How to Recover Deleted Files in Windows 10
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
How to Recover Files Deleted During Windows Update
Windows Update is a Windows service that downloads and installs software and security updates automatically. Some users experience an issue when their files get deleted after a major Windows update.
Many users report that they lost their files or programs after installing an update. After rebooting their computer, they notice that some files and programs are missing.
This problem usually occurs when some major updates are installed or after upgrading the operating system - commonly, the deleted programs are considered incompatible.
Major updates can cause compatibility problems: Windows requires compatible versions of installed programs to run them properly. Before upgrading or updating Windows 10, it states that all files will remain, but this is not entirely true in some cases.
You might restore your missing programs and files, but this depends on the installed update. It is by no means certain that you will recover your files, but follow the guide below to discover various retrieval methods.
Video Showing How to Restore Files Deleted After Windows Update or Upgrade:
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Check Windows.old Folder
- Restore Your System Using Restore Points
- Disable Windows Update Service
- Video Showing How to Restore Files Deleted After Windows Update or Upgrade
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Check Windows.old Folder
The Windows.old folder is created when upgrading Windows to a newer version, reinstalling or upgrading, and during major Windows updates. It contains all data and files from the previous Windows installation and can restore the previous version. The folder often occupies a large area of disk space since frequent upgrades of Windows result in additions to the Windows.old folder.
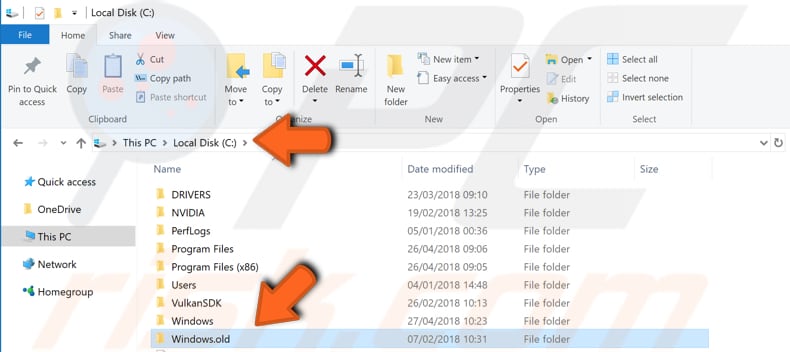
Data saved in Windows.old folder serve only as temporary files on the computer - they are retained for 30 days. If you have not deleted these files using a Disk Cleanup utility, or if 30 days have not expired, you may find your files in the Windows.old folder. Follow this path: "This PC > Local Disk (C:) > Windows.old".
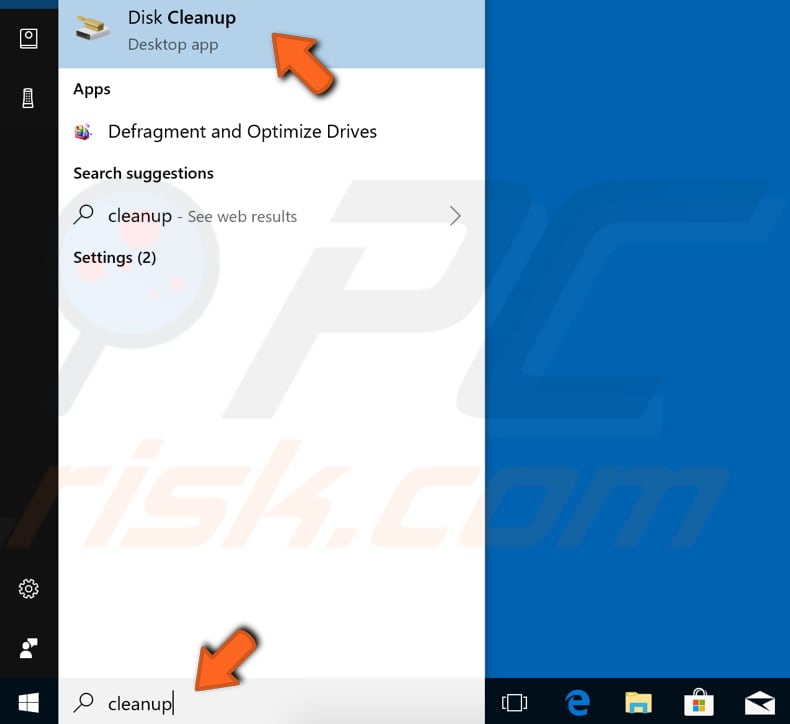
Alternatively, use the Windows Disk Cleanup utility. To access it, type "cleanup" in the Search box near Start. Click the "Disk Cleanup" result.
