File Explorer Is Working Slow. How To Fix It?
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
File Explorer Slow? Find Out How to Fix It
File Explorer is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) component of Microsoft Windows. File Explorer is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) component. Sometimes, the File Explorer may become slow or unresponsive. This article will show you how to fix this issue.

File Explorer is a file manager that allows Windows users to edit and manage data, files, and other content stored on their computers. However, many users report that it can be slow or even extremely slow.
One symptom that might indicate this problem is poor performance when copying or opening files. This can be a significant problem for users working with and managing many files daily. Fortunately, there are several solutions to fixing slow-working File Explorer that we detail in this guide.
Video Showing How to Fix File Explorer if It Is Running Slow:
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Disable Windows Search Service
- Disable Quick Access
- Change Folder Optimization Settings
- Restore Indexing Service
- Run SFC Scan
- Restart File Explorer
- Launch Folder Windows in a Separate Process
- Clear File Explorer History
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
- Create a New File Explorer Shortcut
- Uninstall Daemon Tools
- Video Showing How to Fix File Explorer if It Is Running Slow
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Disable Windows Search Service
Windows Services (also known as services.msc) modify how Windows services run on the system. These services are responsible for running available programs and managing many system settings and resources. You can modify a service's settings for security, troubleshooting, and performance-related reasons.
Windows Search service provides content indexing, property caching, search results for files, e-mail, and other content. To disable the Windows Search service, press Windows (Win) key + R on the keyboard or right-click Start and select "Run" from the contextual menu.
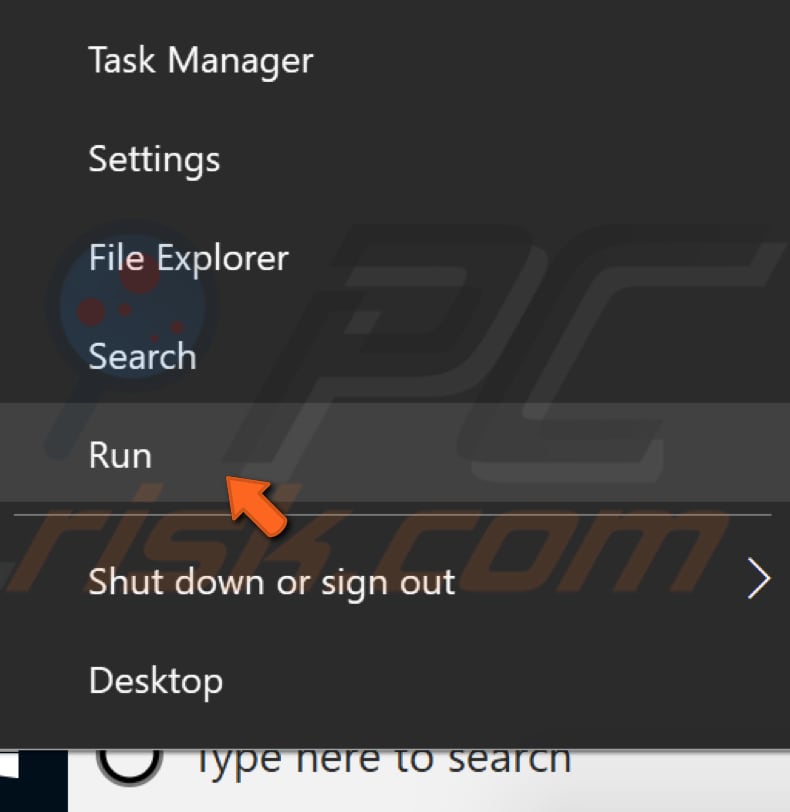
This will open the Run dialog box. Type "msconfig" and press "OK" or press Enter on the keyboard.
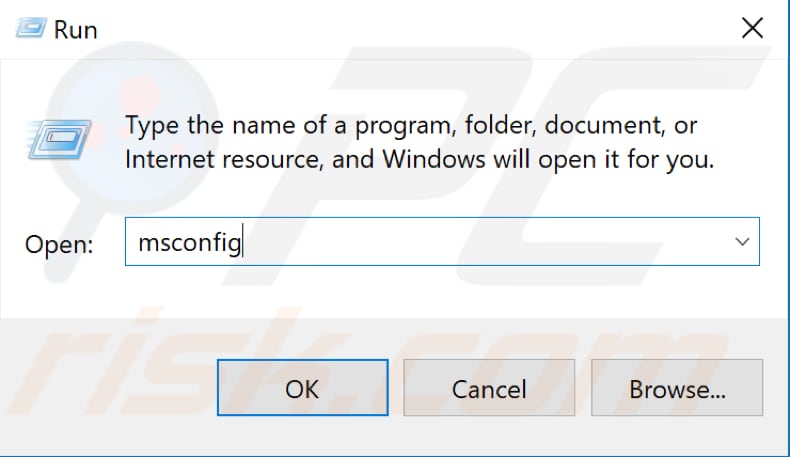
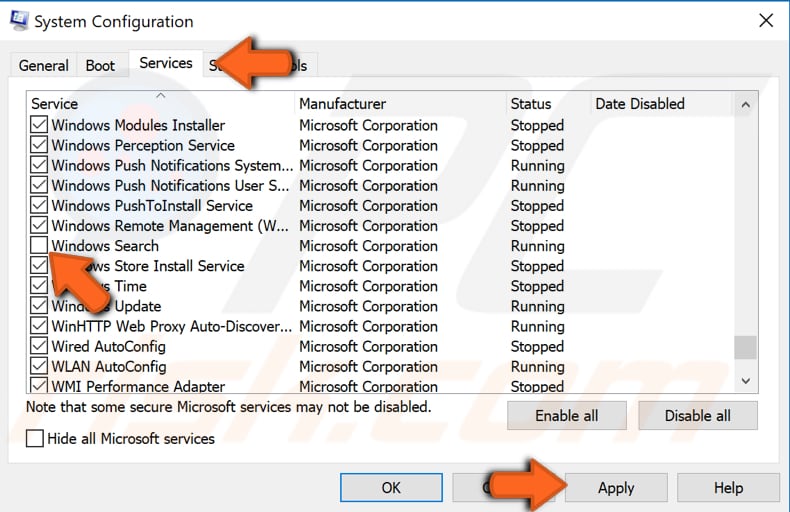
In the System Configuration window, find and click the "Services" tab. Now find the "Windows Search" service in the services list and uncheck it.
