How to Fix MEMORY_MANAGEMENT BSOD Error on Windows 10
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
How to Fix MEMORY_MANAGEMENT Blue Screen Error on Windows 10
If a blue screen suddenly appears when using your computer, it is probably due to a MEMORY_MANAGEMENT error. Many users have encountered this problem, and there could be several reasons for it. This article is dedicated to fixing this error.

What Causes This Error?
This error may occur due to bad memory or insufficient memory in your system. Alternatively, you may be running processes that demand too much memory or are playing complex games, and so on. The MEMORY_MANAGEMENT blue screen error can appear on all Windows versions, including Windows XP.
How to Fix Windows Stop Code MEMORY_MANAGEMENT?
The easiest and most common way to resolve this problem is to restart your computer. You should not get this error message after the restart. Try restarting your computer to see if the issue is fixed. If the MEMORY_MANAGEMENT error still appears, then try other solutions to fix this problem. Try the methods below to fix this error.
Video Showing How to Fix MEMORY_MANAGEMENT Error
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
- Run Full System Scan
- Run SFC Scan
- Check Disk For Errors
- Clean Up Your Disk
- Increase Your Virtual Memory
- Video Showing How to Fix MEMORY MANAGEMENT Error
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Run Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool
This error message might appear due to a problem with your Random Access Memory (RAM). If your RAM is failing, then you should consider replacing it, but you need to be sure that this is where the problem exists. There is a built-in Windows tool called Windows Memory Diagnostic. We recommend that you run it to see if there is a problem with your computer memory. To open Windows Memory Diagnostic tool, type "memory diagnostic" in Search.
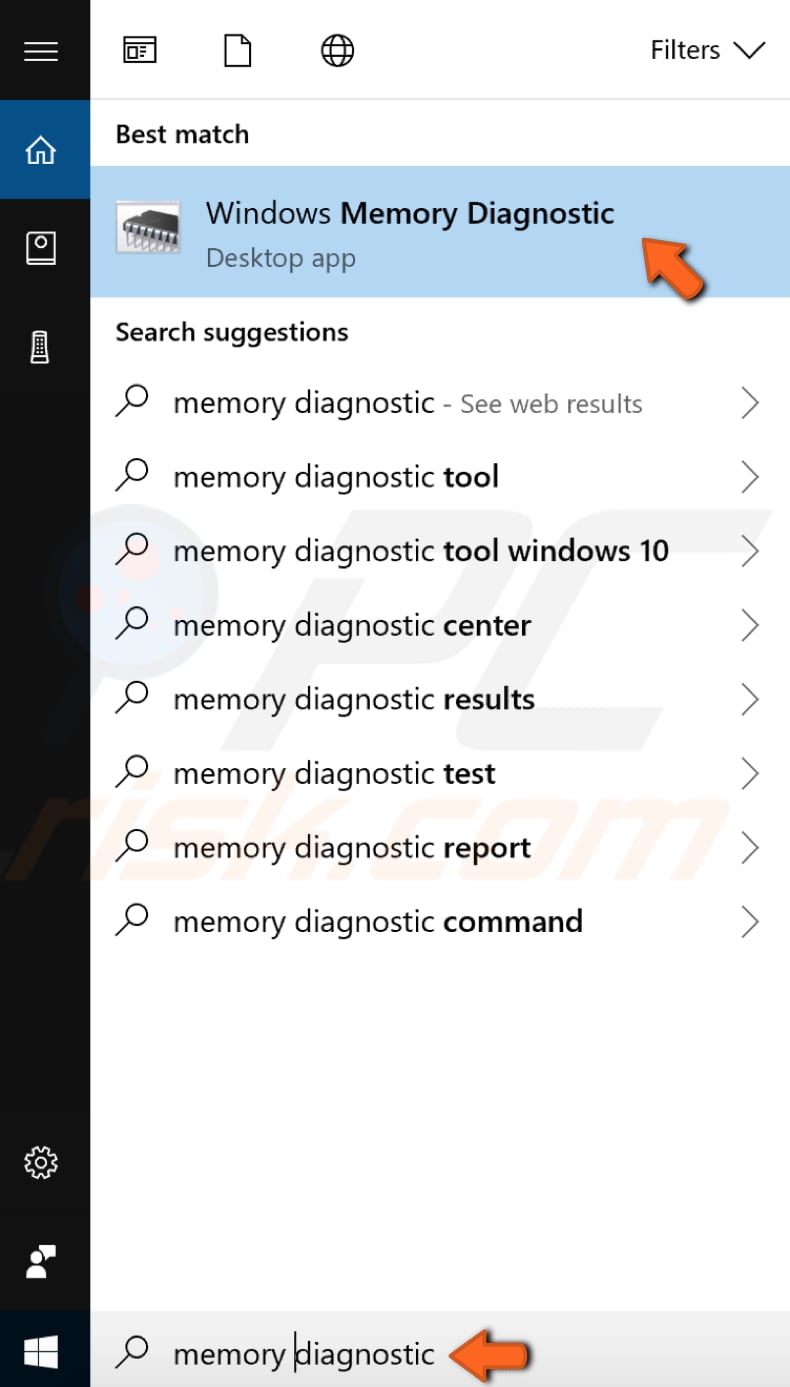
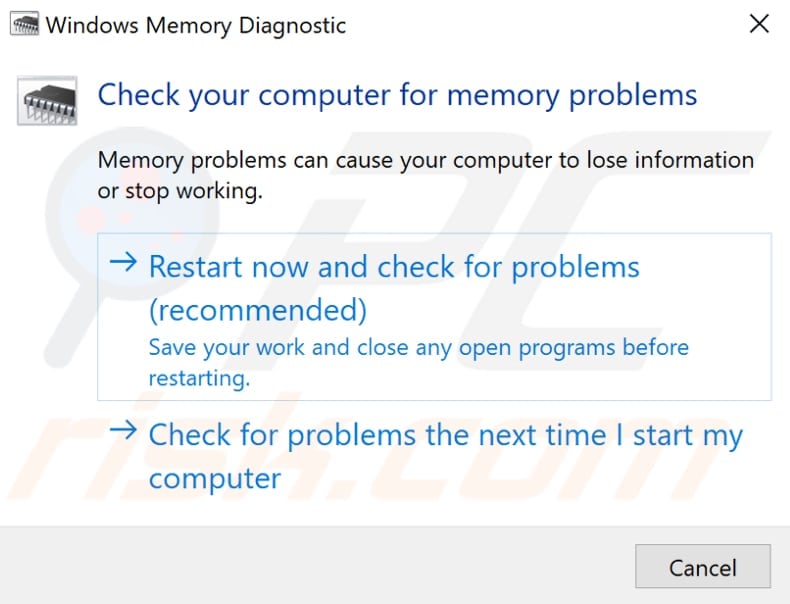
You will be given two options: 1) restart your computer now and check for problems immediately; 2) check for problems the next time you start your computer and let it do a scan before loading the Windows operating system. Choose which option suits you. This tool will report any problems with your RAM.