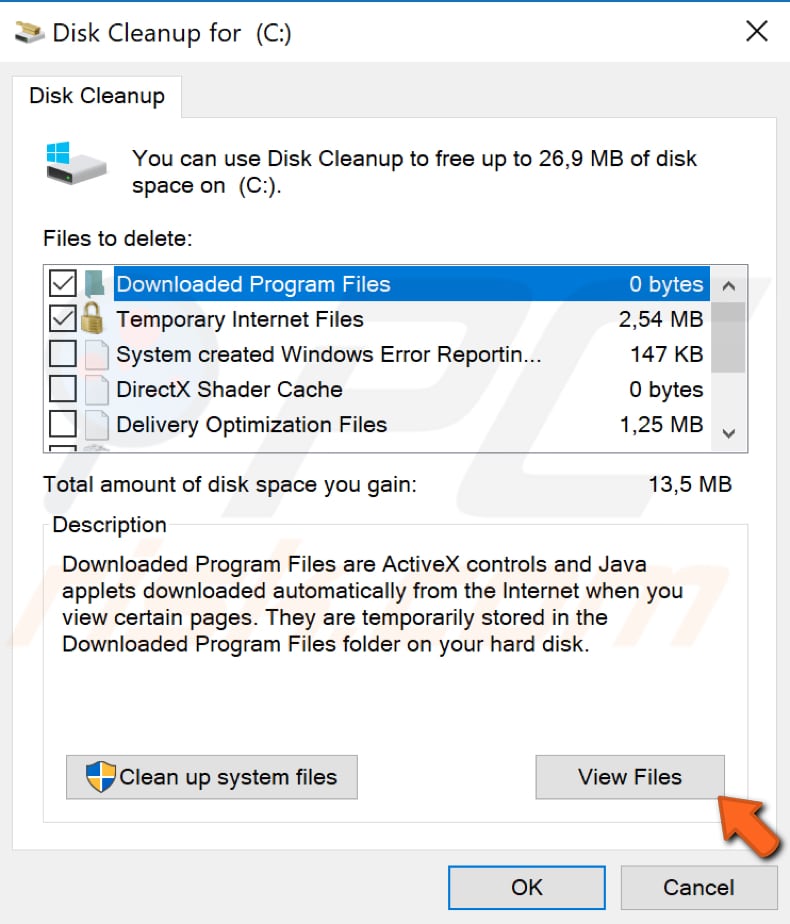
Windows will open the Disk Cleanup tool, and you will see a list of files (with checkboxes marked and unmarked). Find "Temporary Windows Installation files" or "Previous Windows installation(s)", select it and click "View files". This will open the location where the files are being stored.
Restore Your System Using Restore Points
If you were unable to find the files or programs removed during the update or an upgrade, we recommend you try to run System Restore using its restore points. A restore point is a collection of important system files stored by System Restore on a given date and time.
To use this tool, you must have created restore points. This feature will bring your system back to the previous working state with a created restore point without affecting your files and data. If Windows stores any system restore points that were created before you updated or upgraded the Windows operating system, you might be able to fix the problem by performing a System Restore.
To restore your system, launch Run. To start it, press the Windows Key + R and type "rstrui.exe". In the Run dialog box, press Enter or click "OK".
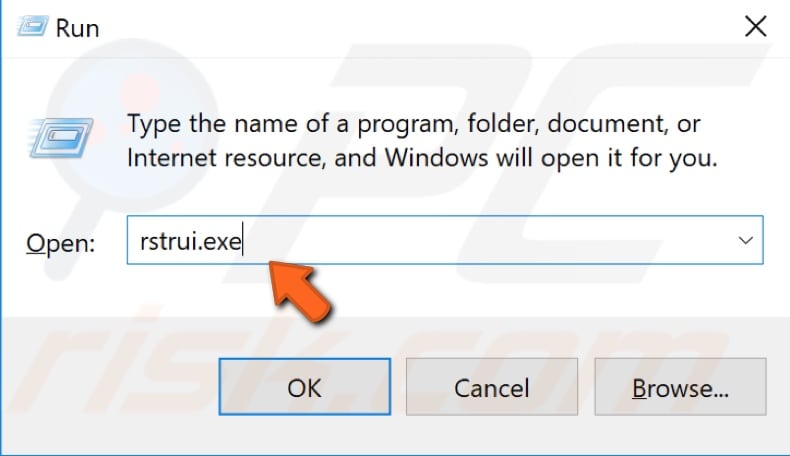
In the System Restore window, click "Next".