Click "Apply" to save changes. Restart the computer and see if you still have problems with File Explorer.
Disable Quick Access
Quick Access is one of File Explorer's components. When you open File Explorer, recently accessed files and folders are shown under the Quick Access icon. Quick Access changed the Favorites list that was present in earlier versions of Windows. It is a useful feature if you want to access your files and folders quickly. However, it can also slow down File Explorer.
One way to improve File Explorer performance is to disable Quick Access.
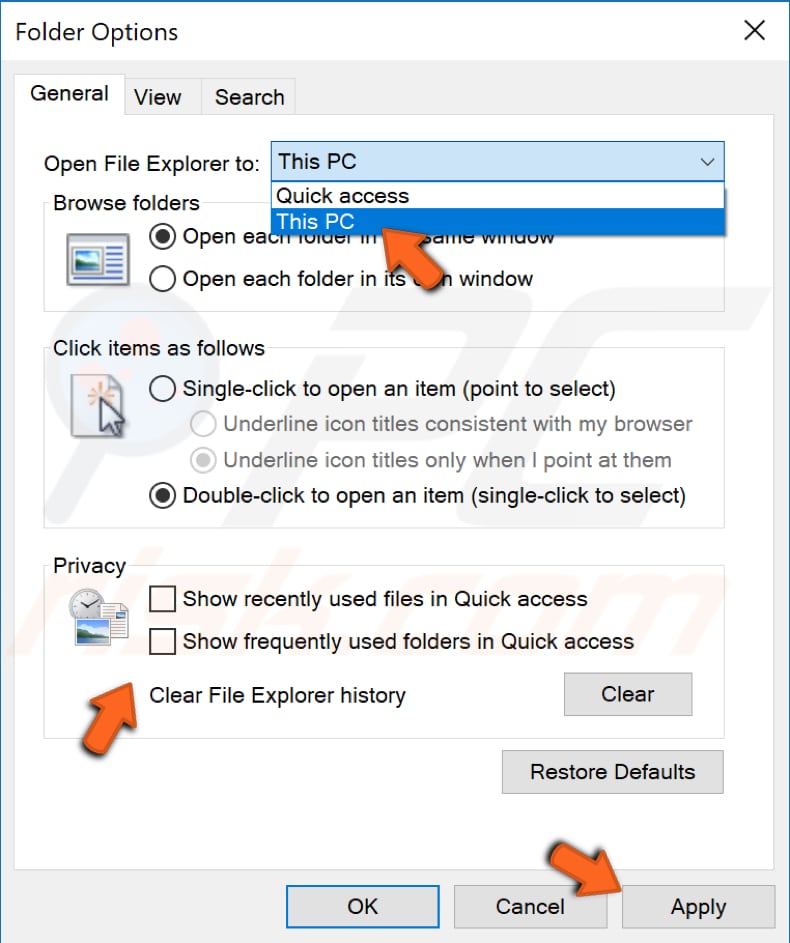
Go to File Explorer and click "File". Select "Change folder and search options".
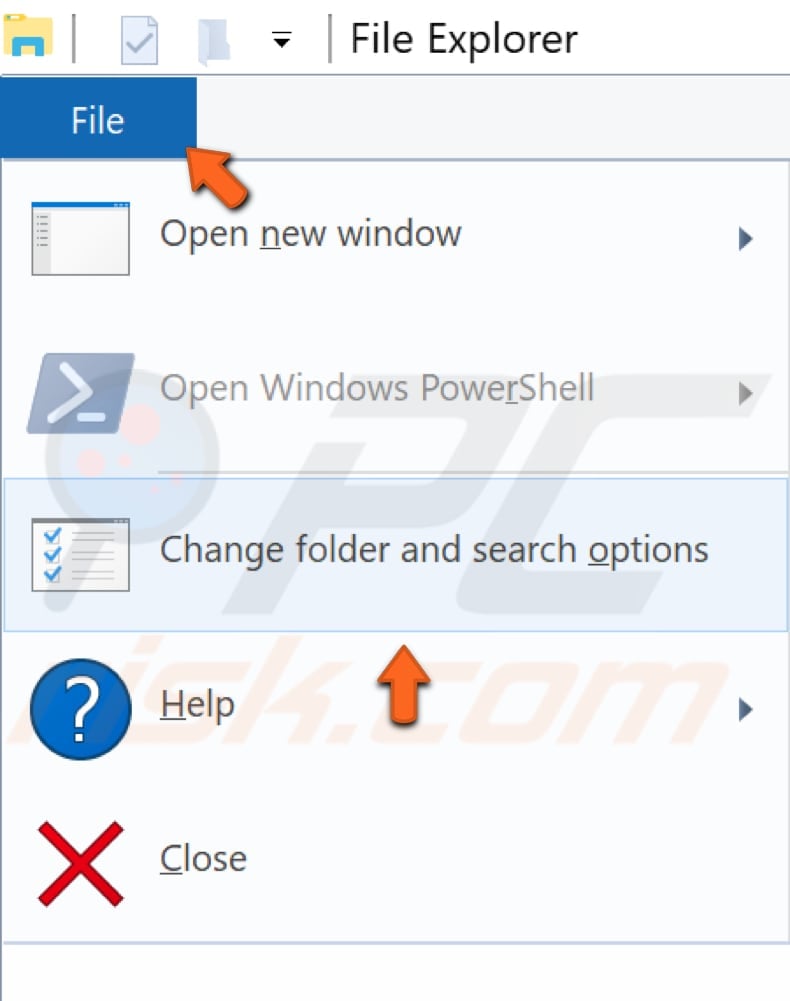
In the Folder Options window (General tab), find "Open File Explorer to:" and change it to "This PC".
Then, uncheck "Show recently used files in Quick access" and "Show frequently used folders in Quick access" and click "Apply" to save the changes and "OK" to exit.
Restart the computer and see if this improves File Explorer performance.
Change Folder Optimization Settings
Windows 10 optimizes your folder in the background. This is a good feature but can be the reason for poor File Explorer performance. If you have problems with File Explorer when trying to access a particular folder, change the folder optimization.