Run Full System Scan
Errors and other issues on your computer can be caused by malware and other virus infections. Run Windows Defender, a built-in Windows tool, to perform a full system scan for viruses. Run other third-party antivirus software if you prefer. In our example, we use Windows Defender on Windows 10. To open Windows Defender, type "defender" in Search and click the "Windows Defender Security Center" result.
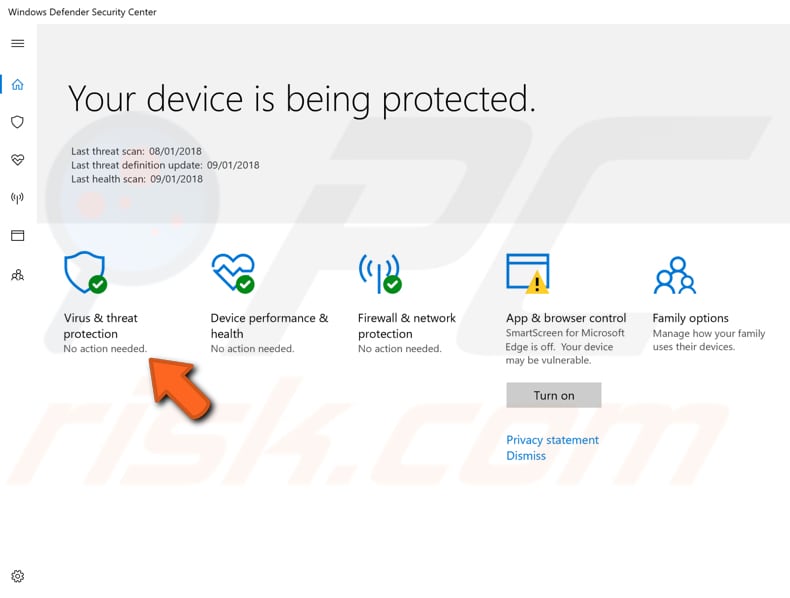
In the Windows Defender Security Center window, click "Virus & threat protection."
In Virus & threat protection, click "Advanced scan" under the "Quick scan" button.
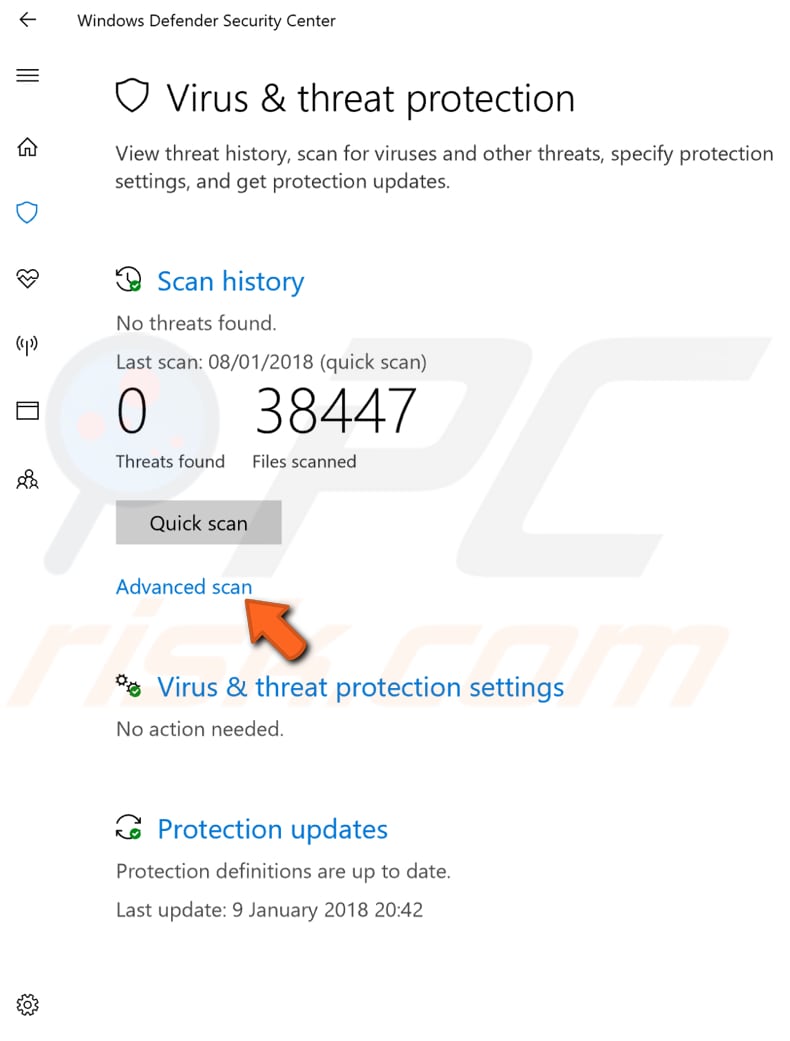
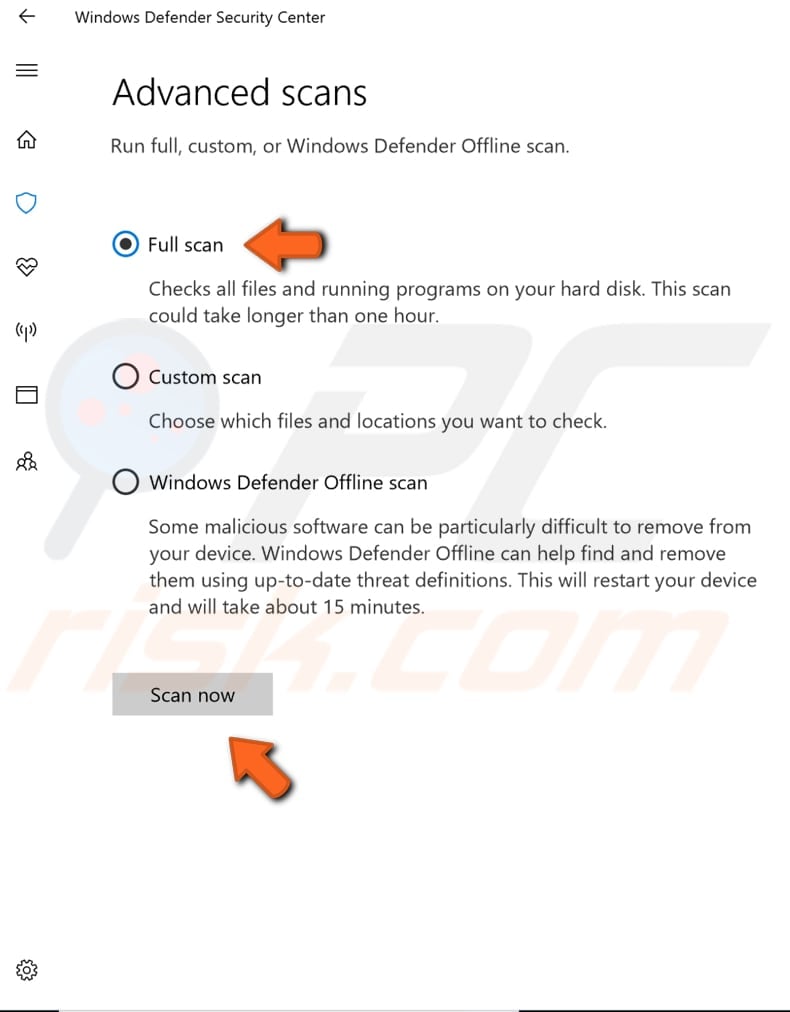
In the Advanced scans window, choose from full, custom, and offline scans. We recommend "Full scan." Click "Scan now" to start the scan. This may take a while, depending on how much data you have on your disk (or disks).