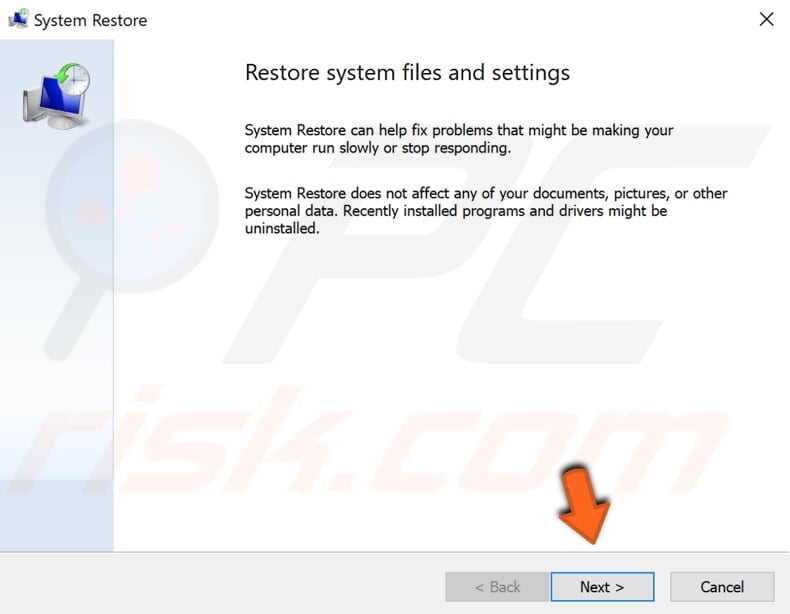
If there are restore points created, you will see a list of them. Mark the "Show more restore points" checkbox - it should display more restore points. Select the most appropriate restore point (depending on the time created, etc.) and click "Next".
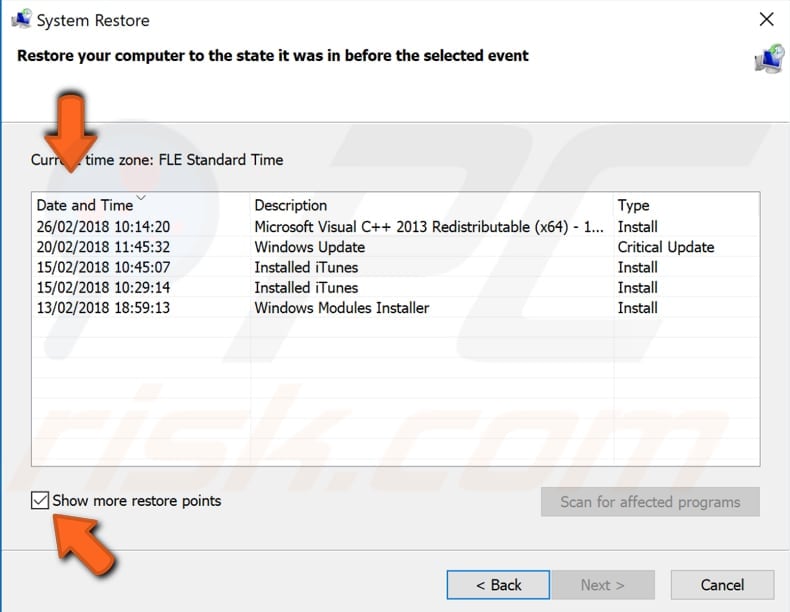
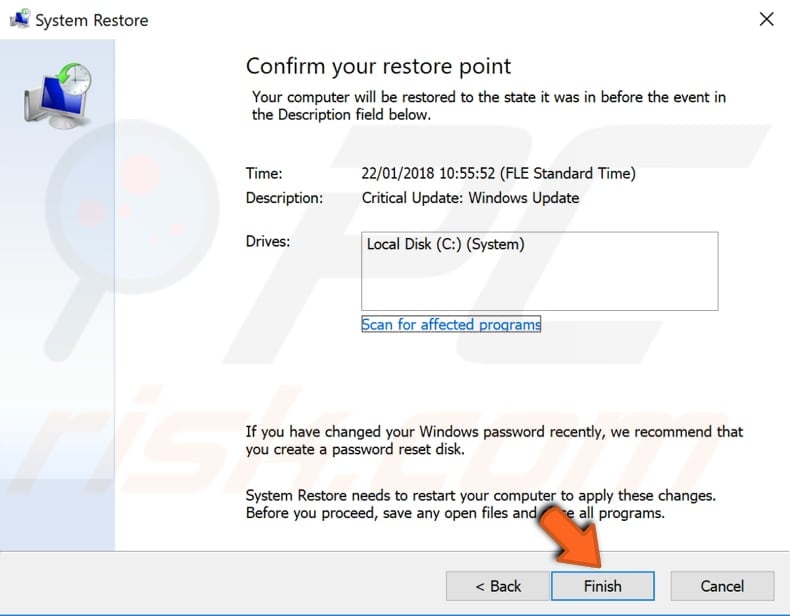
Confirm the restore point. Your computer will be restored to the state before the event detailed in the "Description" field. If you are happy with your choice, click "Finish" and begin the system restore process.
If this did not help recover your missing files, we recommend that you look for some third-party software designed to recover deleted and missing files. To prevent this situation in the future, you could disable Windows Automatic Update.
This feature is not available by default and requires some manual work. However, it is reasonably straightforward. You can disable automatic updates and backup the most important files before updating or upgrading the Windows operating system. The easiest way to do this is by disabling the Windows Update Service.