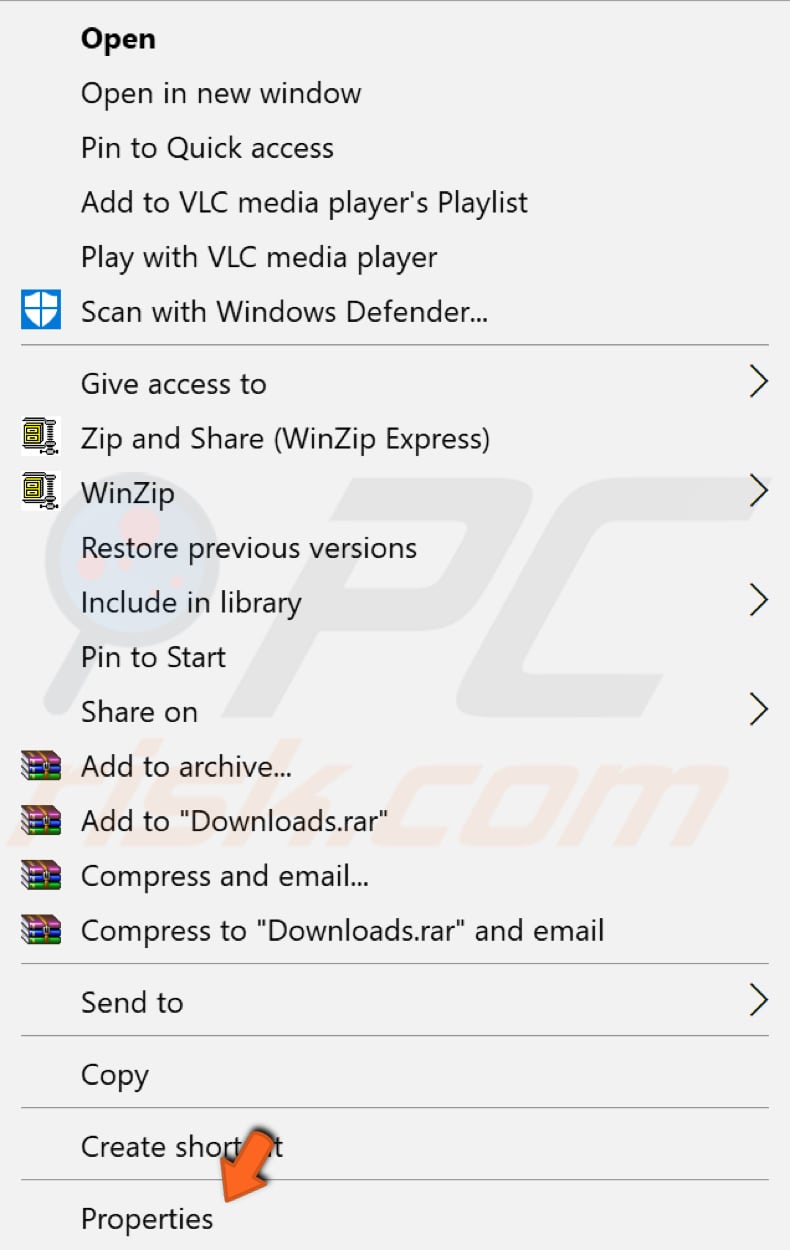
Right-click the folder that is causing problems and select "Properties" from the contextual menu.
In the folder's properties window, go to the "Customize" tab and ensure that "Optimize this folder for:" is set to "General items".
Then, check the "Also apply this template to all subfolders" checkbox and click "Apply" to save the changes made.
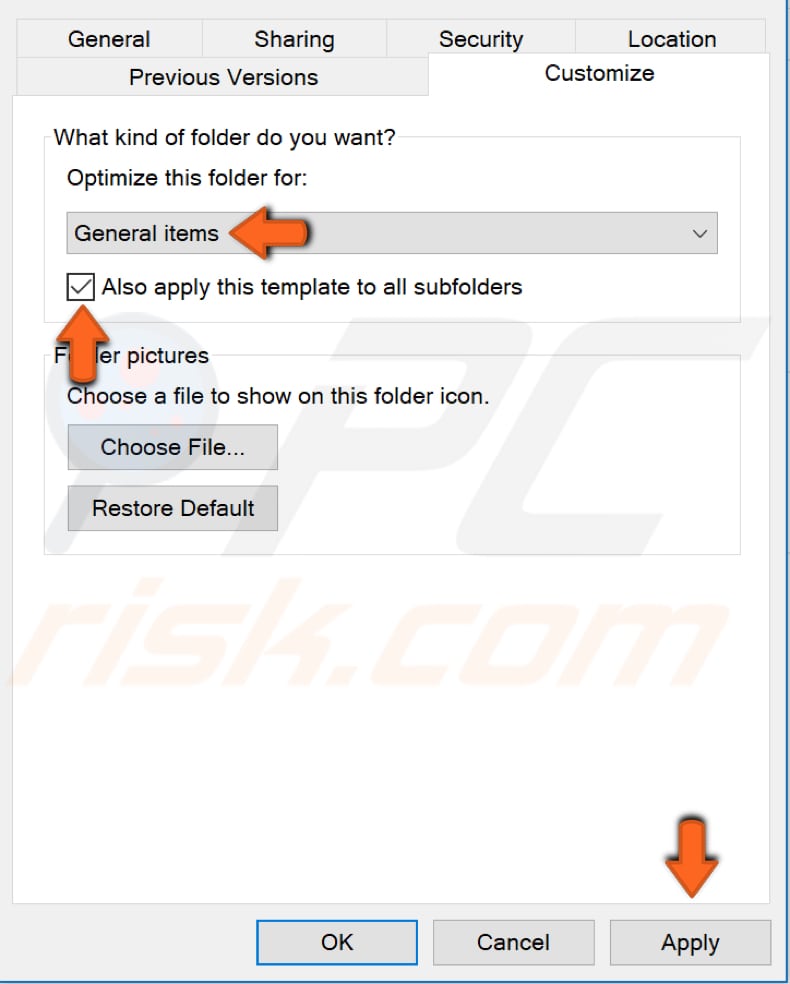
If more than one folder slows down File Explorer, apply the same settings to the other folders.
