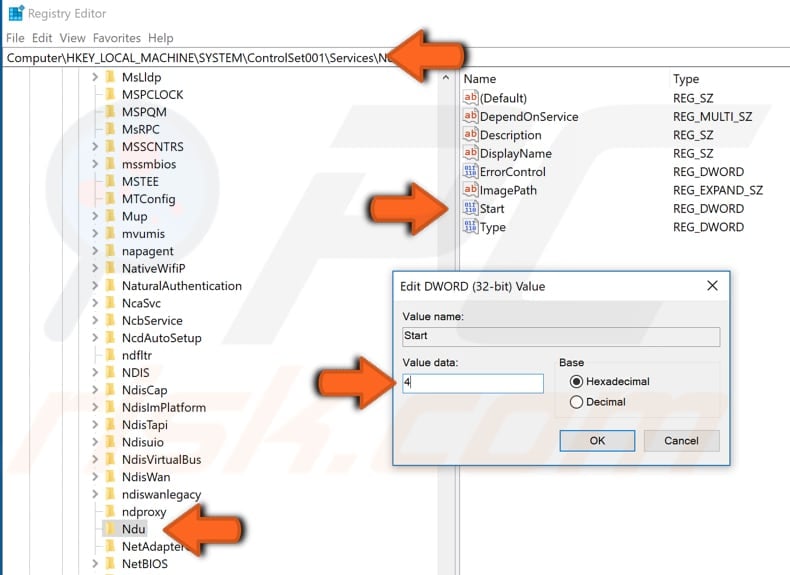
Follow this path by expanding every entry until you find the "Ndu" key: "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Services". Find "Ndu" key under Services and select it.
Now you should see the "Start" REG_DWORD on the right pane. Double-click it and assign the value data to 4. Click "OK" to save the changes.
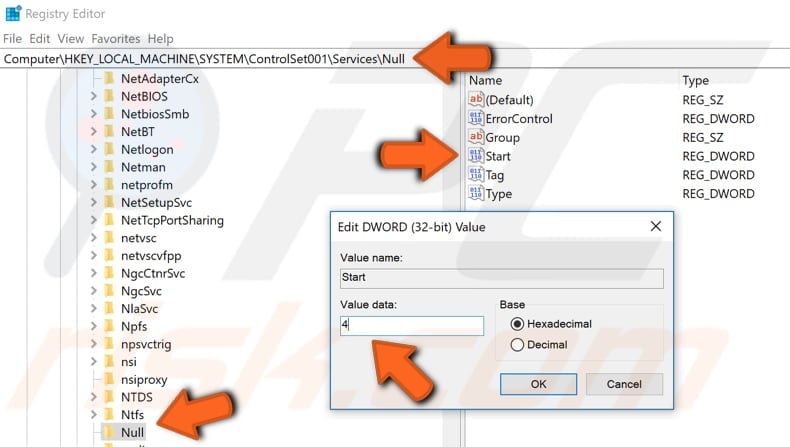
Now find the "Null" key under the same Services key and double-click "Start" REG_DWORD. Also, set its value to 4 . Click "OK" to save the changes.
Now follow this path: "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\Session Manager" and select the "Memory Management" key. Double-click the "NonPagedPoolSize" REG_DWORD on the right pane. Change Base to "Decimal" and set value data to 192.
Click "OK" to save the changes, exit Registry, and see if the memory leak problem is now solved. If not, try to restart your computer after editing the Registry.
Disable Superfetch
Superfetch is a Windows service that is intended to speed up application launching and improve system responsiveness. It caches data so that it can be immediately available to your application. Superfetch achieves this by preloading frequently-used programs into RAM so that they are not required to be called from the hard drive. This can sometimes affect performance and slow down the system or cause memory leaks.
To disable Superfetch, open the Run dialog box and type "services.msc". Press Enter on the keyboard or click "OK".
