How to Fix Firefox High Memory Usage
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
How to Fix Firefox High Memory Usage
Mozilla Firefox is a great web browser that offers many features and customization options and is designed to be fast and secure. However, while the Mozilla Firefox browser's performance is excellent, it could slow down your computer and use too much of your computer's memory (RAM).

One of the things that makes Mozilla Firefox reliable is that it is a multi-process web browser. It splits up different parts of the browser into processes but, this requires more memory. Features such as prerendering are also beneficial and let you save time by loading pages faster, but this feature also requires more memory. If you are using some extensions, the browser will use even more memory.
If you read this, you have probably noticed that Mozilla Firefox started to use way too much memory, and your computer works slower. However, there are things that can be done about that.
Read the guide below and try our described methods, and hopefully, Mozilla Firefox will not use that much memory after that.
Video Showing How to Fix Mozilla Firefox High Memory Usage:
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Update Mozilla Firefox
- Disable Extensions
- Minimize Memory Usage
- Use Default Theme
- Start Firefox in Safe Mode
- Adjust Content Process Limit
- Adjust Preferences
- Video Showing How to Fix Mozilla Firefox High Memory Usage
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Update Mozilla Firefox
The first thing we recommend you to try is to check for Mozilla Firefox updates and update it if there are any updates available. Older versions may have some bugs or performance issues. Newer versions usually offer improved performance and fixed bugs.
To check for Firefox updates, open it and click the three stripes (Open menu) in the top-right corner, then click the "Help" option.

A new contextual menu will show up. Click the "About Firefox" option.
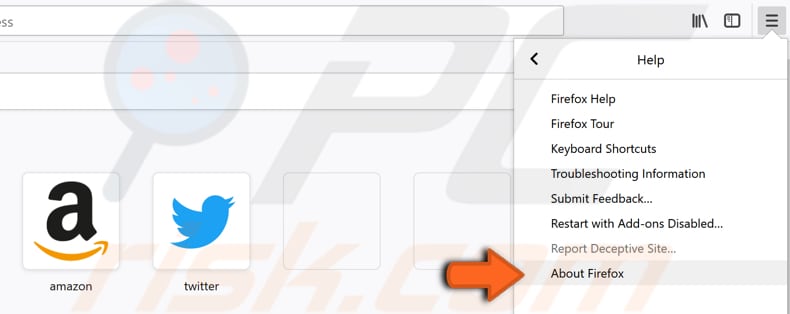
Mozilla Firefox will start checking for updates. If there are any updates found, Mozilla will install them for you. If you already have the latest version, you will see "Firefox is up to date" status.

Disable Extensions
Now that you have the latest version, you can try to disable the installed and enabled extensions. Extensions are software programs that allow users to customize their browsing experience. By using extensions, you can make Mozilla Firefox compatible with your personal needs or preferences. Extensions can (and some of them usually do) cause increased memory usage.
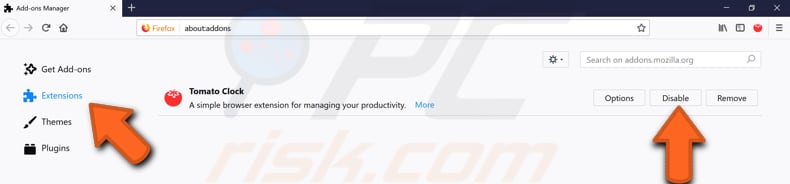
To access installed extensions, click the three stripes (Open menu) in the top-right corner again and select "Add-ons" from the contextual menu or simply press Ctrl + Shift + A keys on your keyboard.