Restore Indexing Service
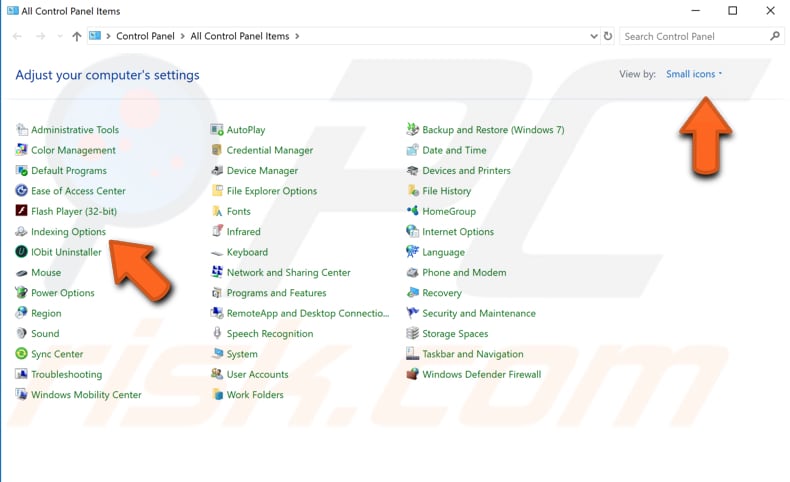
Indexing service (now known as Windows Search indexer) is a Windows service created to improve search performance on Windows computers. If Windows File Explorer stops working properly (or stops working altogether), restoring this service fixes the problem. To restore the Windows Search indexer, go to Control Panel and find "Indexing Options". If it does not appear, ensure that the Control Panel view is set to "Small icons".
In the Indexing Options window, click the "Advanced" button.
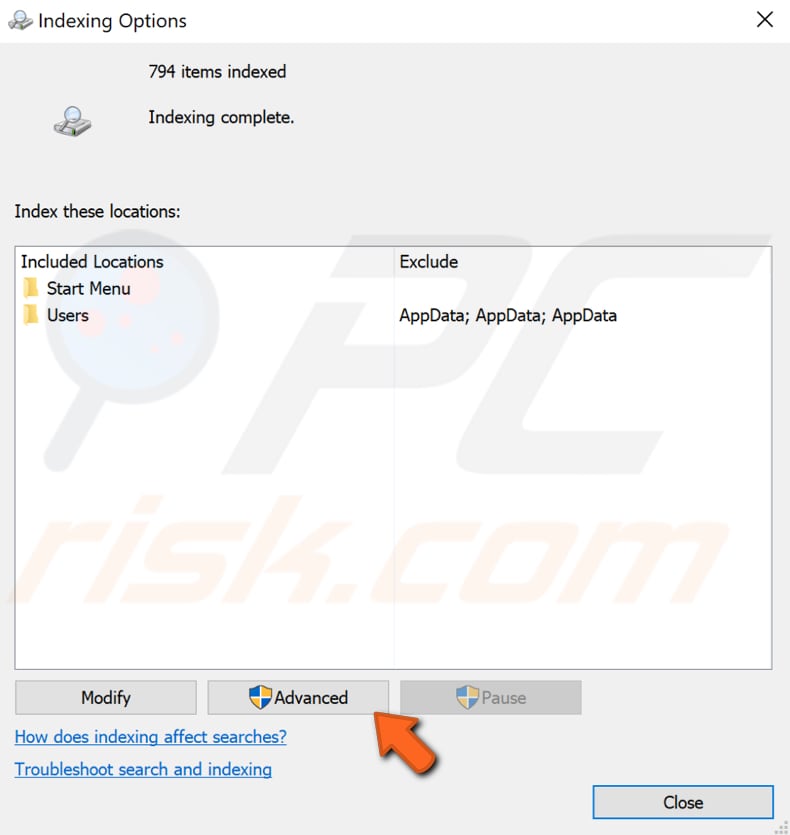
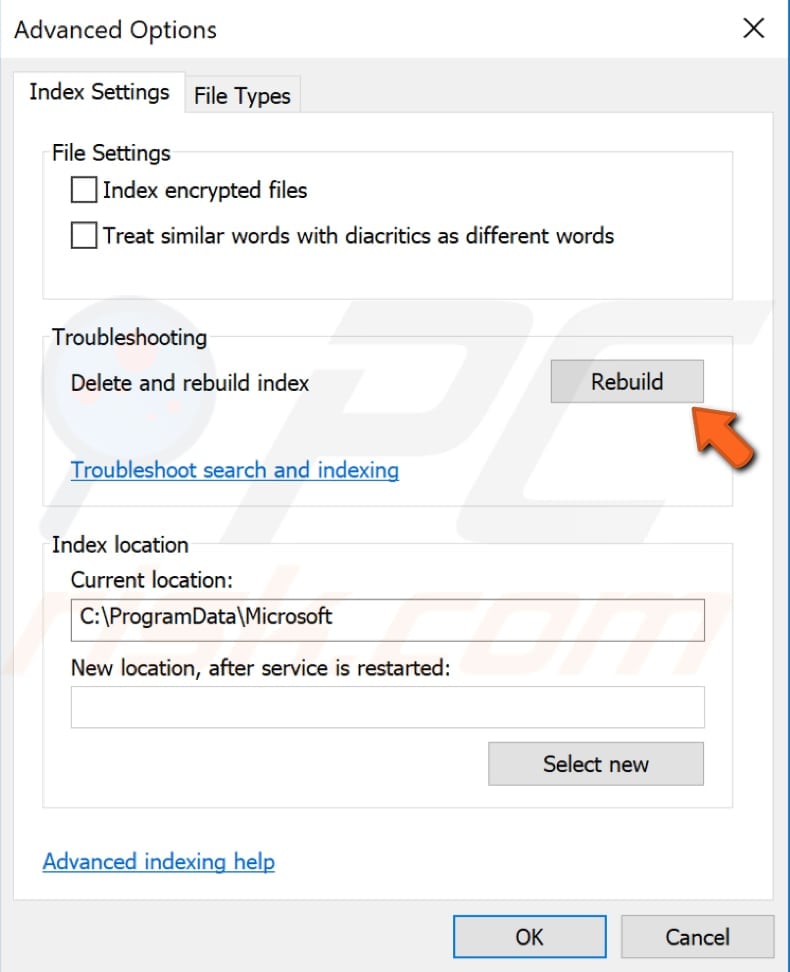
In the "Index Settings" tab, find the "Rebuild" button under Troubleshooting and click it. This will display a notification stating that rebuilding the index might take some time to complete and that some views and search results might be incomplete until rebuilding has finished.
The amount of time required to finish this process will depend on the processing power of the system. If you have an older or slower computer, it might take much longer to complete. Click "OK" to start rebuilding the index.
Run SFC Scan
System File Checker (SFC) is a utility in Windows that allows users to scan for corruptions in Windows system files and restore corrupted files.