Run SFC Scan
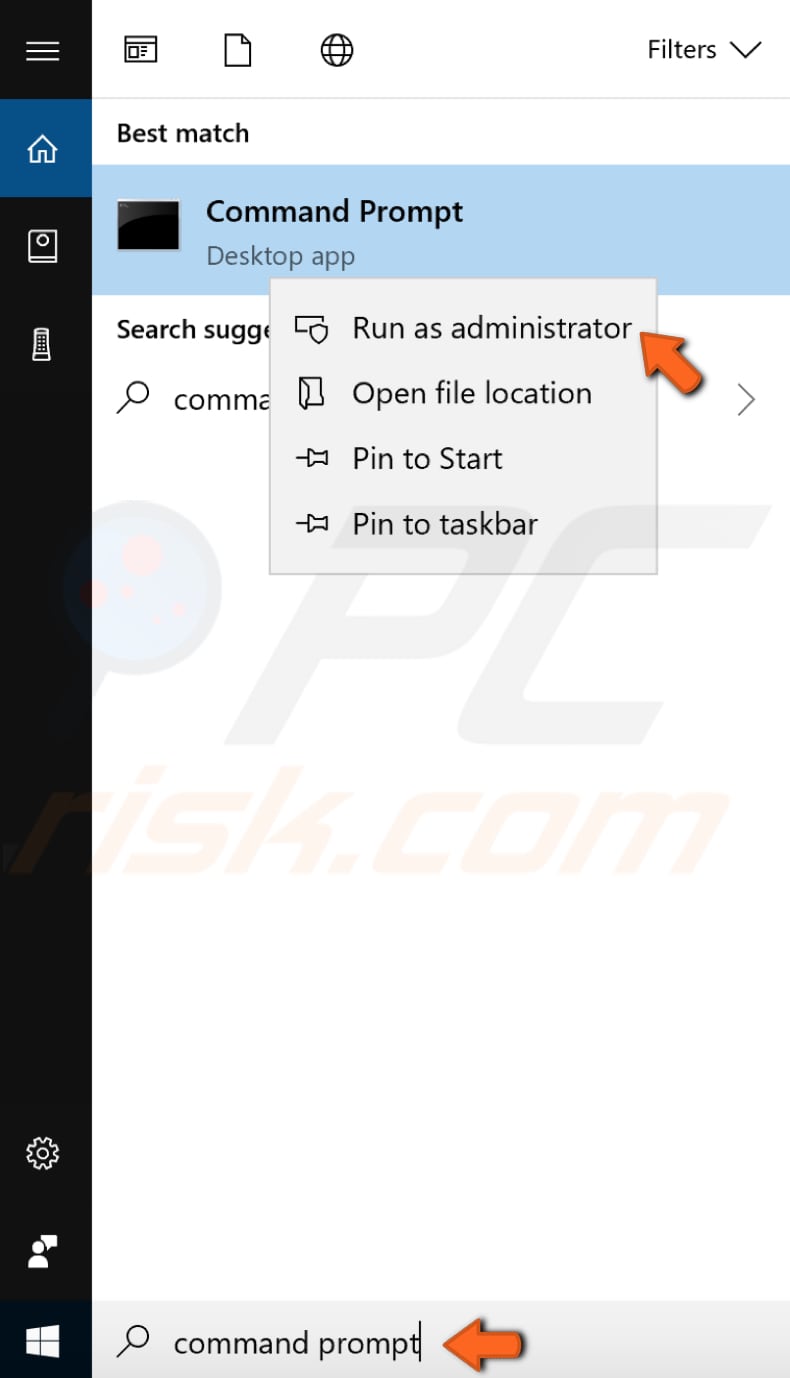
Use Command Prompt and the "sfc/scannow" command for this scan. scannow is one of the switches available in the "sfc" command - a Command Prompt command used to run System File Checker, which can resolve various system problems. This command inspects all important Windows files on your computer, including DLL files. System File Checker replaces protected files if there are any issues with them. Running this tool helped people solve the MEMORY_MANAGEMENT error. To open Command Prompt, type "command prompt" in Search and right-click on the "Command Prompt" result. Select "Run as administrator" from the drop-down menu to run it with administrator privileges.