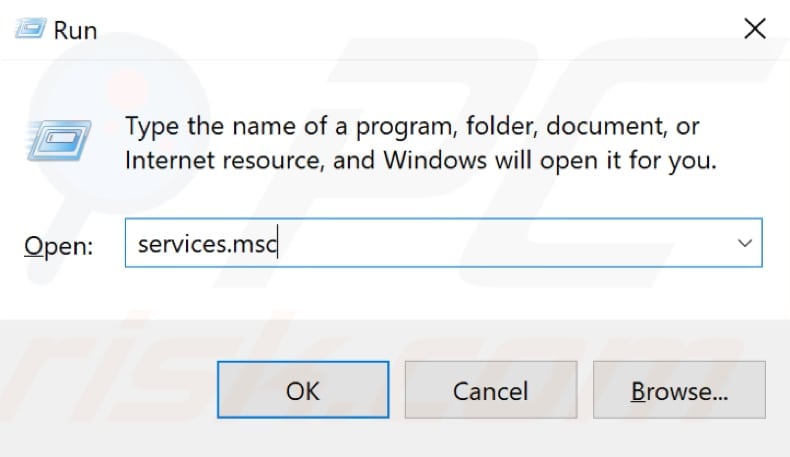
In the Services window, you will see a list of local services. Scroll down to find "Superfetch" and right-click it, select "Properties" from the contextual menu.
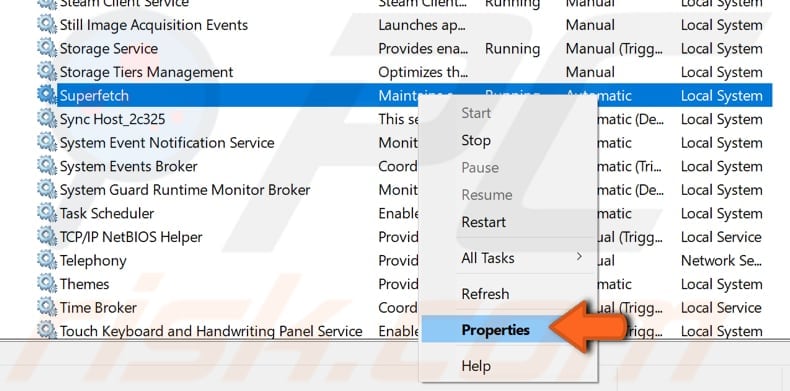
Now set the "Startup type" to "Disabled" and stop the service by pressing the "Stop" button. Click "Apply" to save the changes, restart your computer, and check if this solves the memory leak problem.
Run Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
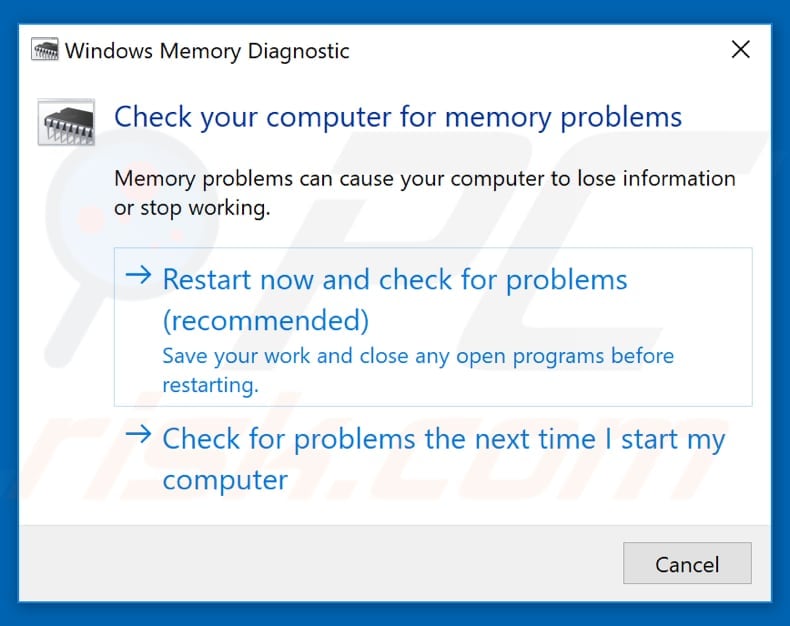
Run the built-in Windows Memory Diagnostic tool. Windows Memory Diagnostic is a memory test tool, which is comprehensive and easy to use.