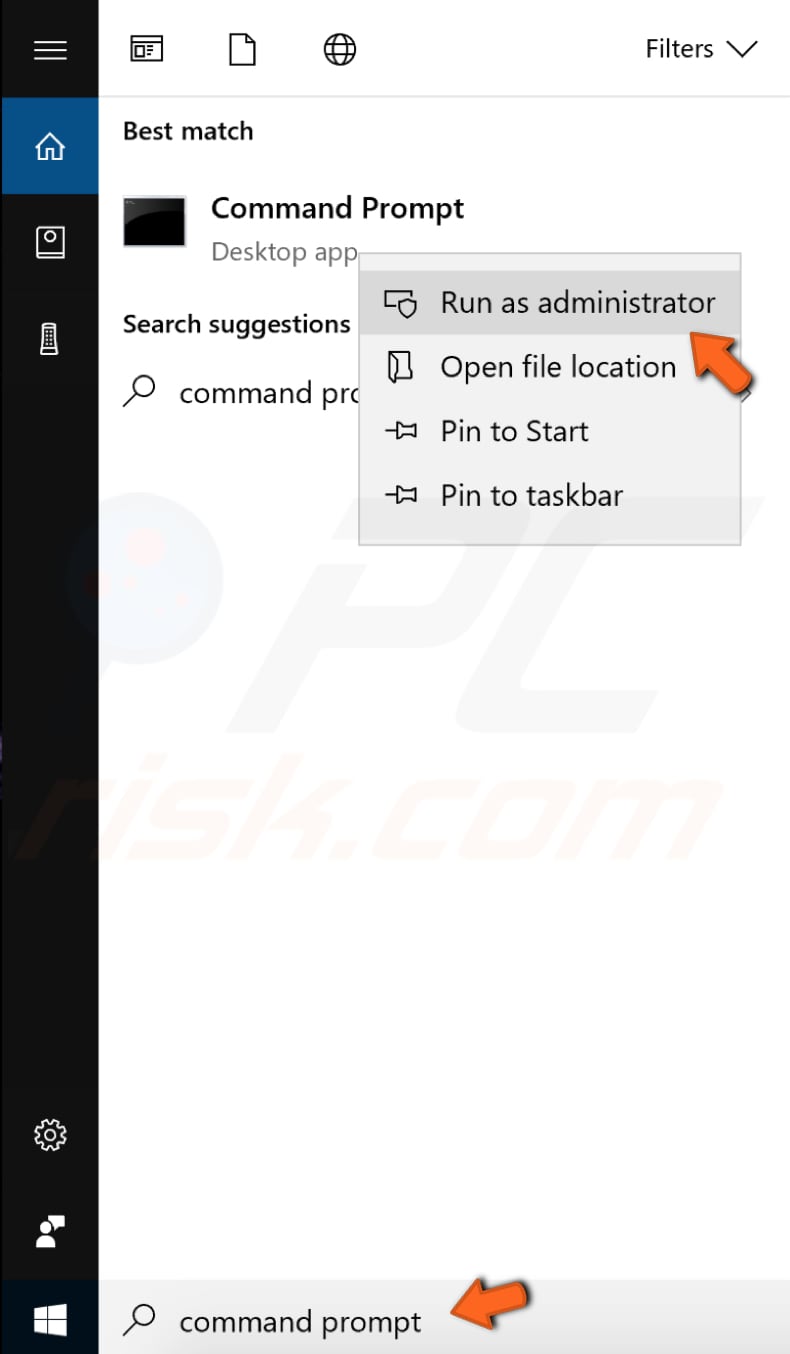
To run it, first open Command Prompt by typing "command prompt" in Search and then right-clicking on "Command Prompt". Select "Run as administrator" from the drop-down menu to run Command Prompt with administrator privileges.
You must run an elevated Command Prompt to perform an SFC scan.
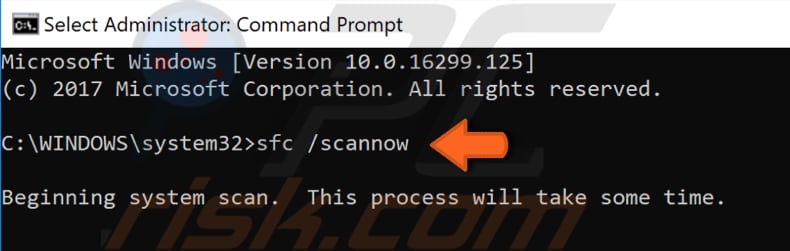
Type "sfc /scannow" in the Command Prompt window and press Enter on the keyboard to execute this command. System File Checker will start and take some time to complete the scan.
Wait for the scanning process to complete and restart the computer.
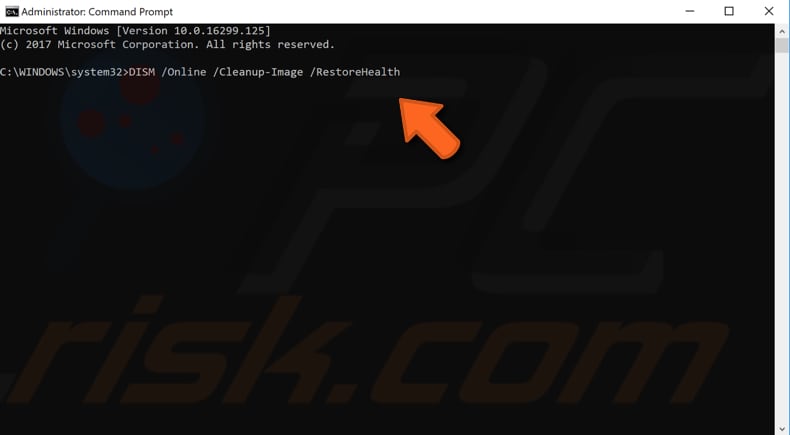
If the SFC scan does not fix the problem with File Explorer, or for some reason you could not run the SFC scan, try to run a Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) scan and then try to run the SFC scan again.
DISM can be used to repair and prepare Windows images, including the Windows Recovery Environment, Windows Setup, and Windows PE.
To run a DISM scan, open Command Prompt as administrator and type this command: "DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth". Press Enter on the keyboard to execute it.