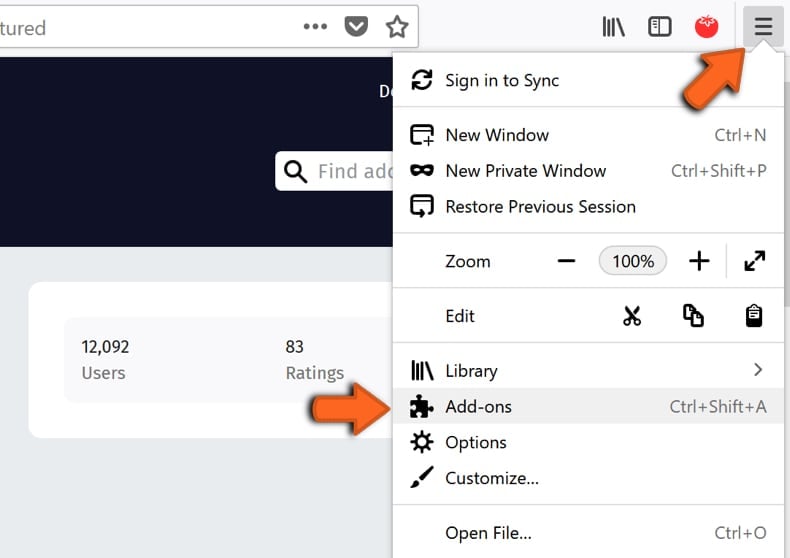
Click "Extensions" on the left pane, and you will see all installed extensions. You can choose whether you want to disable or remove them. We recommend you disable all installed extensions, restart Mozilla Firefox, and see if it still uses too much of your computer's memory.
If disabling extensions solves the problem, you will know that one of the extensions (or more than one) makes Mozilla Firefox use too much memory. If that is the case, enable installed extensions one by one to see which one is causing the problem and remove it permanently.
Minimize Memory Usage
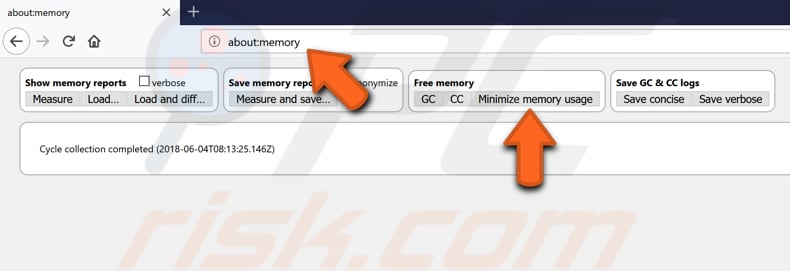
There is a built-in tool in Mozilla Firefox that allows you to minimize memory usage. There is a page called "about:memory" that allows you to troubleshoot specific issues about memory, like issues caused by a website, a theme or an extension. This page allows you to view, save, diff, and load detailed measurements of Mozilla Firefox's memory usage.
It also allows you to do a global garbage collection or cycle collection or save garbage collection or cycle collection logs. By minimizing memory usage using the "Minimize memory usage" tool, you could reduce memory usage in one click.
To do so, type "about:memory" in Firefox's address bar and press Enter. Then click the "Minimize memory usage" button and see if Mozilla Firefox is still using too much of your computer's memory.
Use Default Theme
A theme is an add-on that allows users to change the visual appearance of Mozilla Firefox. It simply changes how the browser looks, and it may make Firefox look not like Firefox at all. However, some themes could be more complex and force Mozilla Firefox to use more memory.
If you are using a theme that is not a default theme, we recommend you switch back to the original default theme. Click the three stripes in the top-right corner and select "Add-ons" again. Now select "Themes" on the left pane and make sure that the "Default" theme is enabled.
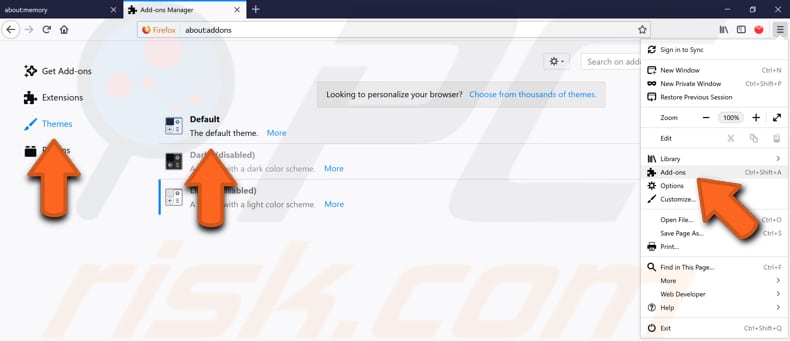
Start Firefox in Safe Mode
Safe Mode is a mode in Mozilla Firefox (a similar one in Windows) that is usually used to troubleshoot and fix various problems with Mozilla Firefox. Safe Mode disables all installed add-ons like extensions, themes, etc., resets some settings, and turns off hardware acceleration.