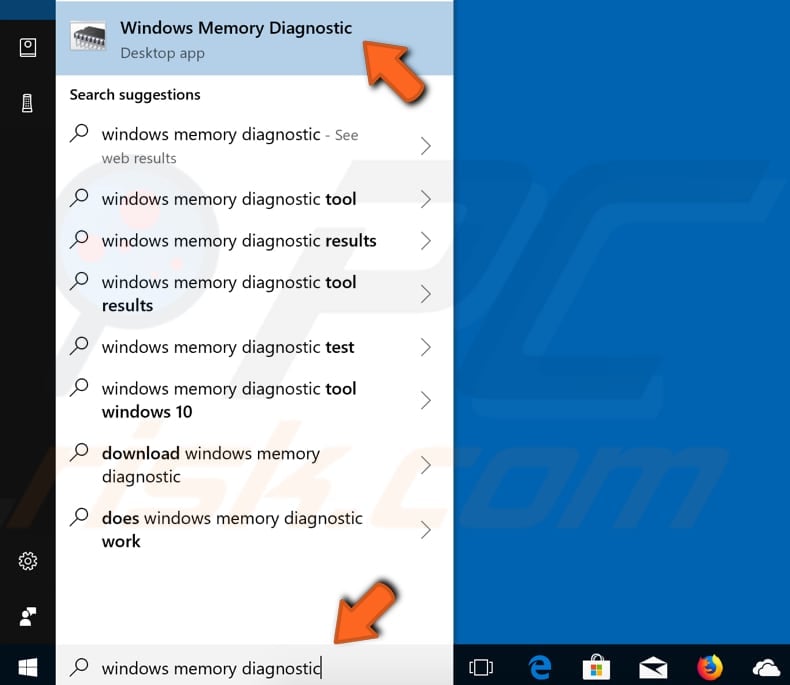
To launch it, type "windows memory diagnostic" or "mdsched" in Search and click the "Windows Memory Diagnostic" result.
To run diagnostics, restart the computer. You will be asked if you want to restart now or run it the next time you start your computer. When you restart the computer, Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool will start automatically. You will be able to see the test process and results on the screen.
Scan your System for Malware
Malware, viruses, and other infections could be the reason for memory leaks. If you suspect this is the case, scan your system using antivirus software. You can use Windows Defender (a built-in antivirus program), which protects your computer against viruses, spyware, and other malicious software. Alternatively, you can run other third-party antivirus software if you have a suitable program installed.
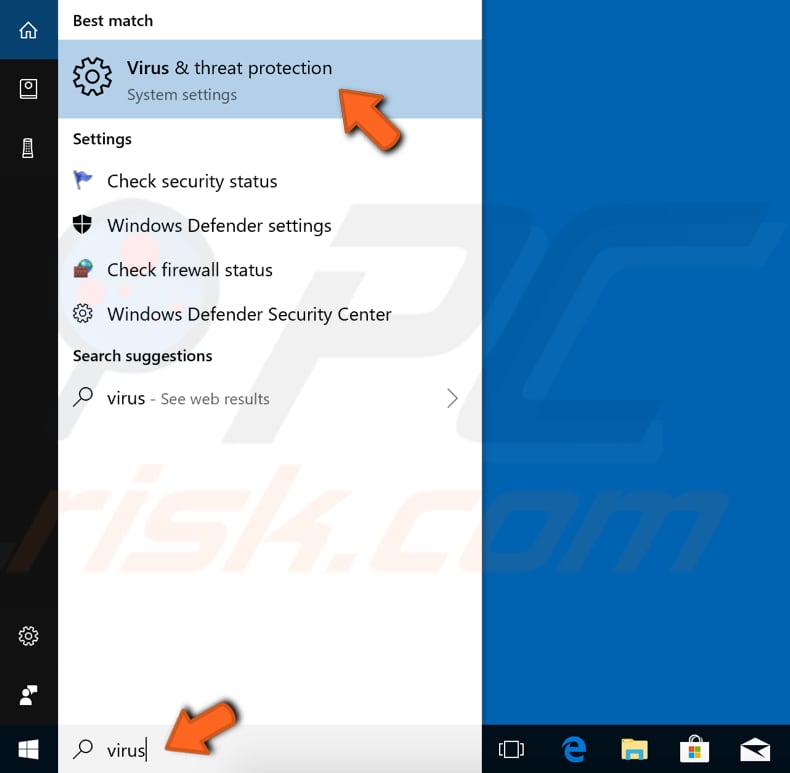
To run a full system scan using Windows Defender, type "virus" in Search and click on the "Virus & threat protection" result.
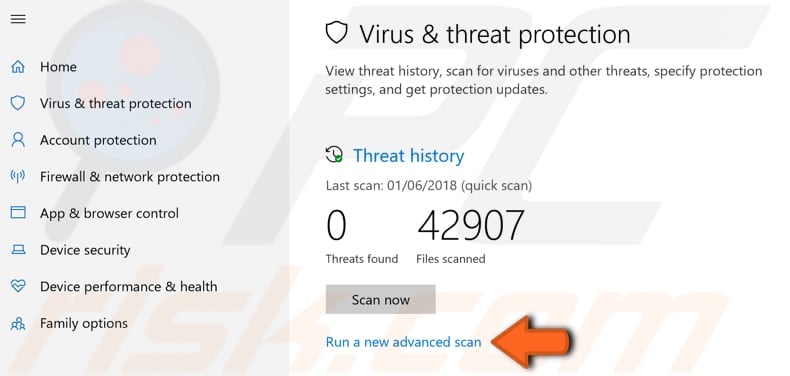
In the Virus & threat protection window, find and click the "Run a new advanced scan" option.