Restart File Explorer
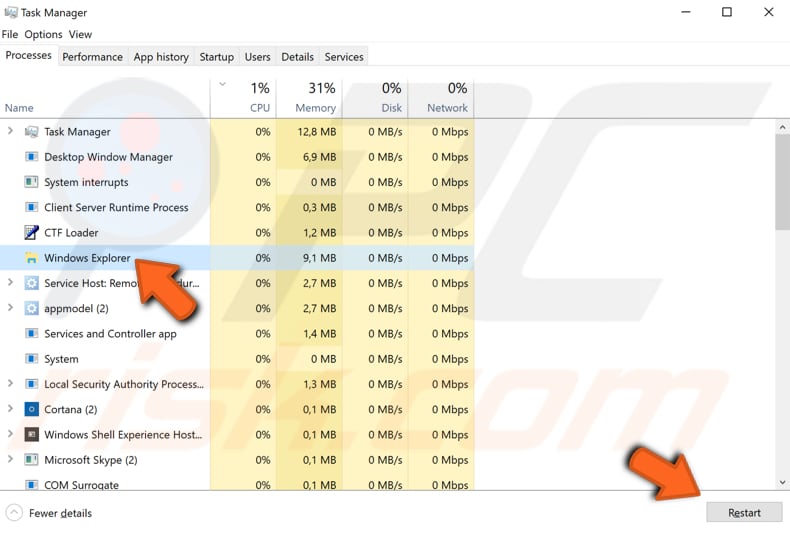
This one might be a temporary solution only, but worth a try. To restart File Explorer, use Task Manager.
To open it, press Ctrl + Shift + Esc keys on the keyboard or right-click the Start menu and select the Task Manager result from the contextual menu.
In Task Manager, find "Windows Explorer" under the "Processes" tab and select it. Then, find the "Restart" button in the bottom-right corner and click it. File Explorer will be restarted and should be working correctly.
Launch Folder Windows in a Separate Process
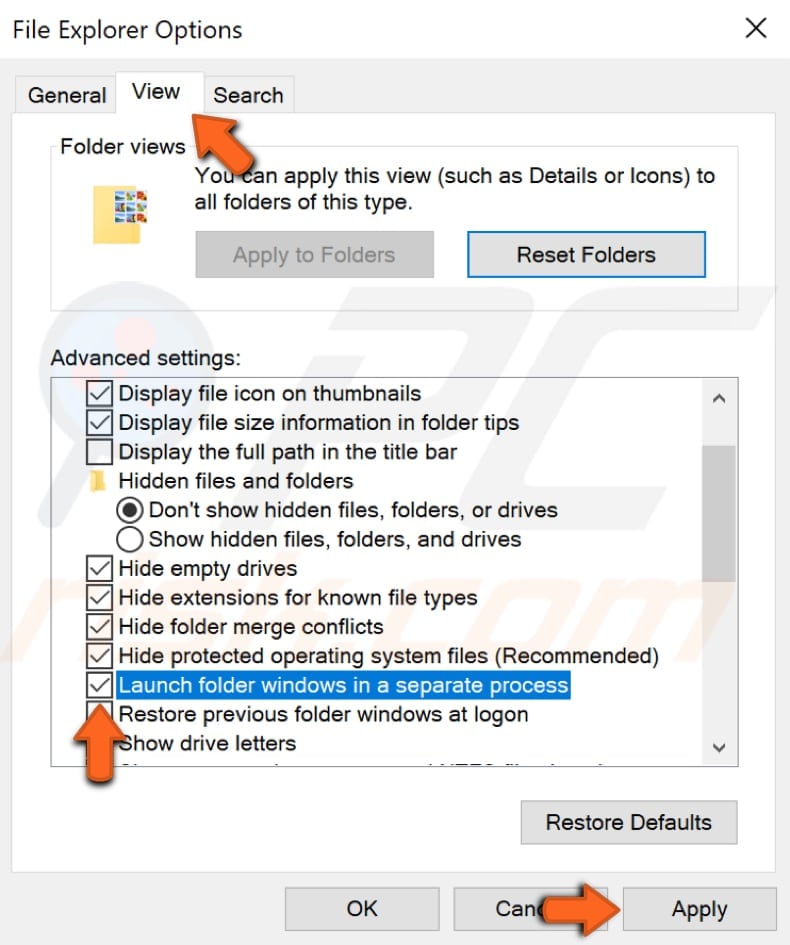
This setting controls whether each folder is opened as a separate Explorer task. If one window crashes, other opened windows should be not affected and remain open. Having this setting enabled, however, will take more system resources to maintain each open folder.
To access this setting, go to Control Panel and select "File Explorer Options".

In the File Explorer Options window, select the "View" tab and then find the "Launch folder windows in a separate process" setting under "Advanced settings" and enable it by checking the checkbox near it. Click "Apply" and "OK" to save the changes made and to exit this window.
See if enabling this setting solves the problem and makes File Explorer work properly.
Clear File Explorer History
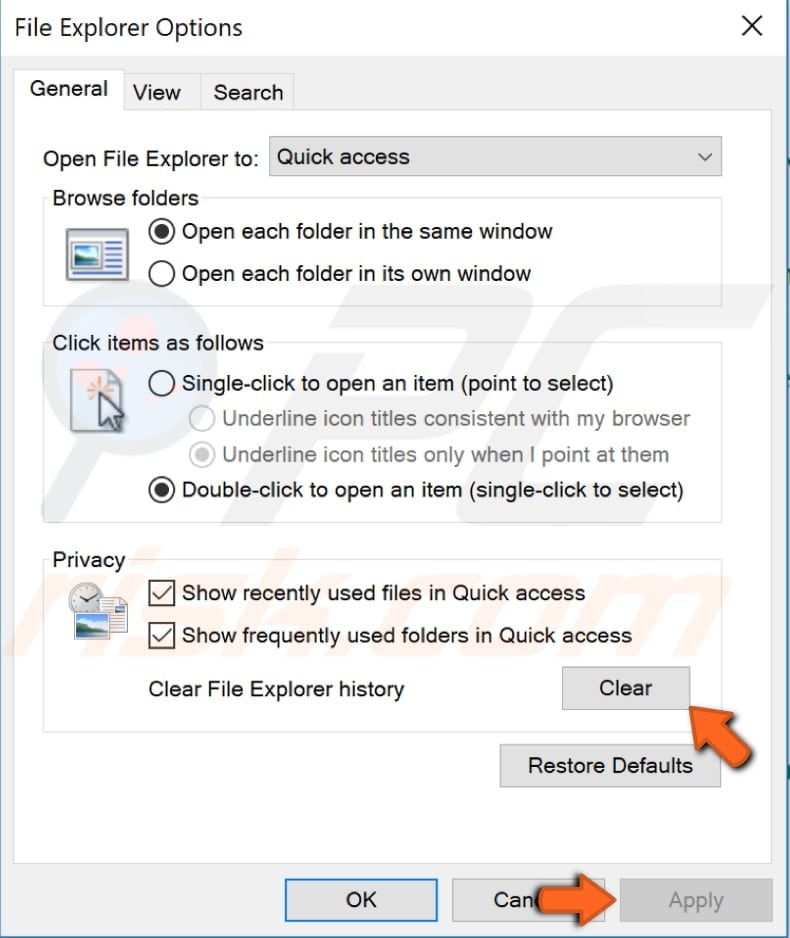
File Explorer keeps a list of files and folders that you have recently opened or frequently used. Clearing File Explorer history deletes the information about those files and folders that the Windows operating system saves in history lists. Some users report that clearing File Explorer history improves File Explorer performance.