Disable Windows Update Service
Windows Services (also known as services.msc), are used to modify how Windows services run on your system. You can modify a service's settings for security, troubleshooting, and performance-related reasons.
One of those services is the Windows Update service. It enables the detection, download, and installation of updates for Windows and other programs. If this service is disabled, users will not be able to use Windows Update or its automatic updating feature, and programs will not use the Windows Update Agent.
To disable the Windows Update service, press the Windows (Win) key + R, or simply right-click Start and select "Run" from the contextual menu. Type "services.msc" in the Run dialog box and press Enter or click "OK".
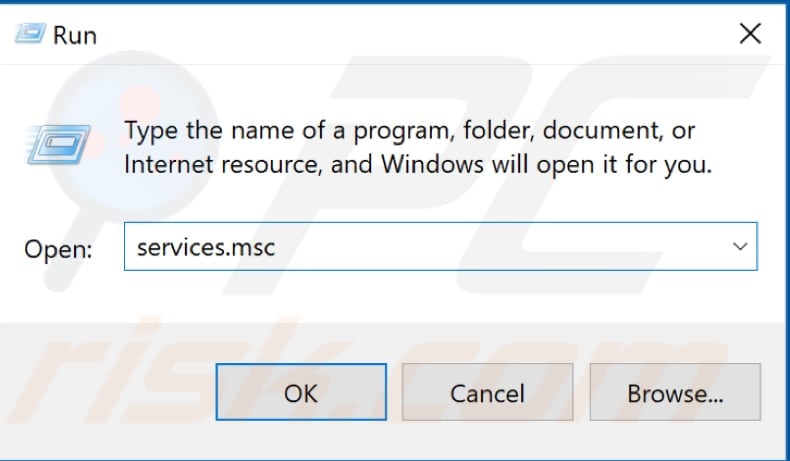
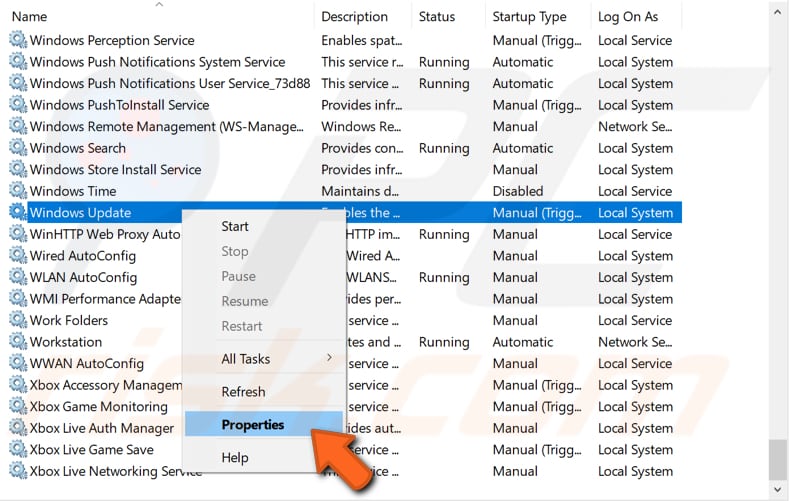
Find the Windows Update service in the services lists. To do this quickly, press "W" on the keyboard and scroll a little until you find "Windows Update". Right-click it and select "Properties" from the contextual menu.