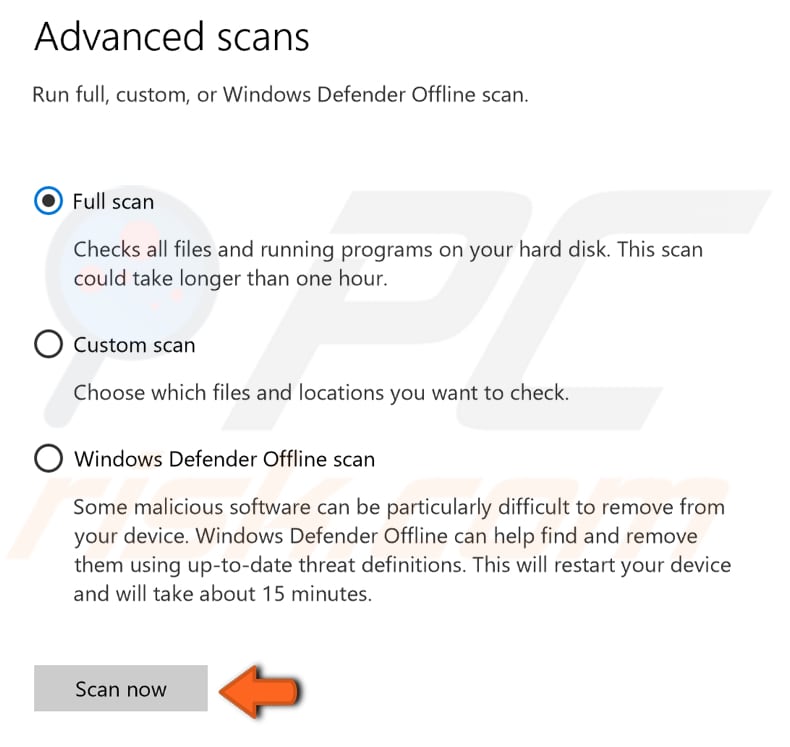
You will see a list of advanced scans. We recommend that you choose the "Full scan", which will check all files and running programs on your hard disk. Note that this will take some time (usually over an hour) to complete.
To start a Full scan, click "Scan now" when the "Full scan" option is selected.
If you wish, choose a virus and malware scanner from our Top anti-malware list. The list contains well-known, top spyware removers and will help you choose the right software for your computer's protection. You can find the list by clicking this link.
Defragment Your Hard Drive
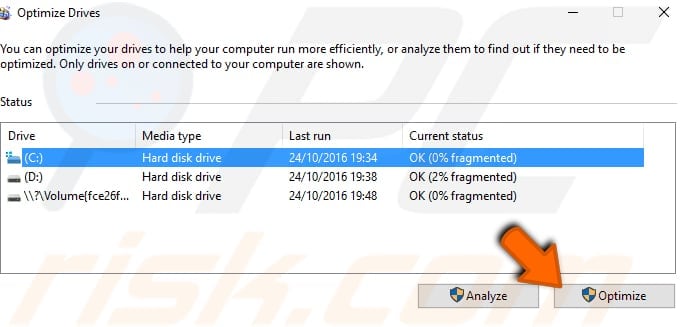
A built-in Windows feature called "Defragment and Optimize Drives" optimizes drives to help the system run more efficiently (or analyzes them to determine if they require optimization).
To launch the defragmentation tool, type "defragment" in Search and click the "Defragment and Optimize Drives" result.
You will see a list of drives connected to the computer. Select the hard drive you want to defragment and click "Optimize". The optimization process should take a while. Wait for it to finish.
NOTE: We do not recommend that you defrag your drive if it is a Solid State Drive (SSD) or Hard Disk Drive (HDD).
Update your Drivers
A device driver informs the operating system and other software how to interact with particular hardware. Outdated drivers are sometimes the reason for memory leaks in the Windows operating system.
To update your drivers, open Device Manager by right-clicking the Start button and selecting the "Device Manager" result from the contextual menu, or type "device manager" in Search and click the "Device Manager" result.