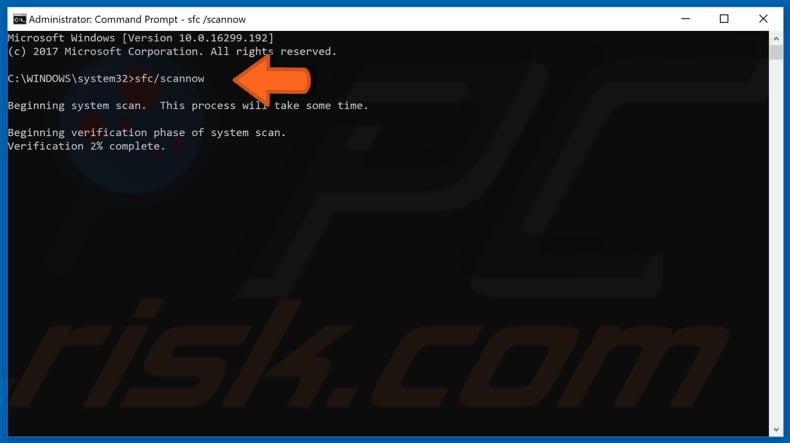
In the Command Prompt window, type "sfc/scannow" and press Enter on your keyboard. It will start scanning your system for errors and may take a while. If any corrupted files are found, they will be replaced on system reboot.
Check Disk For Errors
You should periodically check your disk for errors using a built-in Windows tool to check the integrity of disks. The tool examines disks and can correct many types of common errors. You can run this tool from the command line or through a graphical interface. To run it from the command line, open Command Prompt, type "command prompt," and right-click on the "Command Prompt" result. Select "Run as administrator" from the drop-down menu.
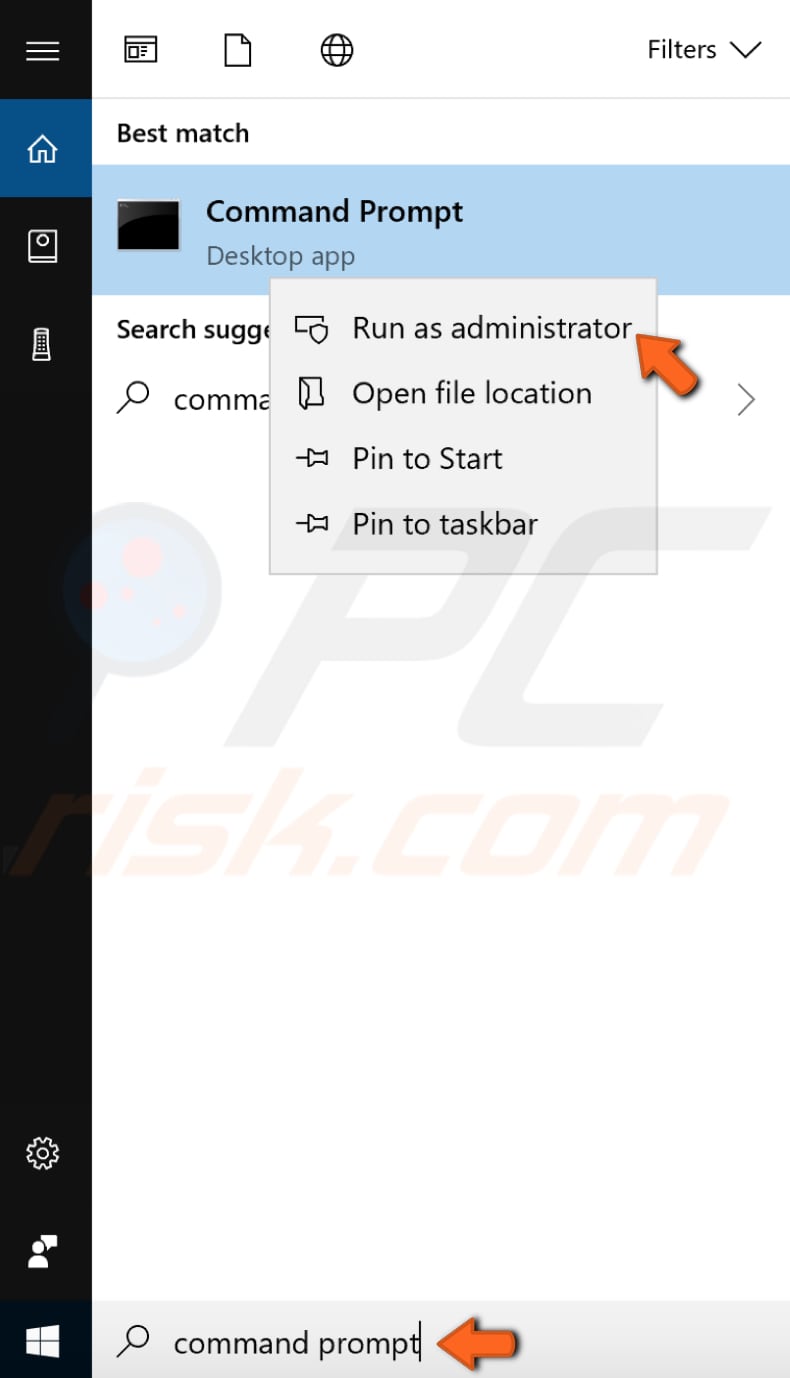
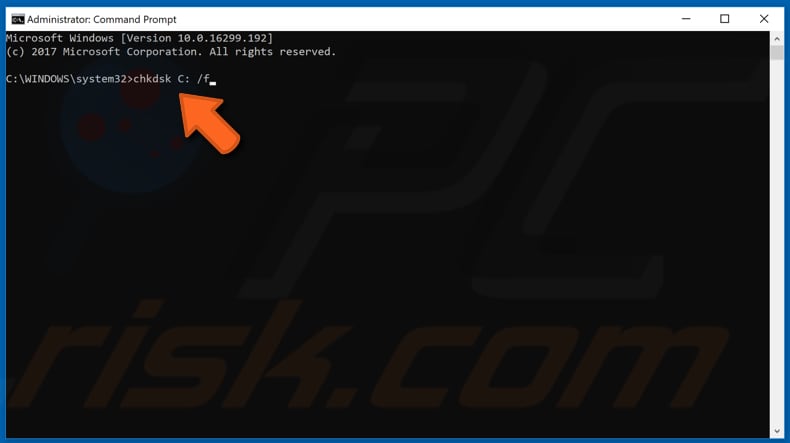
Type the "chkdsk C: /f" command in the Command Prompt window and press Enter on your keyboard. Replace "C:" with the letter of your hard drive you wish to check (if C: is not the drive you wish to inspect). The "chkdsk C: /f" command detects and repairs logical issues affecting your drive. To repair physical issues, run the "chkdsk C: /r" command.