To clear File Explorer history, go to Control Panel and click "File Explorer Options". In the File Explorer Options window, find the "Clear" button and click it. This will clear the File Explorer history. See if this fixes the problem.
Run Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
Windows Memory Diagnostic is a comprehensive memory test and is also very easy to use.
To launch the Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool, type "mdsched" (or "memory diagnostic") in Search and click on "Windows Memory Diagnostic".
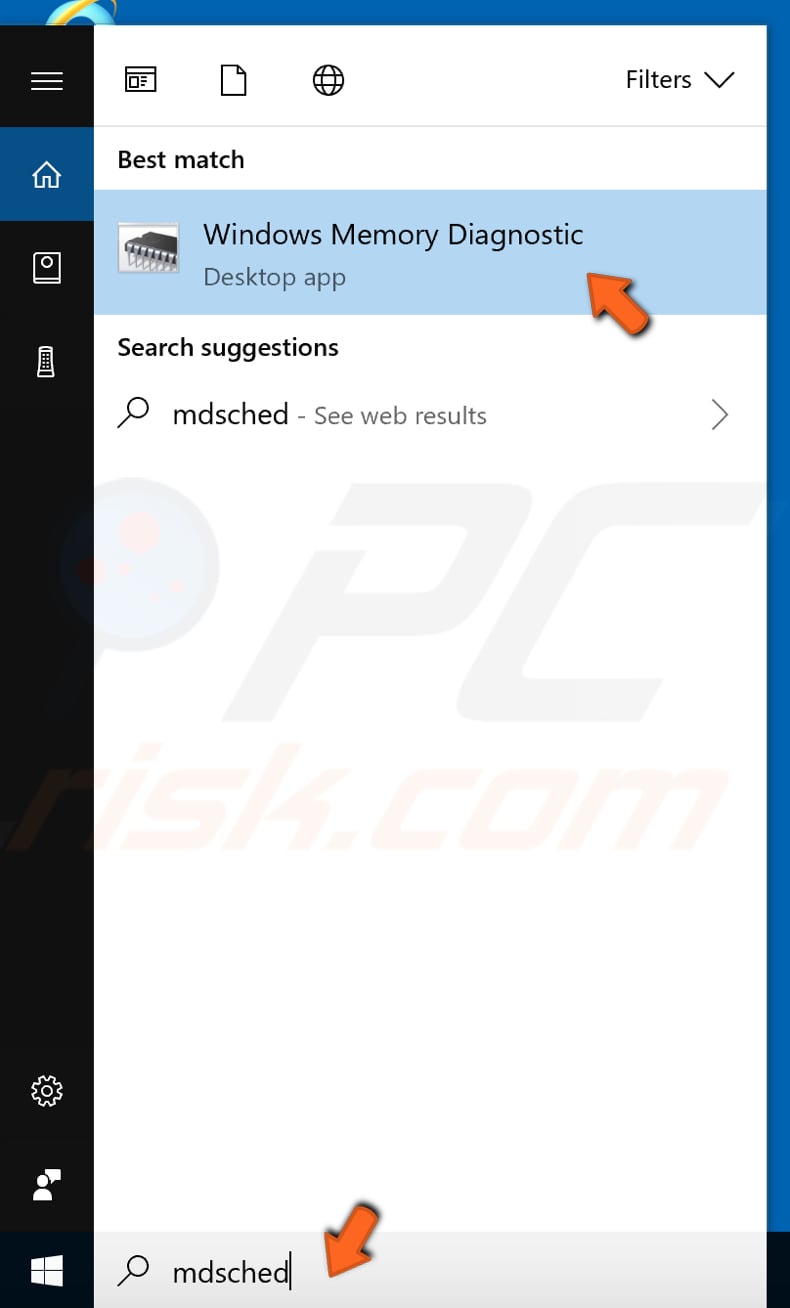
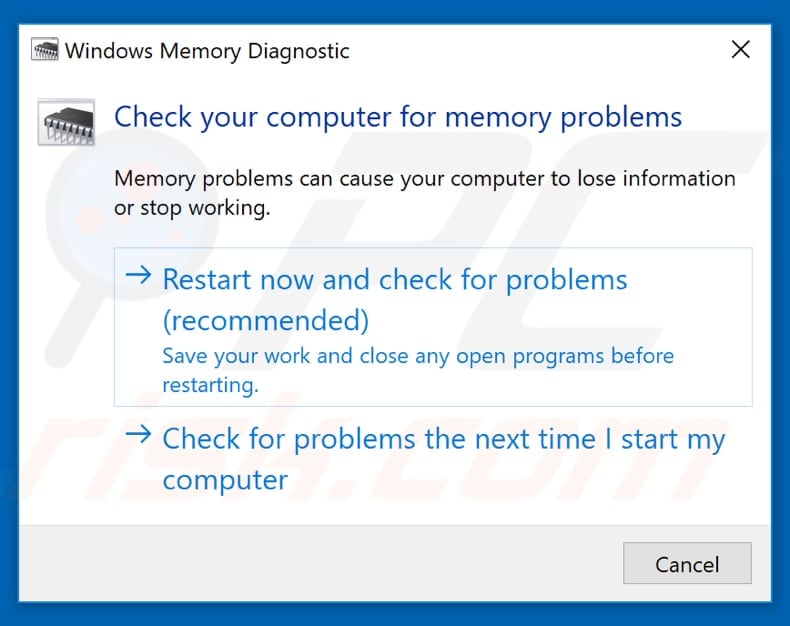
To run diagnostics, you will need to restart the computer. You will be asked if you want to restart now or run it the next time you start the computer.
