My Mac Won't Start: How to Fix the White/Gray Screen Issue?

(updated)
Get Free Scanner and check your computer for errors
Fix It NowTo fix found issues, you have to purchase the full version of Combo Cleaner. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
My Mac Won't Start: How to Fix the White screen issue?
A very disconcerting problem that can appear on MAC computers is when it becomes stuck on a white or grey screen when loading. It may seem as if there is a hardware or software fault, but do not panic. You can try several tips that might help fix this problem or at least troubleshoot the issue.

In this article, we share the most popular and helpful tips to address the issue. Before attempting to solve the problem, make sure you have a copy of your files. If you don't, back up all important data to avoid losing it if something goes wrong. When all data is backed up, follow the methods listed in this article to fix your Mac stuck on a white or gray screen.
Video showing How to Fix White Screen:
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- How to create a backup while Mac OS is stuck on loading?
- Who prevents Mac from loading?
- Try safe boot.
- Launch Disk Utility.
- Reset the NVRAM.
- Reset System Management Controller (SMC).
- Using Terminal in Single User Mode.
- Reinstall MacOS or Mac OS X.
- Video showing How to Fix White Screen.
Download Computer Malware Repair Tool
It is recommended to run a free scan with Combo Cleaner - a tool to detect viruses and malware on your device. You will need to purchase the full version to remove infections. Free trial available. Combo Cleaner is owned and operated by Rcs Lt, the parent company of PCRisk.com read more.
How to create a backup while Mac OS is stuck on loading?
Before creating a backup, connect an external hard drive to your Mac with enough storage space for your copied files.
1. Shut down your Mac.
2. Next, turn your Mac on and, immediately after the startup chime, hold down the Command + R keys on your keyboard until you see the Apple logo.
3. Once the logo appears, release the keys and wait until you see the OS X Utilities window.
4. In the window, choose Disk Utility and click Continue.
5. When the sidebar appears, select the drive to which you will write your backup - usually, it is called Macintosh HD unless you have changed its name.
6. Click Verify Disk. If the disk verifying process indicates a problem, click Repair Disk.
7. In the toolbar, you will find the “New Image” icon. Choose your external drive to which you are going to save the backup. This procedure will create a compressed disk image of your hard drive content.
Note: steps might be slightly different for various Mac OS X and macOS versions.
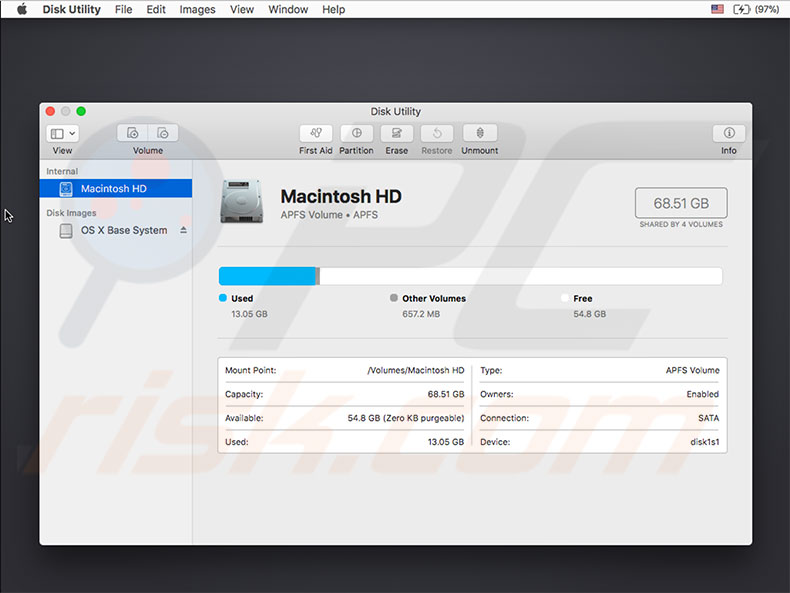
What prevents Mac from loading?
In some cases, white or grey screen problems can be caused by peripherals. The first solution might be to disconnect all unnecessary peripherals, if possible, leaving only the Apple-branded keyboard and mouse.
Try to reboot your computer. If it loads normally, connects your peripherals individually - the best-case scenario would be to reboot your computer with all peripherals connected. There are cases when the problem is caused by a certain combination of connected peripherals. If the computer does not boot without any connected peripherals, try the next tip.