Find "Startup type" and set it to "Disabled". Ensure that "Service status" is "Stopped". If not, click "Stop". Click "Apply" to save the changes and restart the computer.
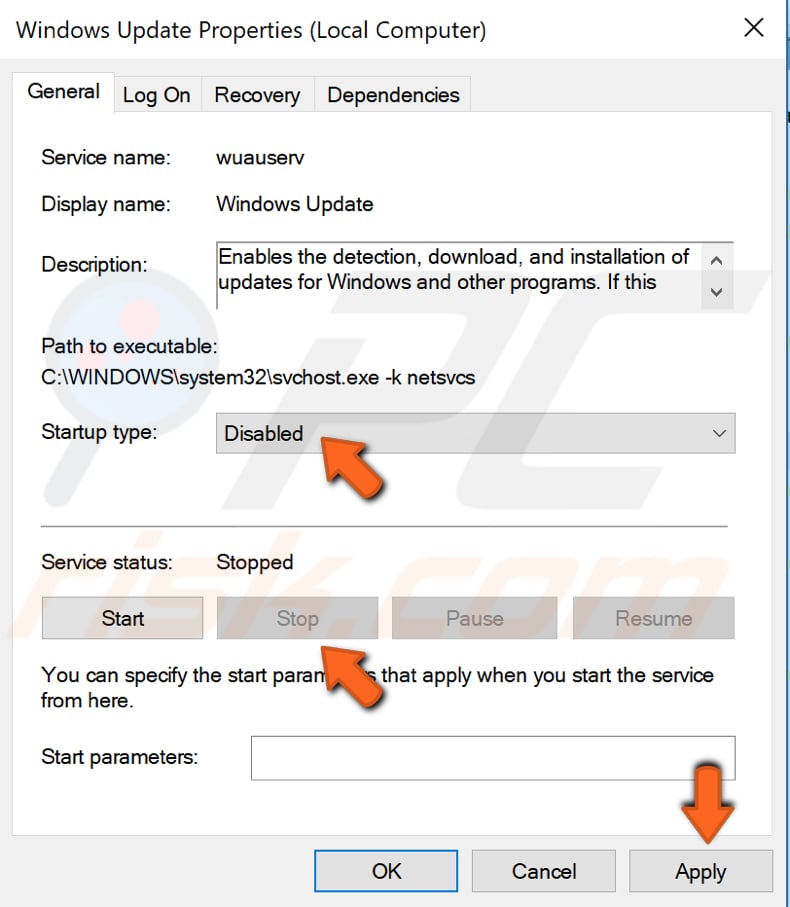
The Windows Update service will now be disabled. Windows will not update automatically unless you undo these changes. This will prevent your system from deleting any files during the update process.
We hope this guide was helpful and you were able to restore the missing files or programs. If you know of other solutions to this problem not mentioned in our guide, please share them with us by leaving a comment below.
Share:

Rimvydas Iliavicius
Researcher, author
Rimvydas is a researcher with over four years of experience in the cybersecurity industry. He attended Kaunas University of Technology and graduated with a Master's degree in Translation and Localization of Technical texts. His interests in computers and technology led him to become a versatile author in the IT industry. At PCrisk, he's responsible for writing in-depth how-to articles for Microsoft Windows.

▼ Show Discussion