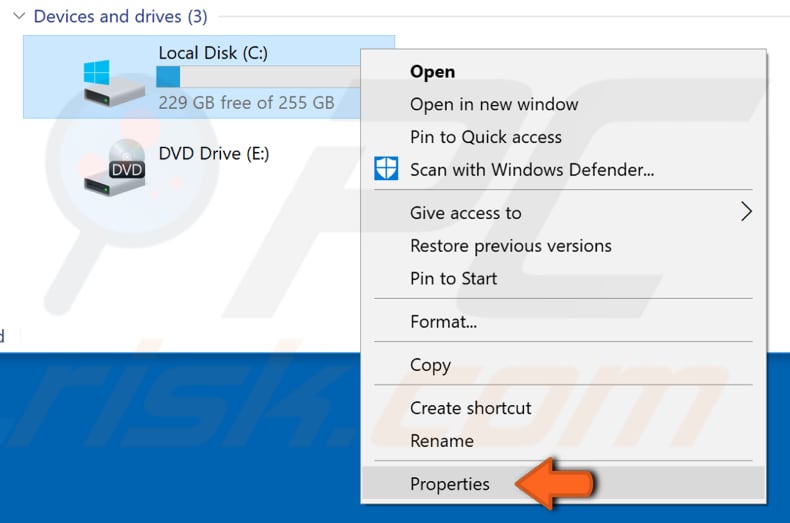
If you want to check your disk for errors through a graphical interface, right-click on your hard drive and select "Properties."
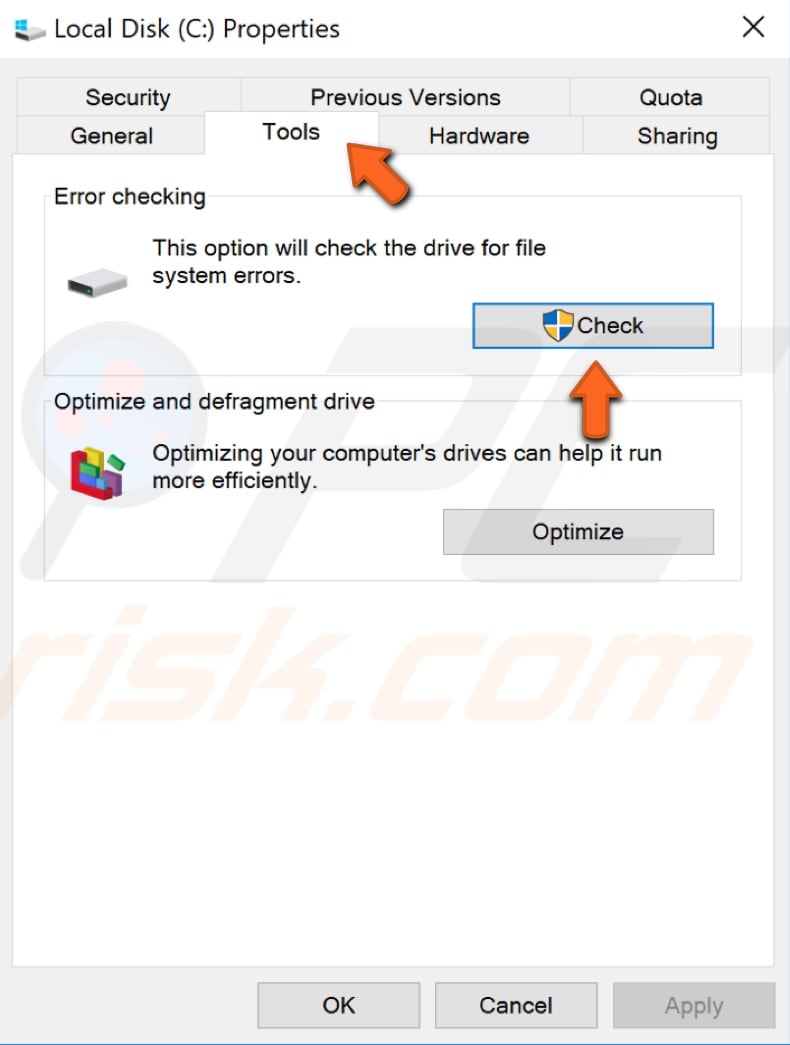
In your Local Disk Properties window, click "Tools" and then click "Check" below "Error checking".
Clean Up Your Disk
Disk Cleanup is a computer maintenance utility included in Microsoft Windows and designed to free up disk space on the computer hard drive. The utility first searches and analyzes the hard drive for files that are no longer used, then removes them. There are several different file categories that Disk Cleanup targets when performing the initial disk analysis. To open the Disk Cleanup tool, type "disk cleanup" in Search and click the "Disk Cleanup" result.