Try a Safe boot
macOS and Mac OS X version 10.2, and subsequent versions, have included a Safe Boot feature, which checks and repairs your hard drive. This feature rebuilds Mac’s boot database on your hard drive and often resolves white or grey screen issues.
1. To launch your computer using the Safe Boot feature, shut down your Mac.
2. Once it is fully turned off, turn it on again by pressing the Power button and holding the Shift key until the Apple logo appears.
3. When your Mac is fully loaded, the first thing you need to do is clean up your Trash.
4. When Trash is empty, open a Finder window and check your hard drive (by default, named Macintosh HD, unless you have renamed it).
5. Check if there is at least 10GB of free space. If not, move or delete some of your files. Media files are usually the biggest and easiest to move to another hard drive, either internal or external.
6. After cleaning your Trash and making space on your hard drive, restart your Mac in the usual way (without holding any keys).
Launch Disk Utility
1. Shut down your Mac by holding down the Power button for a few seconds.
2. Turn on your computer by pressing the Power button and holding down the Command + R key until you see the Apple logo.
3. You should now see the Mac OS X Utilities or macOS Utilities window, depending on your operating system.
4. Choose Disk Utility, select your hard drive, and click verify/repair disk.
5. If the program reports repairing your drive was not possible, it will need replacing. If this is the first time it has happened, you could erase the volume and restore it from backup.
Note: Once a drive fails, it will usually fail again.
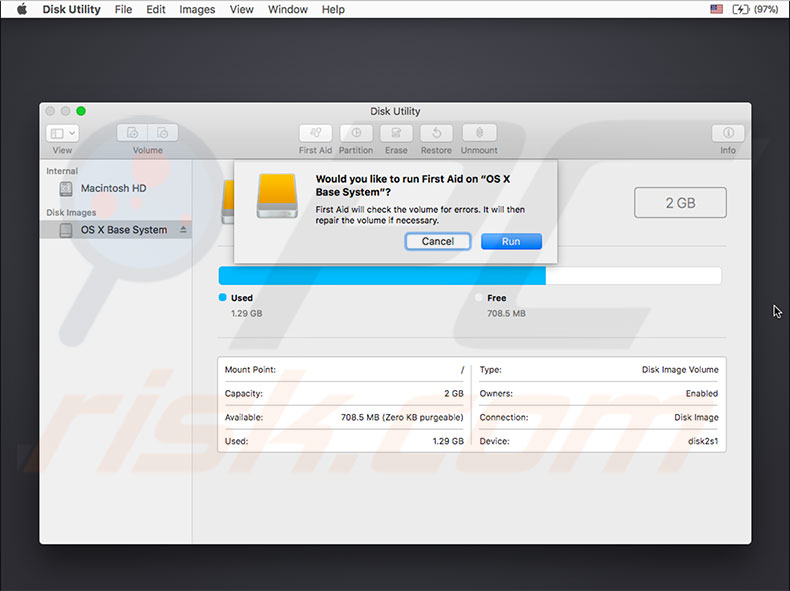
Recovery partition not popping up?
If your Mac fails when booting up into recovery, you can still try to boot using Internet Recovery by holding down the Command + Option + R keys until you see the Apple logo. To use this option, you must have an Internet connection.
If Internet Recovery did not help, try to open Startup Manager by holding down the Option key while launching your Mac. Once Startup Manager is launched, choose how your Mac boots from the options provided on screen, including connected bootable hard drives, recovery partition, USB flash drives, network locations, and other boot sources.
Reset the NVRAM
If disk utility could not solve your boot failure, another solution you might try is resetting NVRAM. NVRAM (non-volatile random-access memory) is a small area of your MAC memory that stores certain settings in a location that the macOS can access. Here, information such as your computer speaker volume, screen resolution, startup disk selection, and recent kernel panic reports is stored. If any of these features cause issues, resetting NVRAM might help to solve them.
1. First, shut down your Mac.
2. Once it's fully turned off, hold down the Command + Option + P + R keys on the keyboard and click the Power button to boot your Mac.
3. The keyboard combination must be pressed and held immediately after you hear the startup sound.
4. Hold down the buttons for at least 20 seconds to ensure the process is completed correctly.
Note: some Macs released before 2016 might have slightly different steps.
Reset System Management Controller (SMC)
This step is mostly related to portable Macs such as MacBook Pro, MacBook, and MacBook Air models.