The main goal of Safe Mode is to find out if one of the disabled features is the culprit of the problem and then take certain actions if one of them was actually the cause.
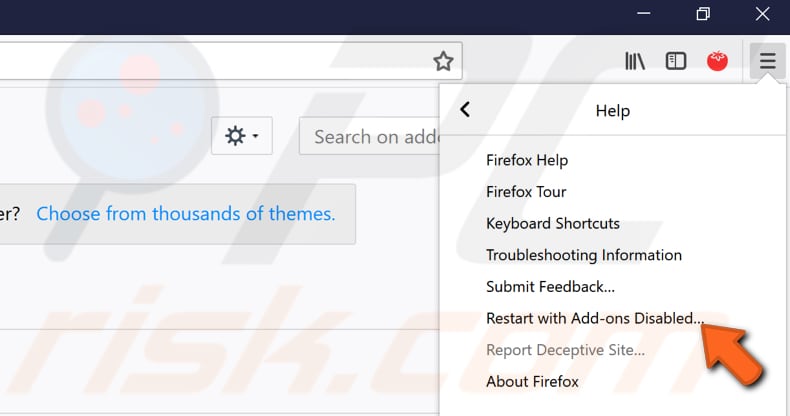
To start Mozilla Firefox in Safe Mode, click the three stripes in the top-right corner and select "Help", and then select "Restart with Add-ons Disabled...". You will be asked if you really want to disable all add-ons and restart, click "Yes".
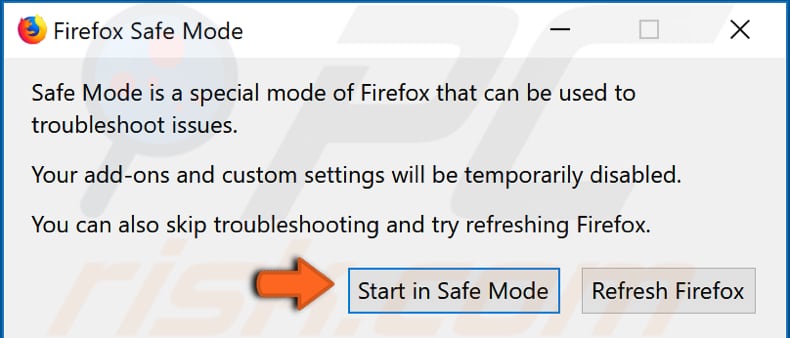
You will be given two options: Start in "Safe Mode" and "Refresh Firefox", select the first one, and see if Mozilla Firefox is now using less of your computer's memory. If this solved the problem, then some of the settings, add-on, or extensions were causing the problem. Selecting the second option, the "Refresh Firefox, " will restore Firefox to its factory default state but save your essential information.
Adjust Content Process Limit
As we mentioned in our introduction, Mozilla Firefox runs web content for all tabs separately from the main Firefox process, increasing security and performance. Using multiple content processes (usually 4 processes) increases performance and minimizes the impact of content process crashes.
However, while additional content processes improve performance when using multiple tabs, they also use more memory. We recommend you try to change these default settings and adjust the content process limit.
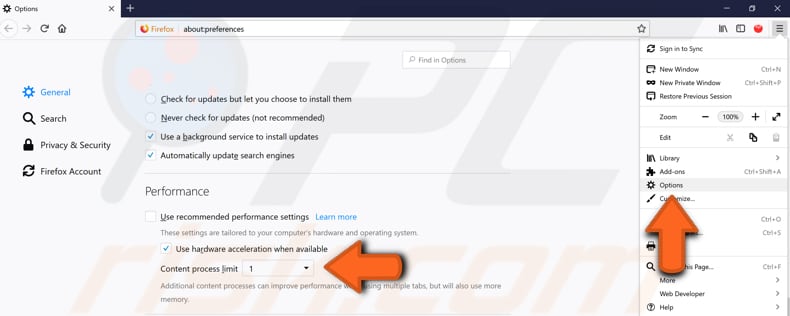
To do so, click the three stripes in the top-right corner and select "Options". Then scroll down through the General section until you find the "Performance". Uncheck the "Use recommended performance settings" option and set "Content process limit" from 4 (default) to 1.