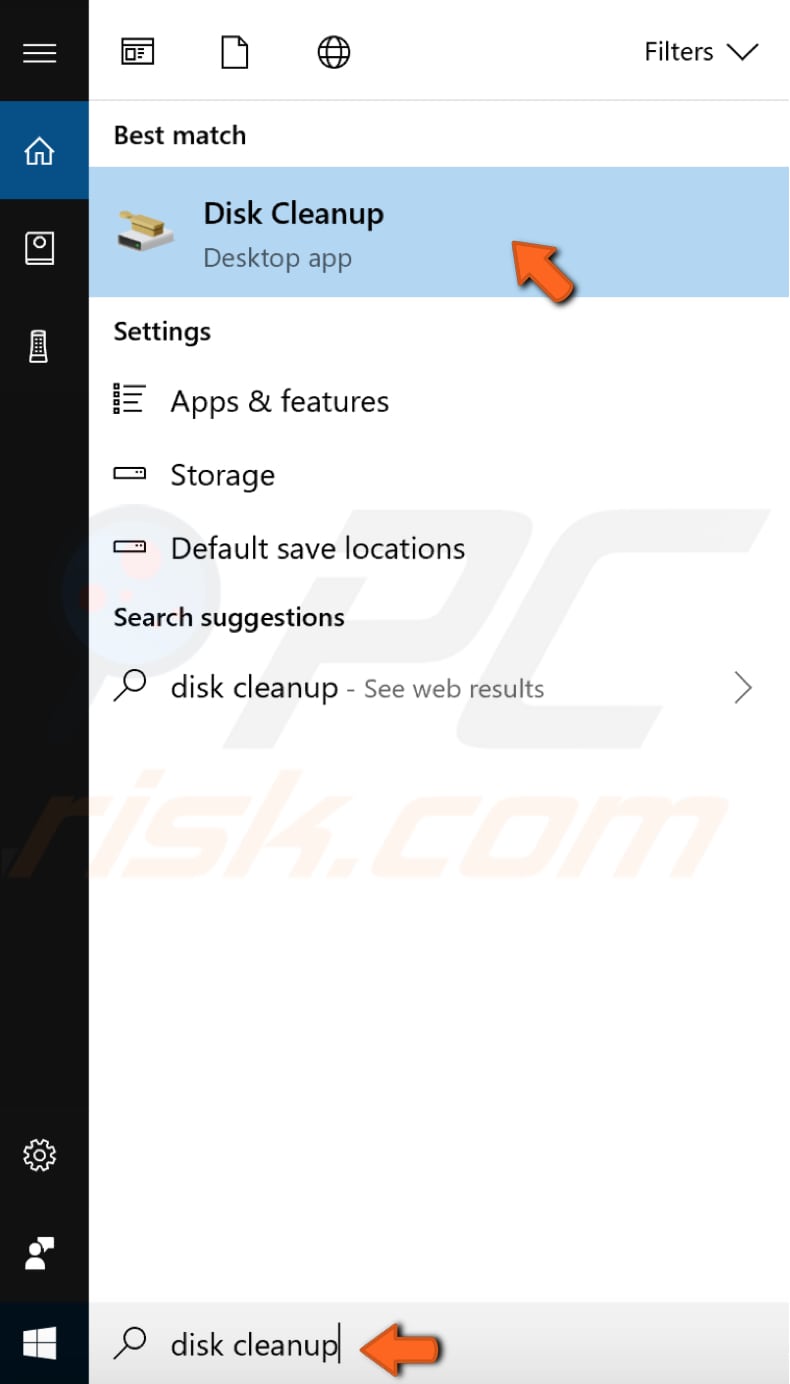
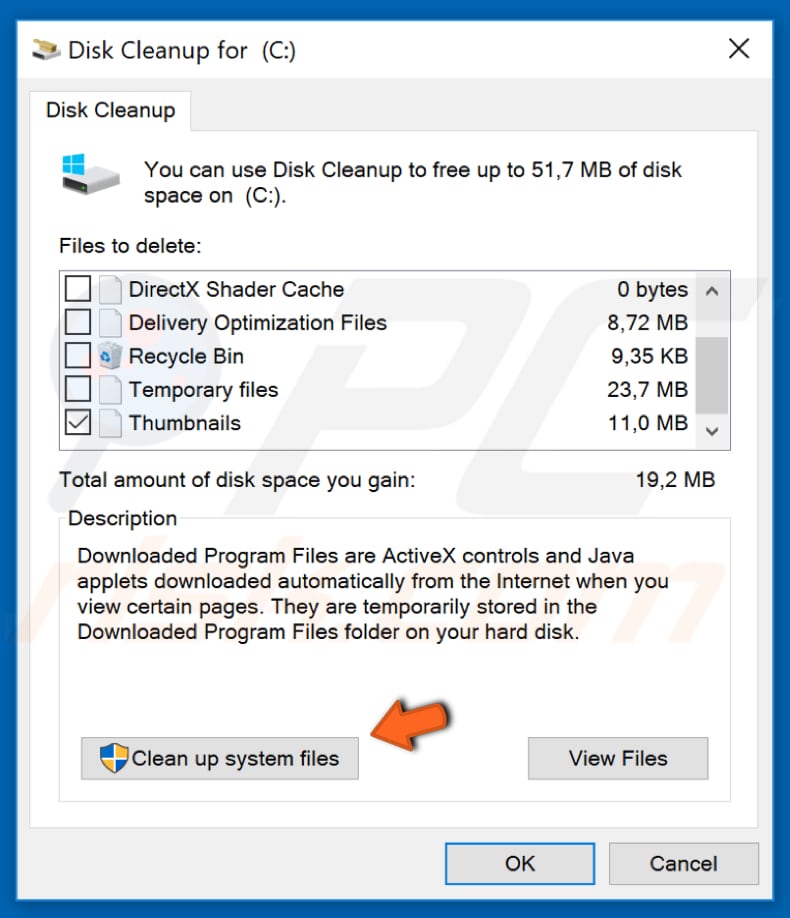
The Disk Cleanup tool will be opened. Choose which files you want to remove from your system by marking checkboxes, and then click "Clean up system files."
Increase Your Virtual Memory
If you increase your virtual memory, then problems with memory management should be solved, and you should not receive alerts. Virtual memory, also known as the swap file, uses part of your hard drive to effectively expand your RAM, thus allowing you to run more programs than it could otherwise handle. Hard drives, however, are much slower than RAM, so this can reflect on performance and slow down your computer. Increasing virtual memory must be done manually - read the instructions below.