1. First, shut down your computer, plug in your power adapter.
2. Hold down the Shift + Control + Option keys and press the power button.
3. Release all buttons simultaneously and reboot your Mac in the usual way.
Using Terminal in Single User Mode
The steps above usually help to solve the white or grey screen issue. If not, however, you can try one more solution before reinstalling your operating system. Run Single User Mode using the command 'fsck', which performs a file system check. When launching single-user mode, you will see commands scrolling on the screen. This is how single user mode works - when it stops, run the commands listed below to analyze your Mac startup disk.
1. Restart your Mac.
2. When you hear the startup sound, press and hold the Command + S keys, and keep holding until you see white letters on a black screen.
3. Your Mac will then boot into single-user mode.
4. On the terminal window, type the command 'fsck - fy' and then press return.
5. Then, type 'mount -uw' and press return.
6. Next, type touch/private/var/db/.AppleSetupDone and press return.
7. For the last command, type 'exit' and click return. After entering these commands, perform a Safe Boot as detailed before.
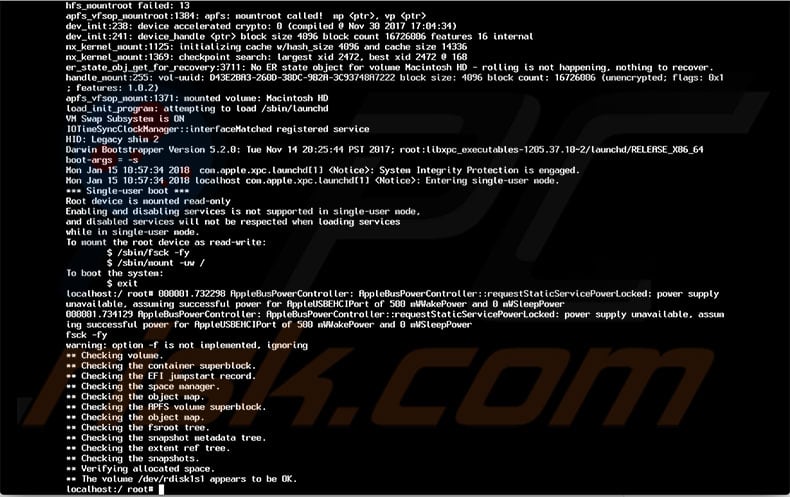
An alternative terminal command
Enter single-user mode once again, and when it has started, type '/sbin/fsck -fy' and press return. This will start the system check, which will report two possible messages: 1) “Macintosh HD appears to be okay”; 2) “File system was modified.”
If it reports that your system is okay, enter the reboot command and press return. If the message reports that your system was modified, type the '/sbin/fsck -fy' command again and click return. Repeat this command until you get a report saying the system is okay. Then, type the reboot command, press return, and then perform a Safe Boot.
Dictionary of Terminal Commands
fsck -fy
Checks the boot volume file system and repairs it if needed. They at the end of the command means 'yes', fix any problems.
mount -uw
Remount the boot volume, enabling write access.
touch/private/var/db/.AppleSetupDone
Reports that it has completed the set-up.
exit
Continue to boot process.
reboot
Reboots the computer.
/sib
Contain executable programs needed to boot the system by the root user.
Reinstall MacOS or Mac OS X
If none of the steps above work, you could try is reinstalling your operating system.
1. To perform an operating system reinstall, shut down your Mac by holding the power button for a few seconds.
2. Hold down the Command + R keys and turn on your computer.
3. When you see the Apple logo, release the keys.
4. You should see the Mac OS X utilities or macOS Utilities window. Select the Reinstall option.
If a simple reinstall does not work on your Mac, try reinstalling using Internet Recovery. To manage a reinstall using Internet recovery, repeat the steps listed above. However, on launching your computer hold down the Command + R + Option keys until the Apple logo appears. When you see the Utilities window, choose to reinstall macOS or Mac OS X and follow the instructions.

{loadposition blog_back_top
Share:

Karolina Peistariene
Author of how-to guides for Mac users
Responsible for collecting, analyzing, and presenting problem-solving solution articles related to macOS issues. Years of macOS experience combined with solid research and analyzing skills help Karolina provide readers with working and helpful solutions as well as introduce various features Mac has to offer.
▼ Show Discussion