What is kernel_task and Why it Uses a Lot of Resources?

(updated)
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
What is a kernel_task, and Why is it Consuming a Lot of Mac's Resources?
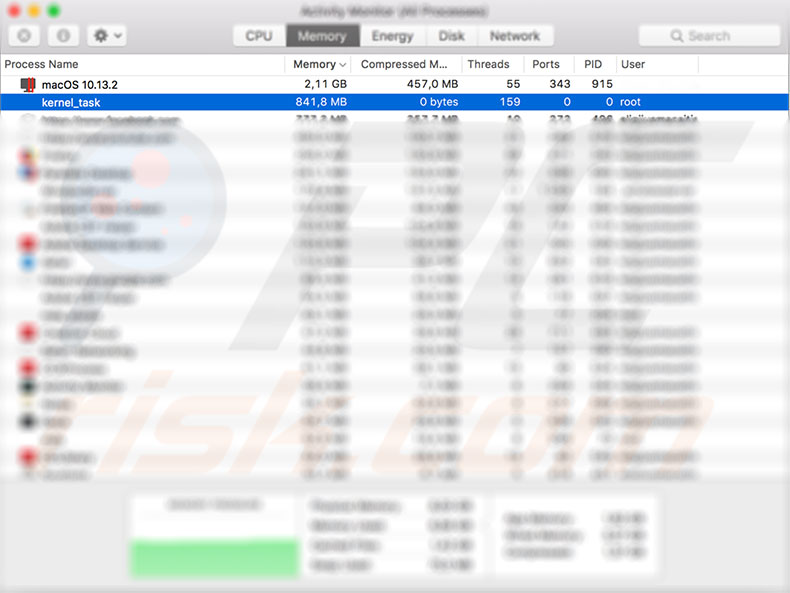
One of the most frequently asked questions within technical support forums is about a kernel_task process found in the Activity Monitor. Users often report reduced computer performance, and once they enter the activity monitor to study the situation, they notice an unknown process consuming extensive CPU and RAM resources. What is this process, and what is its purpose?
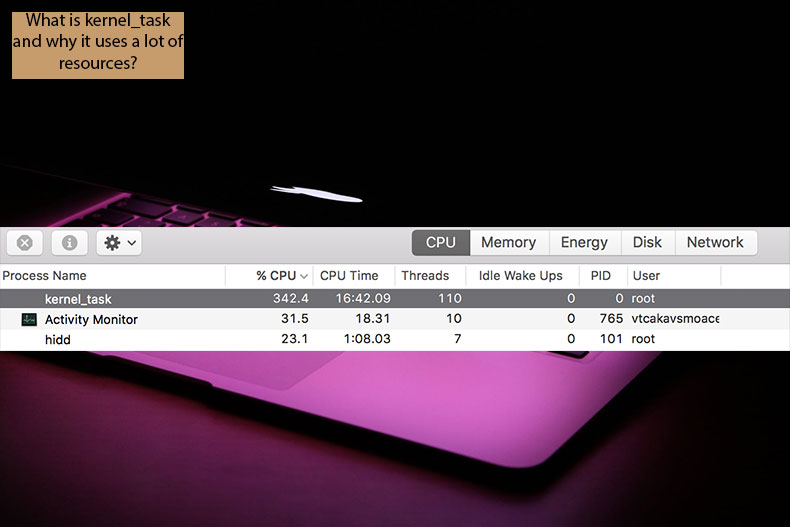
Firstly, this particular process is not a virus or malicious software - it is a part of the operating system, and for this reason, is protected. You are unable to close it.
The 'kernel' is the operating system's core, which allows the CPU, memory, graphic card, and other hardware and software to operate as a working computer system. When you turn on the Mac, the kernel starts first. In fact, every program launched on the computer reaches the kernel process at some point.