When you restart the computer, Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool will start automatically.
Create a New File Explorer Shortcut
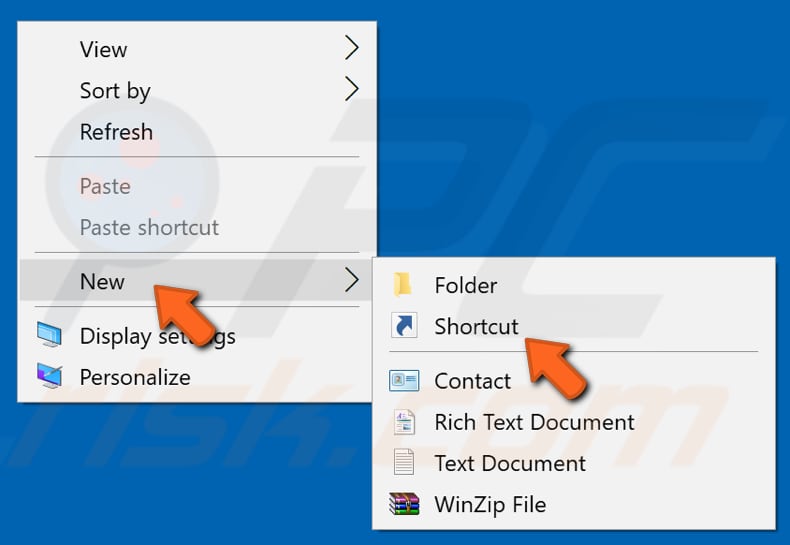
Creating a new shortcut for File Explorer might improve performance. To create a new File Explorer shortcut, right-click the desktop background empty space, select "New", and then "Shortcut".
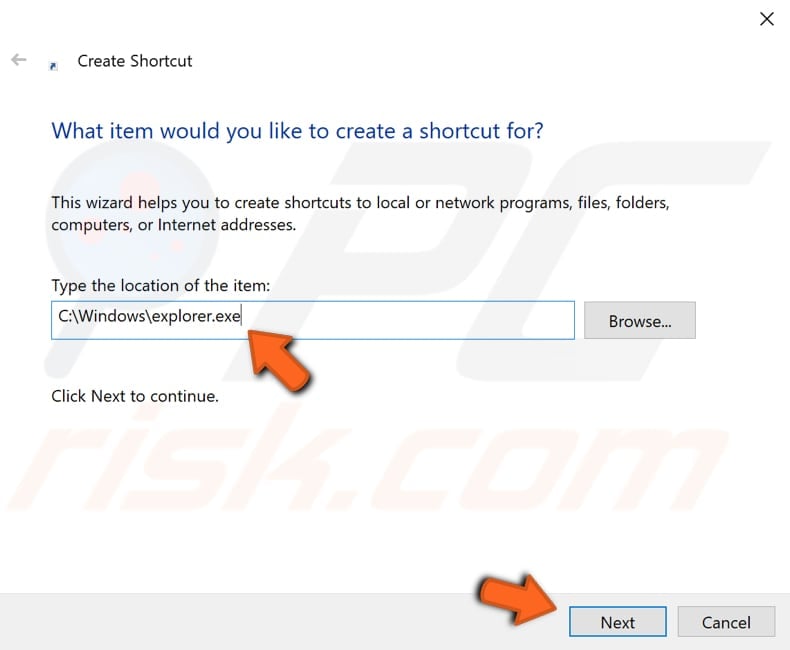
Type (or copy from this guide) the item's location, which will be "C:\Windows\explorer.exe". Click "Next" to continue.
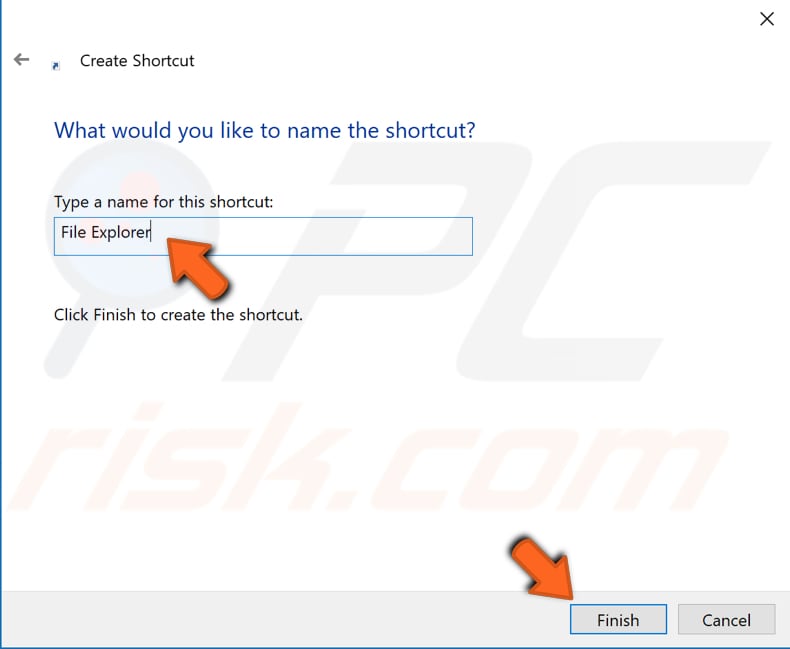
Now, type a name for this shortcut (it can be any name). In our example, we name it "File Explorer". Click "Finish". The shortcut for File Explorer will be placed on the desktop.
Use this newly-created shortcut to access File Explorer. See if this solves the problem.
Uninstall Daemon Tools
Some users report that the DTShellHlp.exe process causes problems with File Explorer. This process is associated with Daemon Tools imaging software, a virtual drive, and an optical disc authoring program. If you use Daemon Tools, uninstall it from Windows and see if this solves the problem with File Explorer.
If File Explorer works properly after this uninstall, switch to another program that serves the same purpose.
We hope that these methods improve File Explorer performance and solve any related issues.
If you know of other ways to address the problem, please share them with us by commenting in the section below.
Share:

Rimvydas Iliavicius
Researcher, author
Rimvydas is a researcher with over four years of experience in the cybersecurity industry. He attended Kaunas University of Technology and graduated with a Master's degree in Translation and Localization of Technical texts. His interests in computers and technology led him to become a versatile author in the IT industry. At PCrisk, he's responsible for writing in-depth how-to articles for Microsoft Windows.

▼ Show Discussion