Restart Mozilla Firefox and see if the memory usage is now decreased.
Adjust Preferences
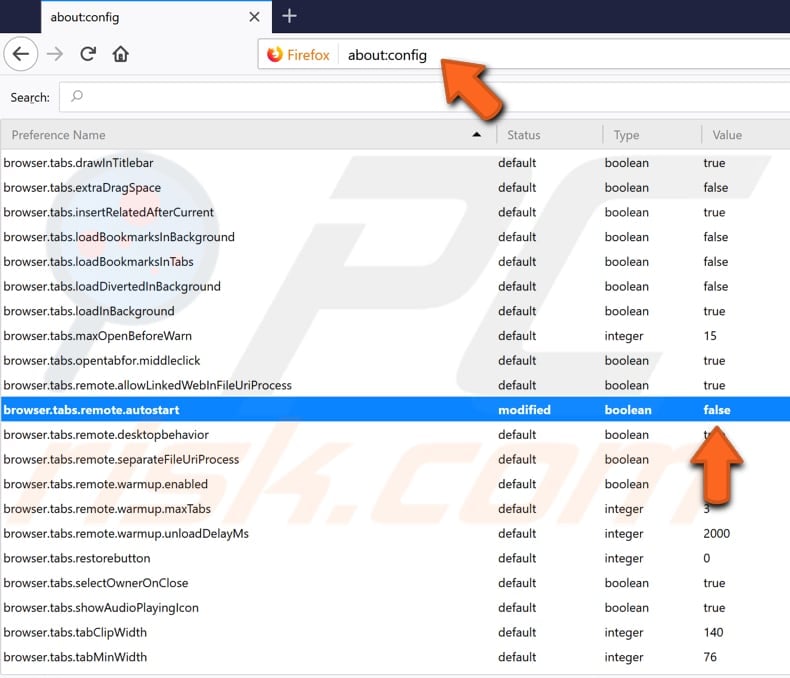
About:config is a feature in Mozilla Firefox that consists of a list with application settings, also known as preferences. The thing is that many of these preferences are not available in the Options or Preferences menu. About:config is a feature that allows users to access "hidden" preferences and adjust them. However, you should keep in mind that you are accessing these preferences at your own risk and know that these advanced settings can be harmful to Mozilla Firefox's stability, security, and performance. To adjust these settings, type "about:config" in the address bar and press Enter.
Scroll through the long list of preferences and find the "browser.tabs.remote.autostart". Double-click it to change its value from "true" to "false". Disabling this preference will disable e10s/multimulti-processh could be the reason why Mozilla Firefox is using so much of your computer's memory.
Restart Mozilla Firefox and see if it began to require less memory.
Another simple thing you could try is to run fewer open tabs. In other words, close the unnecessary tabs, and the memory usage should be reduced then. Check Windows Task Manager and see how many Mozilla Firefox processes are running. See if leaving only one Firefox process running reduces the memory usage.
Hopefully, one of the mentioned solutions solved the problem for you. If there is another method that helped you and reduced the memory usage caused by Mozilla Firefox, and it is not mentioned in our guide - do not hesitate to share it with us and others by leaving a comment in our comment section below.
Share:

Rimvydas Iliavicius
Researcher, author
Rimvydas is a researcher with over four years of experience in the cybersecurity industry. He attended Kaunas University of Technology and graduated with a Master's degree in Translation and Localization of Technical texts. His interests in computers and technology led him to become a versatile author in the IT industry. At PCrisk, he's responsible for writing in-depth how-to articles for Microsoft Windows.

▼ Show Discussion