As these are very different tasks, the activity monitor groups them all into one category labeled kernel_task. If the Mac works appropriately and you do not notice reduced performance, do not be concerned, even if you see high usage of resources by kernel_task processes. The kernel uses them for background tasks, such as caching files. However, there might be other reasons for wasted computer resources.
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- Reset kernel on your Mac
- kernel_task covers the majority of CPU resource
- Troubleshoot kernel problems
- kernel_task taking a lot of RAM
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
Reset kernel on your Mac
Use this method if Mac performance has decreased and the activity monitor reports that a kernel_task uses extensive system resources (CPU or RAM). The only way to reset the kernel is to restart the Mac. This step is usually sufficient to solve the problem and is strongly recommended as a first method before trying anything else.
kernel_task covers the majority of CPU resource
If you are working with various applications that use significant processing power (for example, converting 4K videos or similar), you may notice reduced Mac performance. Launching an activity monitor to investigate will probably reveal that the kernel_task is using extensive CPU resources. That CPU power could be used for your essential work but will already be used for unknown reasons.
This particular case is frustrating, but this is a precautionary measure to prevent the CPU from overheating, according to Apple. Apple support states that one of the kernel_task functions is to help control CPU temperature by making the CPU less available to processes using it extensively. So, kernel_task responds to conditions that cause CPU temperature increase, even if you cannot feel this rise in temperature through the body of the Mac.
According to Apple, this process does not generate conditions that increase CPU temperature. When the temperature of the processor decreases, kernel_task automatically reduces its activity. In summary, this process does not actually use the CPU power indicated - it simply prevents processes with a high CPU usage from accessing it to prevent overheating. Therefore, you should regain access to the full power of the processor when the CPU temperature decreases.
Troubleshoot kernel problems
If you are not working with high CPU usage applications and still notice that kernel_task takes most resources, the system must have another problem. Frequently, people ignore the Flash process, as it is deemed to be trusted software. However, this application quite often consumes significant CPU resources.
In any case, the activity monitor might report that Flash or browser tabs consume CPU power, forcing kernel_task to protect the processor from overheating. You should consider uninstalling or disabling Flash to prevent any unnecessary problems.
Another common issue is caused by third-party kernel extensions called 'kexts' by macOS. These are usually hardware drivers and additional software that communicate directly with the kernel. An erroneous kext often causes the kernel_task to consume considerable system resources. Fortunately, troubleshooting this particular case is simple - boot the Mac into Safe Mode.
Safe Boot does not enable third-party kexts, so if your computer has no problem working in Safe Mode, you have faulty kernel extensions. Remove any recently-installed third party software or hardware drivers and check if the Mac returns to an efficient working state.
If you wish to generate a detailed report about kexts installed on your computer, you can use Etrecheck, which runs many diagnostic functions. This software displays a list of all existing and running kexts on your system.
kernel_task taking a lot of RAM
One kernel function is used to manage resources required by processes and programs. It is responsible for features such as multitasking scheduling, virtual memory, system input and output, and various communication routines between processes.
Kernel extensions (kexts) also improve the functionality of system features such as Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, graphic processors and third-party hardware, access to peripheral devices, and special file system support. Since the Activity monitor displays all of these processes within one process called Kernel_task, the amount of additional hardware and software running on the Mac can result in an excessive amount of RAM used by kernel_task.
In other words, there is nothing to worry about when you see kernel_task consuming RAM memory. If you wish to reduce the amount taken by this particular process, there are just a few options. One is to restart the computer. Another is to disconnect additional devices, such as an external monitor or onboard GPU, etc. If you are not using the Wi-Fi or Bluetooth connections, disabling them might also reduce the amount of RAM used by kernel_task.
Share:

Karolina Peistariene
Author of how-to guides for Mac users
Responsible for collecting, analyzing, and presenting problem-solving solution articles related to macOS issues. Years of macOS experience combined with solid research and analyzing skills help Karolina provide readers with working and helpful solutions as well as introduce various features Mac has to offer.
▼ Show Discussion