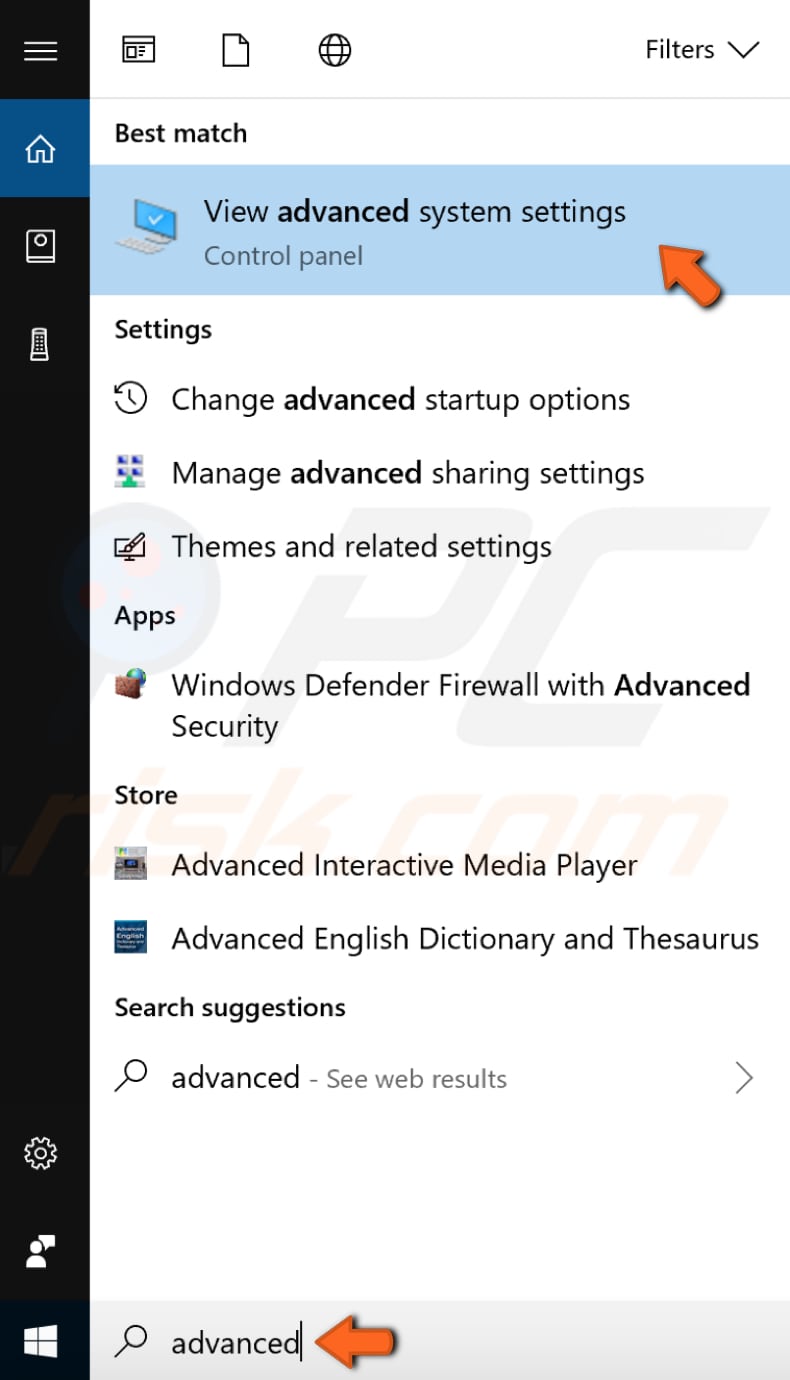
Type "advanced" in Search and click the "View advanced system settings" result.
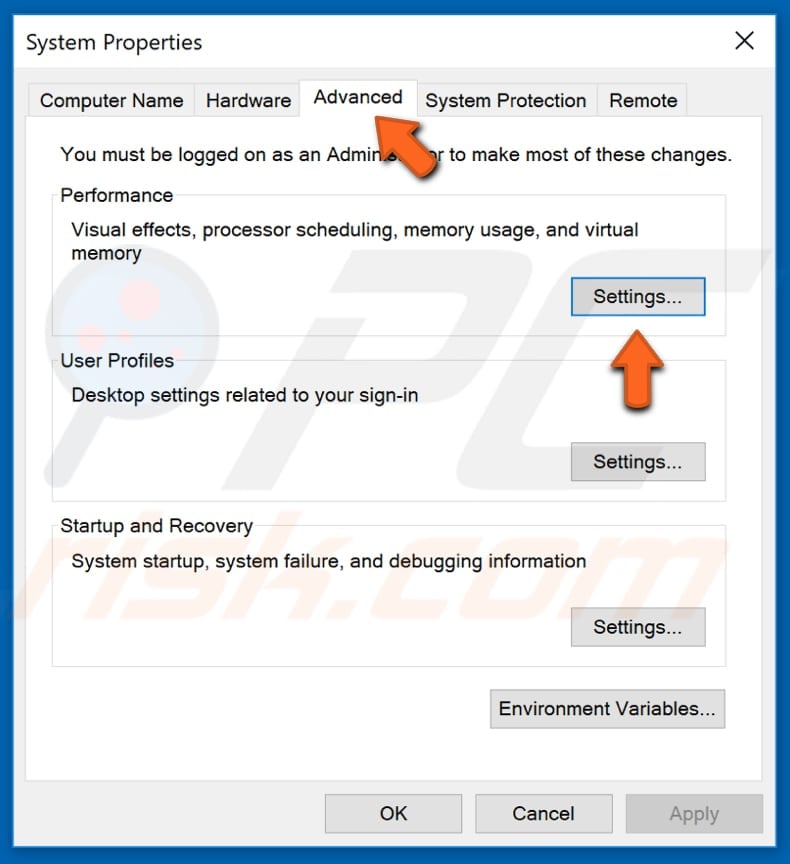
The System Properties window will appear. You should be on the "Advanced" tab - if not, select it and click "Settings..." under Performance. Note: you must be logged in with an administrator account to benefit from these changes.
Select the "Advanced" tab in the Performance Options window and click "Change..." under Virtual memory.