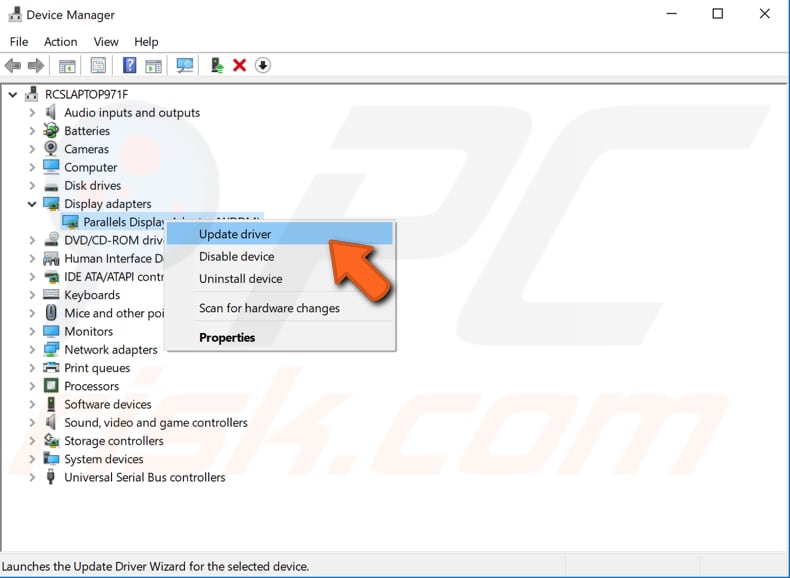
In Device Manager, you will see a list of devices connected to your computer. Try to update your display adapter, network adapter, and sound, video and game controllers first. Expand the device section, right-click the device, select the "Update driver" option.
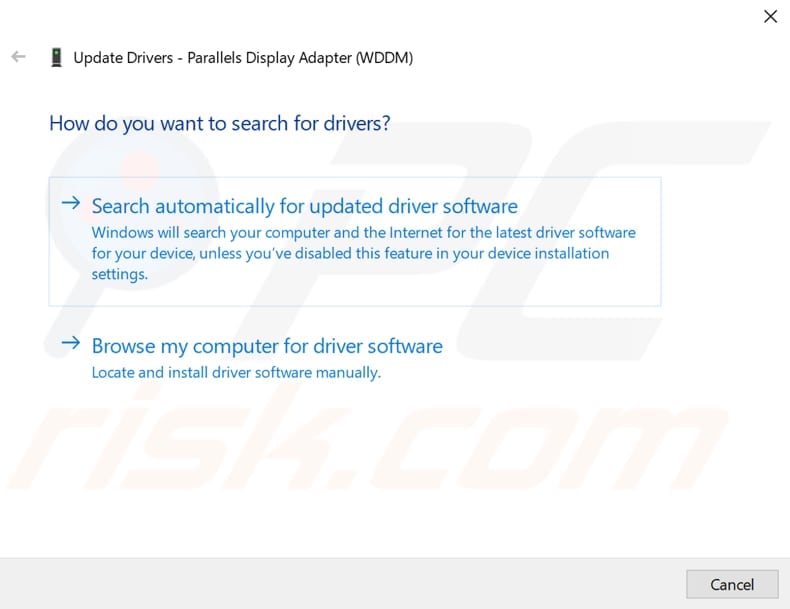
You will be asked if you want to search for updated driver software automatically or to browse your computer for driver software. If you select the first option, Windows will search your computer and the internet for the latest driver software for your device.
If you select the second option, you will must locate and install the drivers manually. Using this option requires having previously downloaded the driver on your computer or USB flash drive. You must download all the latest drivers for all the devices manually by visiting the device manufacturer's official website. Select the option you prefer and follow the instructions.
You can use third-party software to update your drivers automatically without undertaking too much manual work. In this case, we recommend the Snappy Driver Installer, a free driver updater tool for Windows. You can download Snappy Driver Installer here.
We hope that one of these methods solved your memory leak problem. Certain software is likely causing memory leaks, and you might need to restart it every time it starts to cause a problem. Alternatively, stop using/uninstall the software if that is an option.
If you know of other solutions to this problem not mentioned in our guide, please share them with us by leaving a comment below.
Share:

Rimvydas Iliavicius
Researcher, author
Rimvydas is a researcher with over four years of experience in the cybersecurity industry. He attended Kaunas University of Technology and graduated with a Master's degree in Translation and Localization of Technical texts. His interests in computers and technology led him to become a versatile author in the IT industry. At PCrisk, he's responsible for writing in-depth how-to articles for Microsoft Windows.

▼ Show Discussion