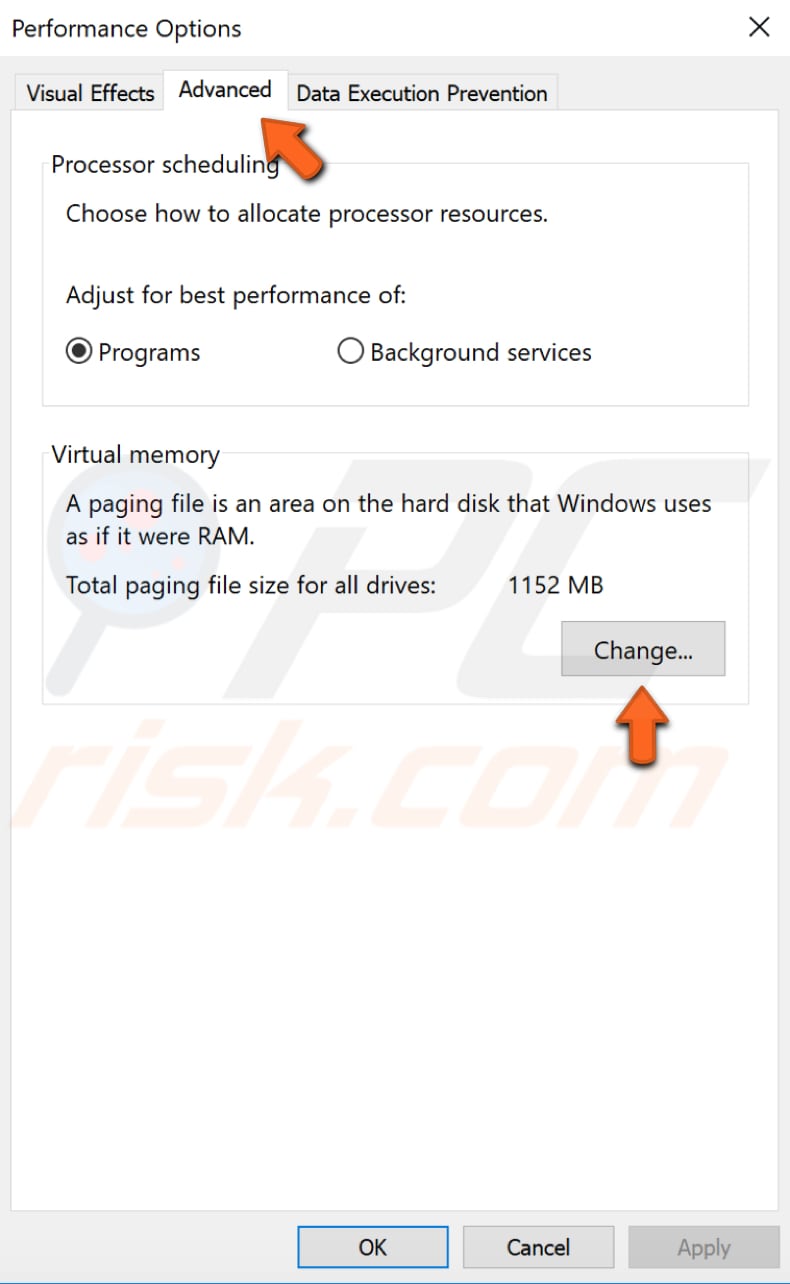
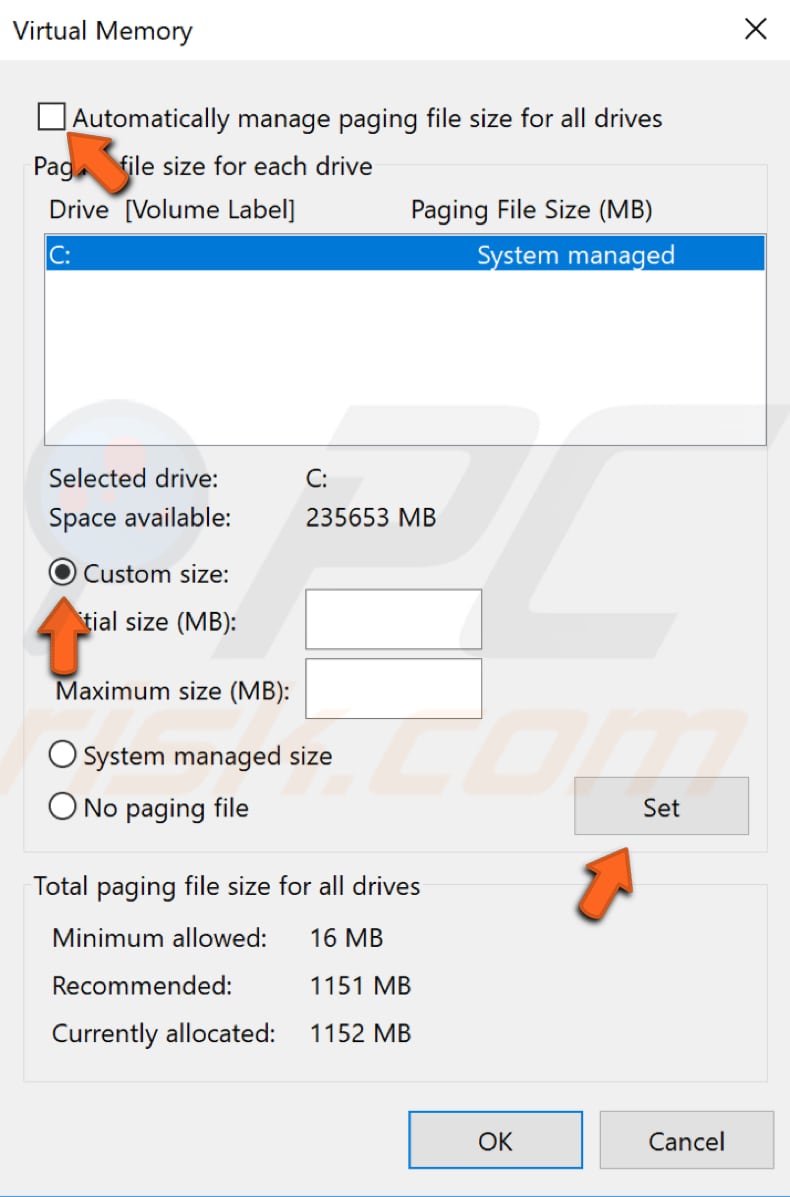
In the Virtual Memory window, unmark the "Automatically manage paging file size for all drives" checkbox. Click your drive (volume label) (in our case, it is volume "C:"), and then click "Custom size." Enter a new size in megabytes in the "Initial size (MB)" box or "Maximum size (MB)" box and click "Set," and then click "OK."
We hope one of these solutions helped you to fix your MEMORY_MANAGEMENT problem. If none of these methods helped, there might be a problem with newly-installed device drivers or software programs causing the MEMORY_MANAGEMENT error on the blue screen. Try uninstalling or updating them and see if the problem is resolved. Some software programs can also conflict to cause this error - if you suspect this, try uninstalling any programs you feel might conflict.
Share:

Rimvydas Iliavicius
Researcher, author
Rimvydas is a researcher with over four years of experience in the cybersecurity industry. He attended Kaunas University of Technology and graduated with a Master's degree in Translation and Localization of Technical texts. His interests in computers and technology led him to become a versatile author in the IT industry. At PCrisk, he's responsible for writing in-depth how-to articles for Microsoft Windows.

▼ Show Discussion